Spinal Cord
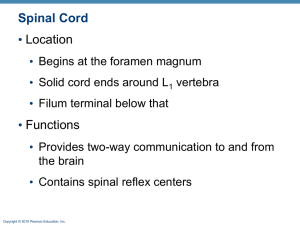
... • Ventral horns—somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots • Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) –sympathetic neurons • Dorsal root (spinal) gangia—contain cell bodies of sensory neurons ...
... • Ventral horns—somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots • Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) –sympathetic neurons • Dorsal root (spinal) gangia—contain cell bodies of sensory neurons ...
Actor-Critic Models of Reinforcement Learning in the Basal Ganglia
... The two main principles of Actor-Critic models that lead to consider them as a good representation of the role of the basal ganglia in reinforcement learning of motor behaviors are (i): the implementation of a Temporal Difference (TD) learning rule which leads to translate progressively reinforcemen ...
... The two main principles of Actor-Critic models that lead to consider them as a good representation of the role of the basal ganglia in reinforcement learning of motor behaviors are (i): the implementation of a Temporal Difference (TD) learning rule which leads to translate progressively reinforcemen ...
fluctuations in somatosensory responsiveness and baseline firing
... dopamine’s ability to modulate corticostriatal transmission, consistent with the suggestion of Freund et al. (1984), based on the pattern by which nigrostriatal and corticostriatal terminals innervate spines of medium spiny neurons. The actions reported here reaffirm the complexity of dopamine’s mod ...
... dopamine’s ability to modulate corticostriatal transmission, consistent with the suggestion of Freund et al. (1984), based on the pattern by which nigrostriatal and corticostriatal terminals innervate spines of medium spiny neurons. The actions reported here reaffirm the complexity of dopamine’s mod ...
Hold your horses: A dynamic computational role
... The details of the BG model are described in Frank (2005a, 2005b). In brief, the premotor cortex represents and “considers” two possible responses (R1 and R2) for each input stimulus. The BG system modulates which one of these responses is facilitated and which is suppressed by signaling Go or NoGo ...
... The details of the BG model are described in Frank (2005a, 2005b). In brief, the premotor cortex represents and “considers” two possible responses (R1 and R2) for each input stimulus. The BG system modulates which one of these responses is facilitated and which is suppressed by signaling Go or NoGo ...
The limbic system. A maze on the essentials: memory, learning and
... are related to complex and devastating disorders, which still are not well known, such as dementia, schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. We will try to clarify this puzzle that is essential in humans. The components of the limbic system are: ...
... are related to complex and devastating disorders, which still are not well known, such as dementia, schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. We will try to clarify this puzzle that is essential in humans. The components of the limbic system are: ...
The Ventral Striatopallidum and Extended Amygdala in
... its morphological and neurochemical composition as well as its projections and pathways. Therefore, it is not surprising that the EA is involved in diverse psychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases such as depression, anxiety and chronic stress, schizophrenia and HD. In recent years scientists disc ...
... its morphological and neurochemical composition as well as its projections and pathways. Therefore, it is not surprising that the EA is involved in diverse psychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases such as depression, anxiety and chronic stress, schizophrenia and HD. In recent years scientists disc ...
Cerebellum
... cerebellar cortex (passing through the restiform body=pedunculus cerebellaris inferior) as climbing fibers. Structure of the Cerebellar Cortex The cerebellar cortex has the same structure all over the cerebellum and the structural arrangement of the neural elements is strictly geometric. The cerebel ...
... cerebellar cortex (passing through the restiform body=pedunculus cerebellaris inferior) as climbing fibers. Structure of the Cerebellar Cortex The cerebellar cortex has the same structure all over the cerebellum and the structural arrangement of the neural elements is strictly geometric. The cerebel ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 38.8 The hypothalamic-neurohypophysial control of vasopressin and oxytocin release is shown (top). Large cells (magnocellular) in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei synthesize vasopressin or oxytocin, which are transported by axonal transport into nerve terminals located in the poster ...
