anterior spinothalamic tract.
... tracts are parts of the extrapyramidal tracts or system. 1- Corticospinal tract: It is concerning with the initiation of voluntary movement. This tract begins from the motor area of the cerebral cortex and then down till the medulla oblongata. The majority of these fibers cross to other side in the ...
... tracts are parts of the extrapyramidal tracts or system. 1- Corticospinal tract: It is concerning with the initiation of voluntary movement. This tract begins from the motor area of the cerebral cortex and then down till the medulla oblongata. The majority of these fibers cross to other side in the ...
The subthalamic nucleus in the context of movement disorders
... Neurosurgery, Memorial-Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, USA ...
... Neurosurgery, Memorial-Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, USA ...
Seizure, neurotransmitter release, and gene expression are closely
... are epileptogenic and excitotoxic to nerve cells both in vitro and in vivo (Whetsell, 1996). The release of these EAAs from the nerve terminals may be Ca2+ -dependent or -independent, although the mechanisms are not fully understood. Extracellular K+ stimulates the EAA efflux from striatal neurons ( ...
... are epileptogenic and excitotoxic to nerve cells both in vitro and in vivo (Whetsell, 1996). The release of these EAAs from the nerve terminals may be Ca2+ -dependent or -independent, although the mechanisms are not fully understood. Extracellular K+ stimulates the EAA efflux from striatal neurons ( ...
Dopamine
... creases DA neuronal activity (31) and DA levels in the striatum in a manner that is dependent on DA neuron impulse flow (29). It is proposed that this subicular-driven DA release may be involved in the modulation of investigatory response to novel and conditioned stimuli (45). Stimulation of the PFC ...
... creases DA neuronal activity (31) and DA levels in the striatum in a manner that is dependent on DA neuron impulse flow (29). It is proposed that this subicular-driven DA release may be involved in the modulation of investigatory response to novel and conditioned stimuli (45). Stimulation of the PFC ...
Acetylcholinesterase in central vocal control nuclei of the zebra finch
... function relation combined with the changes in synaptic efficacy and neurochemical content constitutes a wellsuited model to elucidate neuronal correlates of learning and memory processes. The vocal repertoire in each case needs to be acquired. Once acquired it is either retained throughout life in ...
... function relation combined with the changes in synaptic efficacy and neurochemical content constitutes a wellsuited model to elucidate neuronal correlates of learning and memory processes. The vocal repertoire in each case needs to be acquired. Once acquired it is either retained throughout life in ...
Switching from automatic to controlled behavior: cortico - lsr
... alone. The switching-associated reconfiguration of cognitive processes indicated by the psychological studies is probably composed of serial and parallel neuronal activity changes which occur within a short period before the decision to switch. However, the spatiotemporal resolution of the imaging d ...
... alone. The switching-associated reconfiguration of cognitive processes indicated by the psychological studies is probably composed of serial and parallel neuronal activity changes which occur within a short period before the decision to switch. However, the spatiotemporal resolution of the imaging d ...
DURAL VENOUS SINUSES Channels within meningal layer of dura
... - All sensory tracts, except olfactory nerves, have direct projections to the thalamus. In turn the thalamic nuclei project to the sensory cortex. The conscious awareness of the crude aspects of pain, touch, pressure and temperature are realized in the thalamus ...
... - All sensory tracts, except olfactory nerves, have direct projections to the thalamus. In turn the thalamic nuclei project to the sensory cortex. The conscious awareness of the crude aspects of pain, touch, pressure and temperature are realized in the thalamus ...
Reconstruction of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway in the adult
... microtransplantation approach, which allows precise placement of small cell deposits directly into the host substantia nigra, and fetal donor cells that express green fluorescent protein under the control of the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter, we show that dopamine neuroblasts implanted into the subs ...
... microtransplantation approach, which allows precise placement of small cell deposits directly into the host substantia nigra, and fetal donor cells that express green fluorescent protein under the control of the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter, we show that dopamine neuroblasts implanted into the subs ...
PDF
... indirect, methods to measure dopamine concentration in the striatum. By contrast, many other studies track the firing of dopaminergic neurons by recording electrical activity in the midbrain, where the cell bodies lie (Fig. 1a). Such recordings from rats running through mazes have yet to be reported ...
... indirect, methods to measure dopamine concentration in the striatum. By contrast, many other studies track the firing of dopaminergic neurons by recording electrical activity in the midbrain, where the cell bodies lie (Fig. 1a). Such recordings from rats running through mazes have yet to be reported ...
Print this article - University of Toronto Journal of Undergraduate Life
... Figure 1. A simplified schematic representation of basal ganglia circuits involved in the pathology of PD and LIDs. Sensorimotor and cognitive information from the cortex is transmitted to the striatum through a massive glutamatergic innervation (see black arrow from cortex to striatum). The Substan ...
