Control of Gene Expression
... • Now part of the rest of the bacteria chromosome can be transferred to another bacteria cell: ...
... • Now part of the rest of the bacteria chromosome can be transferred to another bacteria cell: ...
DNA Function II - Complete Vocab with
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
Lecture#5 - Introduction to gene regulation and operons in
... Gene expression involves: 1) Transcription - Information is transferred from the DNA sequence into an RNA sequence - messenger RNA. 2) Translation - Information is transferred from the mRNA to protein sequence. 3) Proteins function to carry out the final actions of expression. Enzyme activity -> str ...
... Gene expression involves: 1) Transcription - Information is transferred from the DNA sequence into an RNA sequence - messenger RNA. 2) Translation - Information is transferred from the mRNA to protein sequence. 3) Proteins function to carry out the final actions of expression. Enzyme activity -> str ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... C. a set of epigenetic modifications that influences gene expression D. the fact that the core histone particle contains an octomer of histone proteins ...
... C. a set of epigenetic modifications that influences gene expression D. the fact that the core histone particle contains an octomer of histone proteins ...
Methyl CpG binding protein 2 binding sites on chromosome 22 in
... Methyl CpG binding protein 2 binding sites on chromosome 22 in hepatocellular carcinoma B cells ...
... Methyl CpG binding protein 2 binding sites on chromosome 22 in hepatocellular carcinoma B cells ...
Gene Regulation - Marblehead High School
... His parents do not have this condition Your Assignment: Do your medical research to find out the cause of this student’s situation. Describe what is happening to him and explain ...
... His parents do not have this condition Your Assignment: Do your medical research to find out the cause of this student’s situation. Describe what is happening to him and explain ...
Unit 4 - University of Colorado Boulder
... 16. Explain why gene regulation is necessary in all organisms, even those that are singlecelled. 17. Explain why gene regulation is essential for multicellular organisms (a) during development and (b) with regard to the existence of specialized tissues. Mechanisms of gene regulation in bacteria and ...
... 16. Explain why gene regulation is necessary in all organisms, even those that are singlecelled. 17. Explain why gene regulation is essential for multicellular organisms (a) during development and (b) with regard to the existence of specialized tissues. Mechanisms of gene regulation in bacteria and ...
Gene Regulation and Expression Notes
... When lactose is not present, the lac genes are turned off by regulatory proteins that bind to DNA and block transcription. ...
... When lactose is not present, the lac genes are turned off by regulatory proteins that bind to DNA and block transcription. ...
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
... Adjacent genes (RNA-coding as well as protein-coding) are often separated by an insulator which helps them avoid cross-talk between each other's promoters and enhancers (and/or silencers). Transcription start site This is where a molecule of RNA polymerase II (pol II, also known as RNAP II) binds. P ...
... Adjacent genes (RNA-coding as well as protein-coding) are often separated by an insulator which helps them avoid cross-talk between each other's promoters and enhancers (and/or silencers). Transcription start site This is where a molecule of RNA polymerase II (pol II, also known as RNAP II) binds. P ...
Brief description of pGLO
... that not only supported replication of foreign DNA sequences but which allowed expression of the genes they carried. This later type of cloning vector is referred to as an “expression vector”. To achieve expression of the foreign gene, it is inserted, in the correct orientation, adjacent to a functi ...
... that not only supported replication of foreign DNA sequences but which allowed expression of the genes they carried. This later type of cloning vector is referred to as an “expression vector”. To achieve expression of the foreign gene, it is inserted, in the correct orientation, adjacent to a functi ...
October 3, 2016 Worksheet
... Do we use introns or exons? Draw a strand of DNA that contains silencer, repressor, basal transcription factors, TATA box, (transcription factors): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysxtZJUeTCE Why does these processes need to happen? ...
... Do we use introns or exons? Draw a strand of DNA that contains silencer, repressor, basal transcription factors, TATA box, (transcription factors): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysxtZJUeTCE Why does these processes need to happen? ...