... FIGURE 38.8 The hypothalamic-neurohypophysial control of vasopressin and oxytocin release is shown (top). Large cells (magnocellular) in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei synthesize vasopressin or oxytocin, which are transported by axonal transport into nerve terminals located in the poster ...
Context Dependency in the Globus Pallidus Internal Segment
... neighboring striatopallidal efferent populations project to functionally specific populations of pallidal neurons with adjacent terminal arborizations that do not intermix (Parent et al. 1997). Likewise, globus pallidus internal segment (GPi) efferents project to thalamic neuron populations that, in ...
... neighboring striatopallidal efferent populations project to functionally specific populations of pallidal neurons with adjacent terminal arborizations that do not intermix (Parent et al. 1997). Likewise, globus pallidus internal segment (GPi) efferents project to thalamic neuron populations that, in ...
Pergamon - Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit
... Neostriatum. Sections of the n e o s t r i a t u m of the rat i n c u b a t e d to reveal i m m u n o r e a c t i v i t y for either D~ or D 2 receptors were densely stained by the peroxidase reaction p r o d u c t (Figs 1A-C, 2A for D~; Figs 1 D - F , 2B for Dz). The distribution of i m m u n o r e ...
... Neostriatum. Sections of the n e o s t r i a t u m of the rat i n c u b a t e d to reveal i m m u n o r e a c t i v i t y for either D~ or D 2 receptors were densely stained by the peroxidase reaction p r o d u c t (Figs 1A-C, 2A for D~; Figs 1 D - F , 2B for Dz). The distribution of i m m u n o r e ...
Goal-direction and top-down control
... We suggest this difference in the way DA influences plasticity in the striatum and PFC leads to a difference in how associations are learned in each region. Specifically, we propose DA strongly influences plasticity in the striatum, producing simple, concrete associations. By contrast, DA has a mild ...
... We suggest this difference in the way DA influences plasticity in the striatum and PFC leads to a difference in how associations are learned in each region. Specifically, we propose DA strongly influences plasticity in the striatum, producing simple, concrete associations. By contrast, DA has a mild ...
chapter 4 the evolution of body, brain, behavior, and mind in
... the developing embryo from desiccation. After hatching, many amphibians spend their early life in the water as tadpoles, with tails used for swimming and gills for breathing. They do not develop functional lungs until they have metamorphosed. Moreover, lacking a diaphragm, the amphibian lung is a le ...
... the developing embryo from desiccation. After hatching, many amphibians spend their early life in the water as tadpoles, with tails used for swimming and gills for breathing. They do not develop functional lungs until they have metamorphosed. Moreover, lacking a diaphragm, the amphibian lung is a le ...
Connectivity of the human pedunculopontine nucleus region and
... in nonhuman primates, it is nevertheless important to demonstrate directly the existence of homologous pathways in the human brain. One important connection below the PPN region is from the cerebellum, which passes via the superior cerebellar peduncle (Fig. 1 left). The cerebellar deep nuclei are kn ...
... in nonhuman primates, it is nevertheless important to demonstrate directly the existence of homologous pathways in the human brain. One important connection below the PPN region is from the cerebellum, which passes via the superior cerebellar peduncle (Fig. 1 left). The cerebellar deep nuclei are kn ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... some somatic neurons which control contraction of skeletal myocytes in muscles of the pharynx during swallowing AND some autonomic neurons controlling contraction of cardiac myocytes and of smooth myocytes in the digestive sstem ...
... some somatic neurons which control contraction of skeletal myocytes in muscles of the pharynx during swallowing AND some autonomic neurons controlling contraction of cardiac myocytes and of smooth myocytes in the digestive sstem ...
avian brain nomenclature forum
... the lobus parolfactorius, the paleostriatum augmentatum, the paleostriatum primitivum, the majority of the septum and several basal forebrain groups that include the large cholinergic cells and the stria terminalis nuclear complex (part of it erroneously named nucleus accumbens in the past; see bel ...
... the lobus parolfactorius, the paleostriatum augmentatum, the paleostriatum primitivum, the majority of the septum and several basal forebrain groups that include the large cholinergic cells and the stria terminalis nuclear complex (part of it erroneously named nucleus accumbens in the past; see bel ...
