HOW TO FIND GENES WITHIN A DNA SEQUENCE?
... Scan for ORFs (open reading frames) - check all 6 reading frames (both strands) ...
... Scan for ORFs (open reading frames) - check all 6 reading frames (both strands) ...
1. Bacterial genomes
... Scan for ORFs (open reading frames) - check all 6 reading frames (both strands) ...
... Scan for ORFs (open reading frames) - check all 6 reading frames (both strands) ...
Chapter 13 Mutations (2)
... If genes are not accessible to RNA polymerase, they cannot be transcribed. In the nucleus, highly condensed chromatin is not available for transcription, while more loosely condensed chromatin is available for transcription. ...
... If genes are not accessible to RNA polymerase, they cannot be transcribed. In the nucleus, highly condensed chromatin is not available for transcription, while more loosely condensed chromatin is available for transcription. ...
10 Worksheet 9 Handout for powerpoint Applying our Knowledg
... b) “Ultimately you would hope all parents would take advantage of screening techniques in an effort to reduce the frequency of children born with genetic abnormalities.” c) “As long as there are strict guidelines controlling gene therapy, society will not have to be concerned about abuses of this te ...
... b) “Ultimately you would hope all parents would take advantage of screening techniques in an effort to reduce the frequency of children born with genetic abnormalities.” c) “As long as there are strict guidelines controlling gene therapy, society will not have to be concerned about abuses of this te ...
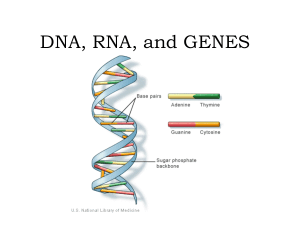
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... molecules. • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
... molecules. • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
Lecture 6, Exam III Worksheet Answers
... first or it may not affect the total protein structure. 3. Nonsense mutation- often lethal. This mutation changes a base pair that results in the creation of a stop codon. Stops protein synthesis before it is finished. 5. How does translation differ between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? What is an ope ...
... first or it may not affect the total protein structure. 3. Nonsense mutation- often lethal. This mutation changes a base pair that results in the creation of a stop codon. Stops protein synthesis before it is finished. 5. How does translation differ between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? What is an ope ...
13 Packet
... sequences, is called an operon. One control sequence, the promoter, is a binding site for an enzyme needed in DNA transcription. The other control sequence, the operator, switches the promoter on and off. A protein called the repressor turns the operator off by binding to it. This process enables pr ...
... sequences, is called an operon. One control sequence, the promoter, is a binding site for an enzyme needed in DNA transcription. The other control sequence, the operator, switches the promoter on and off. A protein called the repressor turns the operator off by binding to it. This process enables pr ...
Lecture 7 Manipulation of gene expression and secretion of foreign
... the translational level. The most active construct contained seven enhancer elements and directed much higher level of foreign gene expression in both transgenic tobacco and rice plants than when the 355 promoter alone was used. These promoter constructs directed a wide range of foreign gene express ...
... the translational level. The most active construct contained seven enhancer elements and directed much higher level of foreign gene expression in both transgenic tobacco and rice plants than when the 355 promoter alone was used. These promoter constructs directed a wide range of foreign gene express ...
Does your DNA define you Qu
... genome on and off at specific times and places so that different genes are expressed at different times; this is achieved through the addition of chemical tags to DNA itself or to the proteins DNA is associated with. Epigenetics is the study of these reactions and the factors that influence them. Ep ...
... genome on and off at specific times and places so that different genes are expressed at different times; this is achieved through the addition of chemical tags to DNA itself or to the proteins DNA is associated with. Epigenetics is the study of these reactions and the factors that influence them. Ep ...
4.2 Sources of DNA
... Viral DNA or RNA molecules are short so easy to manipulate, since they do not create as many proteins as cells do. Viral DNA is sometimes used as a vector because they can open to insert genes of interest. Some companies are exploring the use of gene therapy to treat diabetes by replacing defective ...
... Viral DNA or RNA molecules are short so easy to manipulate, since they do not create as many proteins as cells do. Viral DNA is sometimes used as a vector because they can open to insert genes of interest. Some companies are exploring the use of gene therapy to treat diabetes by replacing defective ...
Plasmids are fragments of double-stranded DNA that can replicate
... Allows for selection of plasmid-containing bacteria. Short segment of DNA which contains several restriction sites allowing for the easy insertion of DNA. In expression plasmids, the MCS is often downstream from a promoter. Gene, promoter or other DNA fragment cloned into the MCS for further study. ...
... Allows for selection of plasmid-containing bacteria. Short segment of DNA which contains several restriction sites allowing for the easy insertion of DNA. In expression plasmids, the MCS is often downstream from a promoter. Gene, promoter or other DNA fragment cloned into the MCS for further study. ...
