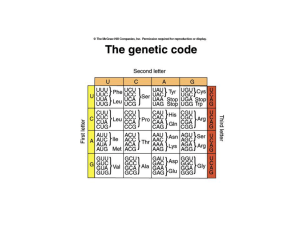
Features of the genetic code
... • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates any of the three stop codons leading a a premature truncation of the polypeptide. ...
... • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates any of the three stop codons leading a a premature truncation of the polypeptide. ...
Gene to Protein
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Helps form ribosomes: the workbench where proteins are assembled ...
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Helps form ribosomes: the workbench where proteins are assembled ...
Molecular Genetics
... • Special sequences upstream of the gene determine gene transcription • Promoter is where the RNA polymerase will bond • Contains TATA box, which is located 25 nucleotides away from the site where transcription is initiated. • Transcription Factors attach first • RNA Polymerase then bonds to comple ...
... • Special sequences upstream of the gene determine gene transcription • Promoter is where the RNA polymerase will bond • Contains TATA box, which is located 25 nucleotides away from the site where transcription is initiated. • Transcription Factors attach first • RNA Polymerase then bonds to comple ...
Systems Microbiology 1
... 3) promoters for expression of the cloned gene. (e.g. M13 phage promoters for generation of single-stranded DNA, etc). The F plasmid is much too large to be useful as a cloning vector and does not contain any selectable markers. ...
... 3) promoters for expression of the cloned gene. (e.g. M13 phage promoters for generation of single-stranded DNA, etc). The F plasmid is much too large to be useful as a cloning vector and does not contain any selectable markers. ...
Reading Guide
... 13. What protein is affected by the Cystic Fibrosis gene mutation? How is the protein affected? 14. About how many genes are found in E. coli? In Yeast? In humans? 15. What percentage of the human genome contains genes which encode protein products? 16. Describe two ways in which genes are identifie ...
... 13. What protein is affected by the Cystic Fibrosis gene mutation? How is the protein affected? 14. About how many genes are found in E. coli? In Yeast? In humans? 15. What percentage of the human genome contains genes which encode protein products? 16. Describe two ways in which genes are identifie ...
Gene_expression
... (a “reporter gene”). The jellyfish green fluorscent protein (GFP) gene is often used, as the encoded protein emits green light when exposed to light of the proper wavelength. We can test for CRM activity in transfected cells in culture, or even better, in a transgenic animal: ...
... (a “reporter gene”). The jellyfish green fluorscent protein (GFP) gene is often used, as the encoded protein emits green light when exposed to light of the proper wavelength. We can test for CRM activity in transfected cells in culture, or even better, in a transgenic animal: ...
Molecular Techniques in Cell & Molecular Biology
... They make possible new ways to study the functions of genes and their protein products and also commercial production of specific gene products such as human insulin in bacteria. (We offer a full-semester course in RDNA techniques; this is by necessity a brief intro) 4 steps: 1. Recombination 2. Sel ...
... They make possible new ways to study the functions of genes and their protein products and also commercial production of specific gene products such as human insulin in bacteria. (We offer a full-semester course in RDNA techniques; this is by necessity a brief intro) 4 steps: 1. Recombination 2. Sel ...
Unit 6B Learning Targets
... 1. I can explain how the sequence of the RNA bases, together with the structure of the RNA molecule, determines RNA function. a. mRNA carries information from DNA to the ribosome. b. tRNA molecules bind specific amino acids and allow information in the mRNA to be translated to a linear peptide seque ...
... 1. I can explain how the sequence of the RNA bases, together with the structure of the RNA molecule, determines RNA function. a. mRNA carries information from DNA to the ribosome. b. tRNA molecules bind specific amino acids and allow information in the mRNA to be translated to a linear peptide seque ...
Transcription Biology Review
... • Proteins that line up several amino acid contacts bind strongly to specific DNA sequences ...
... • Proteins that line up several amino acid contacts bind strongly to specific DNA sequences ...
The Organization and Control of Eukaryotic Genomes
... development. In all organisms, the expression of specific genes is most commonly regulated at the level of transcription by DNA-binding proteins. ...
... development. In all organisms, the expression of specific genes is most commonly regulated at the level of transcription by DNA-binding proteins. ...
MS Word file
... transcription Promoters: Basal transcription apparatus Transcriptional activator proteins RNA polymerase II – mRNA synthesis Core promoter TATA box TATAAAA, −25 to −30 bp, binded by transcription factors Transcription and Nucleosome Structure – Chromatin modification before transcription Promoters: ...