Gene Expression/Mutations
... - Operon: promoter, operator, structural (functional) genes - Promoter: control sequence, site where replication starts - Operator: DNA sequence between promoter and enzyme genes, acts as on/off switch for genes - Functional genes: coding sections - Inducer: protein that initiates gene expression, m ...
... - Operon: promoter, operator, structural (functional) genes - Promoter: control sequence, site where replication starts - Operator: DNA sequence between promoter and enzyme genes, acts as on/off switch for genes - Functional genes: coding sections - Inducer: protein that initiates gene expression, m ...
Lecture Slides
... ASD are in large parte genetic conditions but many ASD-genes are not identified yet Whole exome and whole genome analysis accelerated discoveries ...
... ASD are in large parte genetic conditions but many ASD-genes are not identified yet Whole exome and whole genome analysis accelerated discoveries ...
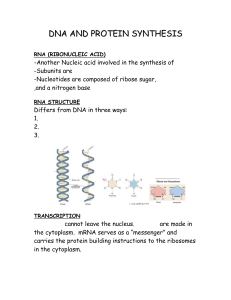
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
From Gene to Protein Protein Synthesis
... RNA polymerase: pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase attaches and where initiation of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA m ...
... RNA polymerase: pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase attaches and where initiation of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA m ...
Postdoc position in Regulation of Gene Transcription by RNA
... A post-doctoral position is available at the Central-European Institute of Technology (CEITEC), Brno, Czech Republic, in the newly established group of Dalibor Blazek (lab pages at: http://www.ceitec.cz/en/inherited-diseases-ii-transcriptional-regulation/rg38? langselect=1 ). The project focuses on ...
... A post-doctoral position is available at the Central-European Institute of Technology (CEITEC), Brno, Czech Republic, in the newly established group of Dalibor Blazek (lab pages at: http://www.ceitec.cz/en/inherited-diseases-ii-transcriptional-regulation/rg38? langselect=1 ). The project focuses on ...
Chapter 19: Eukaryotic Genomes: Organization
... decreases transcription; methylation of DNA may be involved in long-term inactivation of genes Transcriptional regulation Transcription factors (activators) bind with enhancers, then interact with mediator proteins and promoter regions to form transcription initiation complex; repressors can inhibit ...
... decreases transcription; methylation of DNA may be involved in long-term inactivation of genes Transcriptional regulation Transcription factors (activators) bind with enhancers, then interact with mediator proteins and promoter regions to form transcription initiation complex; repressors can inhibit ...
24 October - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the fidelity of replication during DNA synthesis? 2. Define “promoter” and disc ...
... posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the fidelity of replication during DNA synthesis? 2. Define “promoter” and disc ...
Chp 11 Notes
... a. Inducer: a molecule that initiates gene expression b. Lactose binds to the repressor protein and changes its shape causing it to detach from the operator (the switch) c. The RNA polymerase can now make the enzymes needed for lactose metabolism d. Lactose is the inducer in this example 9. The abil ...
... a. Inducer: a molecule that initiates gene expression b. Lactose binds to the repressor protein and changes its shape causing it to detach from the operator (the switch) c. The RNA polymerase can now make the enzymes needed for lactose metabolism d. Lactose is the inducer in this example 9. The abil ...
Subject Description Form
... and the rRNAs. Transposable elements: transposons, jumping genes and retrotransposons. Regulation of prokaryotic gene expression: positive and negative controls, the operon, regulatory RNA (attenuation and termination), phage strategies (lytic vs lysogenic pathways). Regulation of eukaryotic gene ex ...
... and the rRNAs. Transposable elements: transposons, jumping genes and retrotransposons. Regulation of prokaryotic gene expression: positive and negative controls, the operon, regulatory RNA (attenuation and termination), phage strategies (lytic vs lysogenic pathways). Regulation of eukaryotic gene ex ...