Psychological and Neuroscientific Connections with Reinforcement
... Shah: Psychology, Neuroscience, and RL (preprint) presentations are intermixed during training: CSA alone paired with the US, and the simultaneous presentation of CSA and CSB with the US omitted. Subsequent pairing of CSB alone with the US results in a lower rate of CR acquisition relative to anima ...
... Shah: Psychology, Neuroscience, and RL (preprint) presentations are intermixed during training: CSA alone paired with the US, and the simultaneous presentation of CSA and CSB with the US omitted. Subsequent pairing of CSB alone with the US results in a lower rate of CR acquisition relative to anima ...
Hypothalamus15
... Overview of ANS functional anatomy (sympathetic, parasympathetic systems). Regulation of autonomic functions by descending projections from the hypothalamus. Regional anatomy. A. Anterior-posterior sections of hypothalamus and review key nuclei. B. Descending pathway and sc nuclei. C. Clinical Note: ...
... Overview of ANS functional anatomy (sympathetic, parasympathetic systems). Regulation of autonomic functions by descending projections from the hypothalamus. Regional anatomy. A. Anterior-posterior sections of hypothalamus and review key nuclei. B. Descending pathway and sc nuclei. C. Clinical Note: ...
Discharge Rate of Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata Neurons Is
... not been performed on primates. In primates, studies of LID have focused mainly on the activity of the internal segment of the globus pallidus (GPi), the larger of the two output nuclei of the BG, and have neglected the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr). Although these two nuclei are often clum ...
... not been performed on primates. In primates, studies of LID have focused mainly on the activity of the internal segment of the globus pallidus (GPi), the larger of the two output nuclei of the BG, and have neglected the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr). Although these two nuclei are often clum ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
... • Sympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies are housed in the lateral horn of the T1–L2 regions of the spinal cord. • Preganglionic sympathetic axons travel with somatic motor neuron axons to exit the spinal cord and enter first the anterior roots and then the T1–L2 spinal ...
... • Sympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies are housed in the lateral horn of the T1–L2 regions of the spinal cord. • Preganglionic sympathetic axons travel with somatic motor neuron axons to exit the spinal cord and enter first the anterior roots and then the T1–L2 spinal ...
Expectancies in decision making, reinforcement
... neurons, it was found that while the ensemble usually represented locations close to the animal’s actual location (as would be expected from “place cells”), during pauses at the final choice point of the Multiple-T task (Figure 1A), the decoded location could be observed to sweep down one arm of the ...
... neurons, it was found that while the ensemble usually represented locations close to the animal’s actual location (as would be expected from “place cells”), during pauses at the final choice point of the Multiple-T task (Figure 1A), the decoded location could be observed to sweep down one arm of the ...
A Physiologically Plausible Model of Action Selection
... “channel”) in SNr/EP, resulting in selective disinhibition of basal ganglia output targets (Chevalier et al., 1985; Chevalier and Deniau, 1990). (10) Within the BG, there are many candidate mechanisms with the capacity for selection. At the internucleus level, we included in our model the circuit co ...
... “channel”) in SNr/EP, resulting in selective disinhibition of basal ganglia output targets (Chevalier et al., 1985; Chevalier and Deniau, 1990). (10) Within the BG, there are many candidate mechanisms with the capacity for selection. At the internucleus level, we included in our model the circuit co ...
Electrolytic lesion of globus pallidus ameliorates the behavioral and
... After the completion of the water maze task, 15 rats Ž3 sham, 4 striatal, 4 pallidal, and 4 combined. were randomly chosen for histological assessment. ŽThe remaining rats are continuing behavioral testing.. Rats were anaesthetized with an overdose of nembutal and perfused intracardially with 100 ml ...
... After the completion of the water maze task, 15 rats Ž3 sham, 4 striatal, 4 pallidal, and 4 combined. were randomly chosen for histological assessment. ŽThe remaining rats are continuing behavioral testing.. Rats were anaesthetized with an overdose of nembutal and perfused intracardially with 100 ml ...
