The Cerebral Cortex
... parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
... parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
NOTES FOR CHAPTER 13
... * the disease, multiple sclerosis (MS) develops when the myelin sheath becomes hardened and interferes with nerve conduction - it is an autoimmune disease * leukodystrophy disorders are similar but their cause is genetic ...
... * the disease, multiple sclerosis (MS) develops when the myelin sheath becomes hardened and interferes with nerve conduction - it is an autoimmune disease * leukodystrophy disorders are similar but their cause is genetic ...
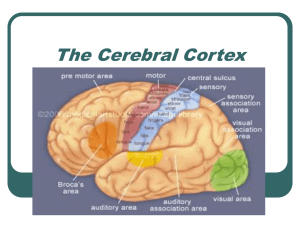
The Cerebral Cortex and Its Functions
... The human brain hemispheres are covered in its greater part by an external layer of gray color called cerebral cortex. A deep cut into the brain would show that this gray surface has a thickness varying from 1 to 4 mm. Its largest part is composed by nerve cells (neurons) which receive impulses from ...
... The human brain hemispheres are covered in its greater part by an external layer of gray color called cerebral cortex. A deep cut into the brain would show that this gray surface has a thickness varying from 1 to 4 mm. Its largest part is composed by nerve cells (neurons) which receive impulses from ...
Psychology Chapter 3
... and detecting cancers. CT scans are widely used in emergency rooms because the procedure takes less than 5 minutes. An MRI, on the other hand, can take up to 30 minutes. An MRI typically costs more than a CT scan. One advantage of an MRI is that it does not use radiation while CAT scans do. This rad ...
... and detecting cancers. CT scans are widely used in emergency rooms because the procedure takes less than 5 minutes. An MRI, on the other hand, can take up to 30 minutes. An MRI typically costs more than a CT scan. One advantage of an MRI is that it does not use radiation while CAT scans do. This rad ...
Physical Development I
... • A 2011 study (Class et al.) found that mothers with high levels of stress during the 5th and 6th month of pregnancy were more likely to deliver pre-term • Maternal depression was found in two research reviews to be linked to preterm birth and low-birth weight ...
... • A 2011 study (Class et al.) found that mothers with high levels of stress during the 5th and 6th month of pregnancy were more likely to deliver pre-term • Maternal depression was found in two research reviews to be linked to preterm birth and low-birth weight ...
Chapter Summary Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception • Sensation
... Rods and cones in the retina at the back of the eye change light into neural impulses. Cones provide detailed vision and help us perceive colour, while rods provide information about intensity of light. Two different theories in combination—trichomatic theory and opponent process theory— explain a g ...
... Rods and cones in the retina at the back of the eye change light into neural impulses. Cones provide detailed vision and help us perceive colour, while rods provide information about intensity of light. Two different theories in combination—trichomatic theory and opponent process theory— explain a g ...
The skin performs all of the following except
... Made up of 100 billion neurons Maintains homeostasis Control center ...
... Made up of 100 billion neurons Maintains homeostasis Control center ...
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
... The temporal lobe of the brain is vulnerable to injury from impacts of the front of the head. The temporal lobe lies upon the bony ridges of the inside of the skull, and rapid acceleration can cause the brain tissue to smash into the bone, causing tissue damage or bleeding. Click image to play or pa ...
... The temporal lobe of the brain is vulnerable to injury from impacts of the front of the head. The temporal lobe lies upon the bony ridges of the inside of the skull, and rapid acceleration can cause the brain tissue to smash into the bone, causing tissue damage or bleeding. Click image to play or pa ...
case studies In-depth examinations of an individual or a single event
... basal ganglia A collection of subcortical structures that are involved in memory. These structures include the caudate nucleus, the putamen, the globus pallidus, and the subthalamic nucleus and are located above and around the thalamus. Important for memories involving habits and motor skills ...
... basal ganglia A collection of subcortical structures that are involved in memory. These structures include the caudate nucleus, the putamen, the globus pallidus, and the subthalamic nucleus and are located above and around the thalamus. Important for memories involving habits and motor skills ...
Brain Bee at MSU Review Session
... – GABA releasing neuron die in the caudate/putamen (striatum) in the basal ganglia – Benzodizepines (e.g., valium) and anticonvulsants binds to GABA receptor to enhance effect of released GABA ...
... – GABA releasing neuron die in the caudate/putamen (striatum) in the basal ganglia – Benzodizepines (e.g., valium) and anticonvulsants binds to GABA receptor to enhance effect of released GABA ...
Exam - McLoon Lab
... C. A strand of mRNA is read by a ribosome and used to determine the sequence in which amino acids are linked together. D. A strand of mRNA is read by a ribosome and used to determine the sequence in which nucleotides are linked together. E. A strand of protein is read by a ribosome and used to deter ...