... Figure 1. A simplified schematic representation of basal ganglia circuits involved in the pathology of PD and LIDs. Sensorimotor and cognitive information from the cortex is transmitted to the striatum through a massive glutamatergic innervation (see black arrow from cortex to striatum). The Substan ...
autonomic accessory ganglia in nerves reaching organs of the
... their branches running to the urogenital organs of sheep there were concentrations of nerve cells forming ganglia which, due to the area of their occurrence and to differentiate them from the main autonomic ganglia of the abdominal and pelvic cavities, were termed the AAG. There were concentrations ...
... their branches running to the urogenital organs of sheep there were concentrations of nerve cells forming ganglia which, due to the area of their occurrence and to differentiate them from the main autonomic ganglia of the abdominal and pelvic cavities, were termed the AAG. There were concentrations ...
14-Cerebrum white matter
... • The amygdaloid nucleus (A) bulges into the terminal part of the inferior horn • Floor and the medial wall are formed by (from medial to lateral) the fimbria, the hippocampus and the ...
... • The amygdaloid nucleus (A) bulges into the terminal part of the inferior horn • Floor and the medial wall are formed by (from medial to lateral) the fimbria, the hippocampus and the ...
$doc.title
... During discrimination learning, goal-directed actions that require attentional function at the prefrontal cortex (PFC) are selected based on behavioral rules acquired through the declarative system (i.e., by following instructions in an experiment to associate a stimulus to a response). This form of ...
... During discrimination learning, goal-directed actions that require attentional function at the prefrontal cortex (PFC) are selected based on behavioral rules acquired through the declarative system (i.e., by following instructions in an experiment to associate a stimulus to a response). This form of ...
View PDF - MRC Brain Network Dynamics Unit
... were assumed to be realizations of stationary, zero-mean time series. Spike trains were assumed to be realizations of stationary, stochastic point processes and were denoted by subscript C (Perkel et al. 1967). All the processes were further assumed to satisfy a mixing condition, whereby sample valu ...
... were assumed to be realizations of stationary, zero-mean time series. Spike trains were assumed to be realizations of stationary, stochastic point processes and were denoted by subscript C (Perkel et al. 1967). All the processes were further assumed to satisfy a mixing condition, whereby sample valu ...
cortical input to the basal forebrain
... have been reinforced. It has been proposed68 that cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain receive information on the expected availability of reinforcement through afferent inputs from the orbitofrontal cortex. Through their widespread corticopetal projections the cholinergic neurons may then be ...
... have been reinforced. It has been proposed68 that cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain receive information on the expected availability of reinforcement through afferent inputs from the orbitofrontal cortex. Through their widespread corticopetal projections the cholinergic neurons may then be ...
High-frequency stimulation in Parkinson`s disease: more
... Deep-brain stimulation at high frequency is now considered the most effective neurosurgical therapy for movement disorders. An electrode is chronically implanted in a particular area of the brain and, when continuously stimulated, it significantly alleviates motor symptoms. In Parkinson’s disease, c ...
... Deep-brain stimulation at high frequency is now considered the most effective neurosurgical therapy for movement disorders. An electrode is chronically implanted in a particular area of the brain and, when continuously stimulated, it significantly alleviates motor symptoms. In Parkinson’s disease, c ...
Dopamine in Schizophrenia
... with an increased DA function, whereas negative symptoms are associated with a decreased DA function (Meltzer 1985; Wyat 1986; Davis et al. 1991). The postulated site of DA dysfunction has been re-conceptualized as well. The advent of the “atypical” neuroleptic clozapine, which had superior efficacy ...
... with an increased DA function, whereas negative symptoms are associated with a decreased DA function (Meltzer 1985; Wyat 1986; Davis et al. 1991). The postulated site of DA dysfunction has been re-conceptualized as well. The advent of the “atypical” neuroleptic clozapine, which had superior efficacy ...
09 - Pierce College
... 9. Damage to the rhombencephalon would most likely produce a damaged a. Thalamus, hypothalamus or epithalamus b. Midbrain c. Pons, cerebellum or medulla d. Cerebrum 10. If during embryological development the prosencephalon is damaged, a damaged _____ would most likely result. a. Midbrain b. Hypotha ...
... 9. Damage to the rhombencephalon would most likely produce a damaged a. Thalamus, hypothalamus or epithalamus b. Midbrain c. Pons, cerebellum or medulla d. Cerebrum 10. If during embryological development the prosencephalon is damaged, a damaged _____ would most likely result. a. Midbrain b. Hypotha ...
Vertebrate brains and evolutionary connectomics: on the origins of
... Examples of such functions included the ability to decode auditory inputs generated by vocal communication, visual pattern recognition, visual stereopsis, deciphering complex somatosensory inputs and most notably, so-called higher cognitive functions. The level of analysis performed was judged to be ...
... Examples of such functions included the ability to decode auditory inputs generated by vocal communication, visual pattern recognition, visual stereopsis, deciphering complex somatosensory inputs and most notably, so-called higher cognitive functions. The level of analysis performed was judged to be ...