PPT
... cluster and is broken down iteratively into sub-clusters with similar expression profiles until each cluster contains only one gene. This information can be represented as a tree, where the terminal nodes represent genes and all branches represent different clusters. The distance from the branch poi ...
... cluster and is broken down iteratively into sub-clusters with similar expression profiles until each cluster contains only one gene. This information can be represented as a tree, where the terminal nodes represent genes and all branches represent different clusters. The distance from the branch poi ...
Chapt16_lecture
... • Methylation (the addition of –CH3) of DNA or histone proteins is associated with the control of gene expression. • Clusters of methylated cytosine nucleotides bind to a protein that prevents activators from binding to DNA. • Methylated histone proteins are associated with inactive regions of chrom ...
... • Methylation (the addition of –CH3) of DNA or histone proteins is associated with the control of gene expression. • Clusters of methylated cytosine nucleotides bind to a protein that prevents activators from binding to DNA. • Methylated histone proteins are associated with inactive regions of chrom ...
Chapter 6
... The evolutionary divergence between two proteins is measured by the percent of positions at which the corresponding amino acids differ. Mutations accumulate at a more or less even speed after genes separate, so that the divergence between any pair of globin sequences is proportional to the time sinc ...
... The evolutionary divergence between two proteins is measured by the percent of positions at which the corresponding amino acids differ. Mutations accumulate at a more or less even speed after genes separate, so that the divergence between any pair of globin sequences is proportional to the time sinc ...
1. Explain how a gene directs the synthesis of an mRNA molecule
... DNA polymerase is the enzyme which carries out DNA replication. ...
... DNA polymerase is the enzyme which carries out DNA replication. ...
lacI
... In bacterial RNA polymerse, the core enzyme consists of four subunits: two copies of alpha (α), a single copy of beta (β), and a single copy of ...
... In bacterial RNA polymerse, the core enzyme consists of four subunits: two copies of alpha (α), a single copy of beta (β), and a single copy of ...
Microbial Genetics
... • The genotype of an individual refers to its particular genetic make-up. It’s the potential for all characteristics we can observe. A particular gene may have some variation in the sequence between individuals, called alleles. • The phenotype is the actual characteristics observed for an individua ...
... • The genotype of an individual refers to its particular genetic make-up. It’s the potential for all characteristics we can observe. A particular gene may have some variation in the sequence between individuals, called alleles. • The phenotype is the actual characteristics observed for an individua ...
April 3 lecture slides
... The transcriptional orientation of the 3 genes coding for enzymes important in galactose utilization in Saccharomyces ...
... The transcriptional orientation of the 3 genes coding for enzymes important in galactose utilization in Saccharomyces ...
Lecture_5
... ~ 1Mb larger than K-12 and contains 1,387 genes specific for O157:H7. – Genomes share a 4.1 Mb backbone with species specific DNA interspersed throughout the genome • K-islands - specific to K-12 (0.53Mb) • O-islands - specific ...
... ~ 1Mb larger than K-12 and contains 1,387 genes specific for O157:H7. – Genomes share a 4.1 Mb backbone with species specific DNA interspersed throughout the genome • K-islands - specific to K-12 (0.53Mb) • O-islands - specific ...
Transcription, RNA Processing, and
... Nascent RNA strand synthesis (elongation) occurs only in the 5’ 3’ direction, with new nucleotides added to the 3’ end of the nascent strand Transcription is catalyzed by DNA-directed RNA polymerases ...
... Nascent RNA strand synthesis (elongation) occurs only in the 5’ 3’ direction, with new nucleotides added to the 3’ end of the nascent strand Transcription is catalyzed by DNA-directed RNA polymerases ...
MOPAC: Motif-finding by Preprocessing and Agglomerative
... 3. the motif does not have to be shared by all genes in the cluster, only a subset ...
... 3. the motif does not have to be shared by all genes in the cluster, only a subset ...
lec3
... 2. Accessory transcription activator proteins a) Can bind to specific DNA sequences and help RNA polymerase initiate transcription via protein-protein interactions or by altering the structure of the DNA. b) Transcription of some promoters requires an accessory transcriptional activator; at other pr ...
... 2. Accessory transcription activator proteins a) Can bind to specific DNA sequences and help RNA polymerase initiate transcription via protein-protein interactions or by altering the structure of the DNA. b) Transcription of some promoters requires an accessory transcriptional activator; at other pr ...
Transcription from DNA Virus Genomes
... • T binds polyomaviridae Oris as a hexamer • Early promoter dampened • Late promoter activated • Early transcripts are decreased relative to Late ...
... • T binds polyomaviridae Oris as a hexamer • Early promoter dampened • Late promoter activated • Early transcripts are decreased relative to Late ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.