... transcription Promoters: Basal transcription apparatus Transcriptional activator proteins RNA polymerase II – mRNA synthesis Core promoter TATA box TATAAAA, −25 to −30 bp, binded by transcription factors Transcription and Nucleosome Structure – Chromatin modification before transcription Promoters: ...
Diversity of genomes and the tree of life
... related genes that have resulted from a gene duplication event within a single genome, and are likely to have diverged in their function ...
... related genes that have resulted from a gene duplication event within a single genome, and are likely to have diverged in their function ...
Mock Exam 2BY330 Summer 2014 Assume that 4 molecules of
... 2. The cytochrome complexes in the mitochondria have _______________ ions in their core, normally present in the (oxidized, reduced) state. 3. Which of the following proteins can be used to synthesize ribosomal RNA in eukaryotes? Circle all that apply. a). RNA polymerase I b). RNA polymerase II c). ...
... 2. The cytochrome complexes in the mitochondria have _______________ ions in their core, normally present in the (oxidized, reduced) state. 3. Which of the following proteins can be used to synthesize ribosomal RNA in eukaryotes? Circle all that apply. a). RNA polymerase I b). RNA polymerase II c). ...
Molecular Biology Primer
... • Example – Prokaryotic RNA polymerases scan along DNA looking for a specific set of approximately 13 nucleotides marking the beginning of genes – 1 nucleotide that serves as a transcriptional start site – 6 that are 10 nucleotides 5' to the start site, and – 6 more that are 35 nucleotides 5' to the ...
... • Example – Prokaryotic RNA polymerases scan along DNA looking for a specific set of approximately 13 nucleotides marking the beginning of genes – 1 nucleotide that serves as a transcriptional start site – 6 that are 10 nucleotides 5' to the start site, and – 6 more that are 35 nucleotides 5' to the ...
Bio 102 Practice Problems
... 1. Which of the following statements is true about gene regulation in bacteria? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 1. Which of the following statements is true about gene regulation in bacteria? A. B. C. D. E. ...
Carcinogenesis
... • Oncogenes are activated, unregulated versions of protooncogenes • Protooncogenes normal genes encoding for protein kinase and other growth signals • Their gene products stimulate cell growth • Viral oncogenes are altered copies of protooncogenes • 20% of human tumours show oncogenes ...
... • Oncogenes are activated, unregulated versions of protooncogenes • Protooncogenes normal genes encoding for protein kinase and other growth signals • Their gene products stimulate cell growth • Viral oncogenes are altered copies of protooncogenes • 20% of human tumours show oncogenes ...
RNA Transcription
... polymerase bumps into the assemblage and is then held there by binding to it. ...
... polymerase bumps into the assemblage and is then held there by binding to it. ...
Lecture 3 - Transcription (student)
... 2. tRNA – transfer RNA *transfer appropriate AAs to build proteins 3. rRNA – ribosomal RNA *structural component of ribosome that is used ...
... 2. tRNA – transfer RNA *transfer appropriate AAs to build proteins 3. rRNA – ribosomal RNA *structural component of ribosome that is used ...
Protein Synthesis
... constantly being transcribed and translated • not all proteins are needed by all cells at all times, so gene regulation is important to an organism's survival ...
... constantly being transcribed and translated • not all proteins are needed by all cells at all times, so gene regulation is important to an organism's survival ...
Protein Synthesis - Helena High School
... 1. DNA codes for what macromolecule? Provide three examples of proteins necessary in our bodies a. b. c. 2. Where is the code within the DNA molecule that provides the instructions for making proteins? ...
... 1. DNA codes for what macromolecule? Provide three examples of proteins necessary in our bodies a. b. c. 2. Where is the code within the DNA molecule that provides the instructions for making proteins? ...
Molecular Pathology - Charles River Laboratories
... By combining a strong history in molecular biology and histopathology, Charles River can relate gene expression to tissue histomorphology in both normal tissues and therapeutic models of disease, providing you with that valuable functional genomics information. The end result is the best possible in ...
... By combining a strong history in molecular biology and histopathology, Charles River can relate gene expression to tissue histomorphology in both normal tissues and therapeutic models of disease, providing you with that valuable functional genomics information. The end result is the best possible in ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.