I:\Physio Psych\PSN.shw
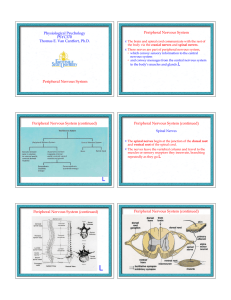
... the neighboring ganglia above and below, thus forming the sympathetic chain. ‚ The axons that leave the spinal cord through the ventral root are part of the preganglionic neurons. Ú With one exception, all sympathetic preganglionic axon enter the ganglia of the sympathetic chain, Ú but not all of th ...
... the neighboring ganglia above and below, thus forming the sympathetic chain. ‚ The axons that leave the spinal cord through the ventral root are part of the preganglionic neurons. Ú With one exception, all sympathetic preganglionic axon enter the ganglia of the sympathetic chain, Ú but not all of th ...
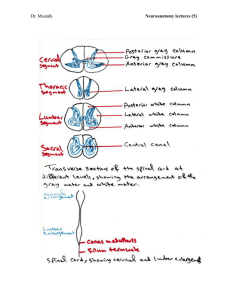
Lecture 2: The Spinal Cord
... • contains a red nucleus and a substantia nigra – Red nucleus contains numerous blood vessels and receives info from the cerebrum and cerebellum and issues subconscious motor commands concerned w/ muscle tone & posture – Lateral to the red nucleus is the melanin-containing substantia nigra which sec ...
... • contains a red nucleus and a substantia nigra – Red nucleus contains numerous blood vessels and receives info from the cerebrum and cerebellum and issues subconscious motor commands concerned w/ muscle tone & posture – Lateral to the red nucleus is the melanin-containing substantia nigra which sec ...
Lab 2. Medulla - Stritch School of Medicine
... – concerned with horizontal eye movement via its connections with the abducens nucleus, which is found more rostrally. ...
... – concerned with horizontal eye movement via its connections with the abducens nucleus, which is found more rostrally. ...
PDF
... * Each injection contained 0 1 mg NGF. All injections started with 6-day embryos. t This embryo received injections on day 6 (1 injection), day 7 (2 injections) and day (2 injections). ...
... * Each injection contained 0 1 mg NGF. All injections started with 6-day embryos. t This embryo received injections on day 6 (1 injection), day 7 (2 injections) and day (2 injections). ...
MS Word DOC - AvianBrain.org
... having the same initials but different meaning? As long discussed by many authors through the avi-eaters list and dinner meetings during the past years, all of these options have advantages and disadvantages, which we will not enter to explain here again. In our own search of good and useful names ...
... having the same initials but different meaning? As long discussed by many authors through the avi-eaters list and dinner meetings during the past years, all of these options have advantages and disadvantages, which we will not enter to explain here again. In our own search of good and useful names ...
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (or basal nuclei) comprise multiple subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates, which are situated at the base of the forebrain. Basal ganglia nuclei are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions including: control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, routine behaviors or ""habits"" such as bruxism, eye movements, cognition and emotion.The main components of the basal ganglia – as defined functionally – are the dorsal striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen), ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), globus pallidus, ventral pallidum, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus. It is important to note, however, that the dorsal striatum and globus pallidus may be considered anatomically distinct from the substantia nigra, nucleus accumbens, and subthalamic nucleus. Each of these components has a complex internal anatomical and neurochemical organization. The largest component, the striatum (dorsal and ventral), receives input from many brain areas beyond the basal ganglia, but only sends output to other components of the basal ganglia. The pallidum receives input from the striatum, and sends inhibitory output to a number of motor-related areas. The substantia nigra is the source of the striatal input of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which plays an important role in basal ganglia function. The subthalamic nucleus receives input mainly from the striatum and cerebral cortex, and projects to the globus pallidus.Currently, popular theories implicate the basal ganglia primarily in action selection; that is, it helps determine the decision of which of several possible behaviors to execute at any given time. In more specific terms, the basal ganglia's primary function is likely to control and regulate activities of the motor and premotor cortical areas so that voluntary movements can be performed smoothly. Experimental studies show that the basal ganglia exert an inhibitory influence on a number of motor systems, and that a release of this inhibition permits a motor system to become active. The ""behavior switching"" that takes place within the basal ganglia is influenced by signals from many parts of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, which plays a key role in executive functions.The importance of these subcortical nuclei for normal brain function and behavior is emphasized by the numerous and diverse neurological conditions associated with basal ganglia dysfunction, which include: disorders of behavior control such as Tourette syndrome, hemiballismus, and obsessive–compulsive disorder; dystonia; psychostimulant addiction; and movement disorders, the most notable of which are Parkinson's disease, which involves degeneration of the dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra pars compacta, and Huntington's disease, which primarily involves damage to the striatum. The basal ganglia have a limbic sector whose components are assigned distinct names: the nucleus accumbens, ventral pallidum, and ventral tegmental area (VTA). There is considerable evidence that this limbic part plays a central role in reward learning, particularly a pathway from the VTA to the nucleus accumbens that uses the neurotransmitter dopamine. A number of highly addictive drugs, including cocaine, amphetamine, and nicotine, are thought to work by increasing the efficacy of this dopamine signal. There is also evidence implicating overactivity of the VTA dopaminergic projection in schizophrenia.