... C. A strand of mRNA is read by a ribosome and used to determine the sequence in which amino acids are linked together. D. A strand of mRNA is read by a ribosome and used to determine the sequence in which nucleotides are linked together. E. A strand of protein is read by a ribosome and used to deter ...
CNS_notes
... Lumbar puncture: getting a sample of CSF by withdraw CSF from subarach space at L3-L4 level White & gray matter in cord Gray matter: many cell bodies of neurons posterior (sensory) lateral (visceral motor neurons) anterior (somatic motor neurons) horns Neurons in gray matter nuclei organized by type ...
... Lumbar puncture: getting a sample of CSF by withdraw CSF from subarach space at L3-L4 level White & gray matter in cord Gray matter: many cell bodies of neurons posterior (sensory) lateral (visceral motor neurons) anterior (somatic motor neurons) horns Neurons in gray matter nuclei organized by type ...
Sheep Brain Dissection - Michigan State University
... to electrically stimulate this area in a sheep that was alive? The entire surface of the body is represented in the primary sensory cortex. Interestingly, some parts of the body have more cortical space that others. The figure below (right) is known as the homunculus and illustrates what the body wo ...
... to electrically stimulate this area in a sheep that was alive? The entire surface of the body is represented in the primary sensory cortex. Interestingly, some parts of the body have more cortical space that others. The figure below (right) is known as the homunculus and illustrates what the body wo ...
09. Assessment of Neurologic System
... Carotid arteries supply 80% to brain and two vertebral arteries supply 20% Blood to cerebrum by posterior, middle and anterior cerebral arteries Posterior and anterior communicating arteries to circle of Willis Blood leaves brain through venous sinuses into jugular veins ...
... Carotid arteries supply 80% to brain and two vertebral arteries supply 20% Blood to cerebrum by posterior, middle and anterior cerebral arteries Posterior and anterior communicating arteries to circle of Willis Blood leaves brain through venous sinuses into jugular veins ...
Word - ACM TIST
... Intelligent agents are autonomous hardware or software entities capable of performing specific tasks on behalf of human users. Viewed by many as the new wave of Artificial Intelligence, agents have found applications in many areas, including information management, E-Commerce, decision support, logi ...
... Intelligent agents are autonomous hardware or software entities capable of performing specific tasks on behalf of human users. Viewed by many as the new wave of Artificial Intelligence, agents have found applications in many areas, including information management, E-Commerce, decision support, logi ...
1. Receptor cells
... • Not all perceptual process are learned, some arise from the way our sensory system work, e.g. feeling of hunger or diaper wetting. ...
... • Not all perceptual process are learned, some arise from the way our sensory system work, e.g. feeling of hunger or diaper wetting. ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... and left hemispheres of the cerebrum specialize in different functions Both sides communicate with each other to accomplish complex functions Left hemisphere is responsible for: Language functions Dominating control of certain hand movements Right hemisphere is responsible for: ...
... and left hemispheres of the cerebrum specialize in different functions Both sides communicate with each other to accomplish complex functions Left hemisphere is responsible for: Language functions Dominating control of certain hand movements Right hemisphere is responsible for: ...
Neurons- We will be making neurons out of different color pipe
... production of speech. The parietal lobe is critical to integrating processed information from all primary sensory areas, processing taste information, and in the comprehension of spoken language. The occipital lobe is crucial to our ability not only to see but to read, and the temporal lobe is criti ...
... production of speech. The parietal lobe is critical to integrating processed information from all primary sensory areas, processing taste information, and in the comprehension of spoken language. The occipital lobe is crucial to our ability not only to see but to read, and the temporal lobe is criti ...
The Nervous System 9.14 Brain
... In most people, dominant hemisphere is a side of the cerebrum that controls understanding and using language. (usually left, some people have right dominance, and some have both). ...
... In most people, dominant hemisphere is a side of the cerebrum that controls understanding and using language. (usually left, some people have right dominance, and some have both). ...
CytoFactors - What is anti
... structural and functional elements within the body. At a molecular level, damages accumulate with time on DNA, proteins and lipids as they overcome the intrinsic repair mechanisms of the body. This build-up of molecular changes eventually affects physiological processes leading to the point where it ...
... structural and functional elements within the body. At a molecular level, damages accumulate with time on DNA, proteins and lipids as they overcome the intrinsic repair mechanisms of the body. This build-up of molecular changes eventually affects physiological processes leading to the point where it ...
Lies outside the central nervous system
... impulses travelling up to the cerebrum -Involved in higher mental functions such as memory and emotion ...
... impulses travelling up to the cerebrum -Involved in higher mental functions such as memory and emotion ...
The Nervous System and Senses
... • Some are sensitive to light tough • Some are sensitive to pain • Some are only sensitive to deep touch • Some are wrapped around hair follicles and sense hair movement ...
... • Some are sensitive to light tough • Some are sensitive to pain • Some are only sensitive to deep touch • Some are wrapped around hair follicles and sense hair movement ...