Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University ...
... Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University ...
Section 15.1 – Totipotency and cells specialisation
... Under certain conditions they can specialise and develop into certain cells There are also embryonic stem cells that occur in the earliest stage of the development of an embryo Mature plants have many totipotent cells Growing cells outside of an organism is called in vitro development ...
... Under certain conditions they can specialise and develop into certain cells There are also embryonic stem cells that occur in the earliest stage of the development of an embryo Mature plants have many totipotent cells Growing cells outside of an organism is called in vitro development ...
Lecture 14 Student Powerpoint
... transcription that involved the production of a primary transcript and the processing of this into aspects of how this is processed into an mRNA in Eukaryotes. This lecture focuses on these topics and on how signals are perceived that modulate the expression of eukaryotic genes. The next lecture wil ...
... transcription that involved the production of a primary transcript and the processing of this into aspects of how this is processed into an mRNA in Eukaryotes. This lecture focuses on these topics and on how signals are perceived that modulate the expression of eukaryotic genes. The next lecture wil ...
Chapter 17 - Denton ISD
... All translation begins with free ribosomes. If a growing polypeptide includes a signal peptide, a ___________________(SRP) helps attach it to the ER. ...
... All translation begins with free ribosomes. If a growing polypeptide includes a signal peptide, a ___________________(SRP) helps attach it to the ER. ...
The On’s and Off’s of Gene Expression
... – Why are liver cells liver and not brain? – Why are leaf cells leaf and not root? ...
... – Why are liver cells liver and not brain? – Why are leaf cells leaf and not root? ...
Topic 4 Genetics
... pathways, you have the same genes. [Allele: one specific form of a gene differing from other alleles by one or a few bases only and occupying the same gene locus as other alleles of the gene.] You get one set of alleles from your mom, and one from your dad. Which allele that gets expressed depends u ...
... pathways, you have the same genes. [Allele: one specific form of a gene differing from other alleles by one or a few bases only and occupying the same gene locus as other alleles of the gene.] You get one set of alleles from your mom, and one from your dad. Which allele that gets expressed depends u ...
G
... Transcript databases: Wider coverage and gives hints about alternative splicing. However sometimes gives only partial information and is error prone and noisy. ...
... Transcript databases: Wider coverage and gives hints about alternative splicing. However sometimes gives only partial information and is error prone and noisy. ...
Ch17_note_summary
... 3) Termination- stop codons (UAG, UAA, and UGA) cause that addition of water instead of amino acid, hydrolyzing and releasing the polypeptide. ...
... 3) Termination- stop codons (UAG, UAA, and UGA) cause that addition of water instead of amino acid, hydrolyzing and releasing the polypeptide. ...
8.6 Gene Expression and Regulation
... our cells are not the same! • Cells differ from each other because different sets of genes are expressed in different types of cells. • Eukaryotic cells can control/ regulate gene expression at several different points BUT one of the most highly regulated steps is at the start of transcription. ...
... our cells are not the same! • Cells differ from each other because different sets of genes are expressed in different types of cells. • Eukaryotic cells can control/ regulate gene expression at several different points BUT one of the most highly regulated steps is at the start of transcription. ...
Lecture 5
... We start as a single fertilized egg which divides into identical cells So why aren’t we born as blobs of identical cells? Why do we stop growing? Every cell has identical DNA, so what makes cells different? Genes are not operating in the same places in the same manner Certain genes are turned on, ot ...
... We start as a single fertilized egg which divides into identical cells So why aren’t we born as blobs of identical cells? Why do we stop growing? Every cell has identical DNA, so what makes cells different? Genes are not operating in the same places in the same manner Certain genes are turned on, ot ...
Gene Expression
... genetic makeup of a cell, organism or species. Though most of the genome is non-coding, the coding regions (“genes”) are what primarily determine the traits of organisms. Triplet codes found in a gene code for amino acids. The genetic code is considered to be universal. Structural and functional dif ...
... genetic makeup of a cell, organism or species. Though most of the genome is non-coding, the coding regions (“genes”) are what primarily determine the traits of organisms. Triplet codes found in a gene code for amino acids. The genetic code is considered to be universal. Structural and functional dif ...
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Objectives: The objective of this course is to
... to distinguish between different molecular biology techniques that are used to isolate, separate, and probe for specific proteins, nucleic acids, and their interactions; to identify limitations of these techniques; to given a particular biological question, identify which experimental techniques are ...
... to distinguish between different molecular biology techniques that are used to isolate, separate, and probe for specific proteins, nucleic acids, and their interactions; to identify limitations of these techniques; to given a particular biological question, identify which experimental techniques are ...
A Tale of Three Inferences
... statistical mechanical (hence concentration dependent) way. • Controversial: interaction among different transcription factor-binding events. ...
... statistical mechanical (hence concentration dependent) way. • Controversial: interaction among different transcription factor-binding events. ...
GENE REGULATION 12-5 - Somers Public Schools
... EUKARYOTES are more COMPLEX Additional regulatory sequences: ENHANCER regions 1. ___________ upstream from promoters bind many different regulatory proteins that help or prevent transcription TATA box 2. __________ (TATATA or TATAAA) helps position RNA POLYMERASE ...
... EUKARYOTES are more COMPLEX Additional regulatory sequences: ENHANCER regions 1. ___________ upstream from promoters bind many different regulatory proteins that help or prevent transcription TATA box 2. __________ (TATATA or TATAAA) helps position RNA POLYMERASE ...
Some transcription factors ("Enhancer
... varying distances and upstream, within, or downstream, of the genes they control. The portions of the gene that encode the amino acid sequence of a protein are called the exons. These protein-coding regions can be interrupted by intervening sequences, or introns. Introns can vary in number from 0 to ...
... varying distances and upstream, within, or downstream, of the genes they control. The portions of the gene that encode the amino acid sequence of a protein are called the exons. These protein-coding regions can be interrupted by intervening sequences, or introns. Introns can vary in number from 0 to ...
Slide 1
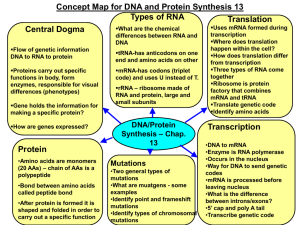
... functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for visual differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein? How are genes expressed? ...
... functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for visual differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein? How are genes expressed? ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzymes involved. We will also look more specifically at mutations; how they can occur and what effects they might have. Pages in the b ...
... We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzymes involved. We will also look more specifically at mutations; how they can occur and what effects they might have. Pages in the b ...
Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Control of Transcription in
... ~1.5% of the human genome, but ~90% of the genome appears to be transcribed… ...
... ~1.5% of the human genome, but ~90% of the genome appears to be transcribed… ...
Gene Expression and Regulation
... “turned on and off”. For example, the gene that codes for melanin is activated/expressed or “turned on” in skin cells but not for liver cells. This is called gene regulation. ...
... “turned on and off”. For example, the gene that codes for melanin is activated/expressed or “turned on” in skin cells but not for liver cells. This is called gene regulation. ...