Emo7onal decision‐making systems and their role in addic7on
... 6. Habits (implicit) mechanisms of drug reward seeking: While addicted behaviors all start out under some “conscious” control through these ventral striatal motivational neural circuitries, prolonged drug use results in the strengthening of motivation‐relevant associative memories, which promote ...
... 6. Habits (implicit) mechanisms of drug reward seeking: While addicted behaviors all start out under some “conscious” control through these ventral striatal motivational neural circuitries, prolonged drug use results in the strengthening of motivation‐relevant associative memories, which promote ...
neural projections from nucleus accumbens to globus pallidus
... electrophysiological recordings were made from single neurons in these regions to map the location of units that respond to electrical stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. Recordings also were made from neurons in dorsal parts of the GP (GPd) before the microelectrode was lowered to the GP, and the ...
... electrophysiological recordings were made from single neurons in these regions to map the location of units that respond to electrical stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. Recordings also were made from neurons in dorsal parts of the GP (GPd) before the microelectrode was lowered to the GP, and the ...
The neural basis of the speed–accuracy tradeoff - Eric
... fast and stimulus onset. Under the assumption that the observed BOLD signal in these areas is produced by the activity of integrator neurons, the data from these three fMRI studies suggest that speed instructions increase the baseline activity of these neurons. We are not aware of any neurophysiolog ...
... fast and stimulus onset. Under the assumption that the observed BOLD signal in these areas is produced by the activity of integrator neurons, the data from these three fMRI studies suggest that speed instructions increase the baseline activity of these neurons. We are not aware of any neurophysiolog ...
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (or basal nuclei) comprise multiple subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates, which are situated at the base of the forebrain. Basal ganglia nuclei are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions including: control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, routine behaviors or ""habits"" such as bruxism, eye movements, cognition and emotion.The main components of the basal ganglia – as defined functionally – are the dorsal striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen), ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), globus pallidus, ventral pallidum, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus. It is important to note, however, that the dorsal striatum and globus pallidus may be considered anatomically distinct from the substantia nigra, nucleus accumbens, and subthalamic nucleus. Each of these components has a complex internal anatomical and neurochemical organization. The largest component, the striatum (dorsal and ventral), receives input from many brain areas beyond the basal ganglia, but only sends output to other components of the basal ganglia. The pallidum receives input from the striatum, and sends inhibitory output to a number of motor-related areas. The substantia nigra is the source of the striatal input of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which plays an important role in basal ganglia function. The subthalamic nucleus receives input mainly from the striatum and cerebral cortex, and projects to the globus pallidus.Currently, popular theories implicate the basal ganglia primarily in action selection; that is, it helps determine the decision of which of several possible behaviors to execute at any given time. In more specific terms, the basal ganglia's primary function is likely to control and regulate activities of the motor and premotor cortical areas so that voluntary movements can be performed smoothly. Experimental studies show that the basal ganglia exert an inhibitory influence on a number of motor systems, and that a release of this inhibition permits a motor system to become active. The ""behavior switching"" that takes place within the basal ganglia is influenced by signals from many parts of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, which plays a key role in executive functions.The importance of these subcortical nuclei for normal brain function and behavior is emphasized by the numerous and diverse neurological conditions associated with basal ganglia dysfunction, which include: disorders of behavior control such as Tourette syndrome, hemiballismus, and obsessive–compulsive disorder; dystonia; psychostimulant addiction; and movement disorders, the most notable of which are Parkinson's disease, which involves degeneration of the dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra pars compacta, and Huntington's disease, which primarily involves damage to the striatum. The basal ganglia have a limbic sector whose components are assigned distinct names: the nucleus accumbens, ventral pallidum, and ventral tegmental area (VTA). There is considerable evidence that this limbic part plays a central role in reward learning, particularly a pathway from the VTA to the nucleus accumbens that uses the neurotransmitter dopamine. A number of highly addictive drugs, including cocaine, amphetamine, and nicotine, are thought to work by increasing the efficacy of this dopamine signal. There is also evidence implicating overactivity of the VTA dopaminergic projection in schizophrenia.























