Slide 1
... of skin pigmentation during exposure to sunlight in humans. How do organs develop in their proper positions? How do cells "know" where they are within a developing organism? Morphogens are chemicals found in the developing embryo. They are distributed unevenly and different concentrations of morphog ...
... of skin pigmentation during exposure to sunlight in humans. How do organs develop in their proper positions? How do cells "know" where they are within a developing organism? Morphogens are chemicals found in the developing embryo. They are distributed unevenly and different concentrations of morphog ...
Study Guide MBMB 451A Fall 2002
... and IIH. What are TAFs and are they important for basal transcription. 7. What is an enhancer? What is a response element? 8. Describe two models for how an enhancer could effect the level of transcription. 9. What are the transcription factors called that are used by Pol I and Pol III? 10. Discuss ...
... and IIH. What are TAFs and are they important for basal transcription. 7. What is an enhancer? What is a response element? 8. Describe two models for how an enhancer could effect the level of transcription. 9. What are the transcription factors called that are used by Pol I and Pol III? 10. Discuss ...
Controls - Warren`s Science Page
... of different tissues are differentiated (specialized) because of selective gene expression Every body cell arose by mitotic division from the same fertilized eggs Nearly all of your body cells become specialized in composition, structure, and function (Cell ...
... of different tissues are differentiated (specialized) because of selective gene expression Every body cell arose by mitotic division from the same fertilized eggs Nearly all of your body cells become specialized in composition, structure, and function (Cell ...
HANDOUT: CH 17 pt 1 Study
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
Slide 1
... four proteins (see Figures 7-52 and 7-53). The expression of eve in stripe 2 occurs only at the position where the two activators (Bicoid and Hunchback) are present and the two repressors (Giant and Krüppel) are absent. In fly embryos that lack Krüppel, for example, stripe 2 expands posteriorly. Lik ...
... four proteins (see Figures 7-52 and 7-53). The expression of eve in stripe 2 occurs only at the position where the two activators (Bicoid and Hunchback) are present and the two repressors (Giant and Krüppel) are absent. In fly embryos that lack Krüppel, for example, stripe 2 expands posteriorly. Lik ...
Transcription factors - Raleigh Charter High School
... • Enhancer - specific DNA sequences which bind with activators to enhance transcription. • Activator - transcription factor which binds to an enhancer and stimulates transcription of gene. help position of the initiation complex on the promoter. • TATA Box - the DNA sequence which indicates where th ...
... • Enhancer - specific DNA sequences which bind with activators to enhance transcription. • Activator - transcription factor which binds to an enhancer and stimulates transcription of gene. help position of the initiation complex on the promoter. • TATA Box - the DNA sequence which indicates where th ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 17. What is not different between prokaryote and eukaryote transcription a. the number of RNA polymerases b. use of uracil nucleotides in place of thymine nucleotides c. separation of transcription and translation d. simultaneous polysomes during transcription e. RNA peocessing 18. Combinatorial re ...
... 17. What is not different between prokaryote and eukaryote transcription a. the number of RNA polymerases b. use of uracil nucleotides in place of thymine nucleotides c. separation of transcription and translation d. simultaneous polysomes during transcription e. RNA peocessing 18. Combinatorial re ...
outline File - selu moodle
... Stop codon Start codon Wobble effect at third position Near universal 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the t ...
... Stop codon Start codon Wobble effect at third position Near universal 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the t ...
Bio 313 worksheet 14 - Iowa State University
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
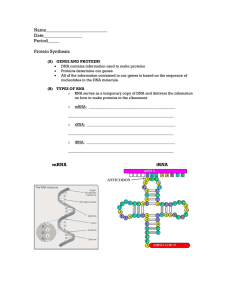
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
4.2.08 105 lecture
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the coding region is part of the transcription unit. The coding region is the genetic information in the DNA that tells the specific structure (primary ami ...
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the coding region is part of the transcription unit. The coding region is the genetic information in the DNA that tells the specific structure (primary ami ...
Regulation of gene expression
... Genetic regulation • Genotype is not phenotype: bacteria possess many genes that they are not using at any particular time. • Transcription and translation are expensive; why spend ATP to make an enzyme you don’t need? • Operon – Genes physically adjacent regulated together ...
... Genetic regulation • Genotype is not phenotype: bacteria possess many genes that they are not using at any particular time. • Transcription and translation are expensive; why spend ATP to make an enzyme you don’t need? • Operon – Genes physically adjacent regulated together ...
Chapt16_lecture
... • Methylation (the addition of –CH3) of DNA or histone proteins is associated with the control of gene expression. • Clusters of methylated cytosine nucleotides bind to a protein that prevents activators from binding to DNA. • Methylated histone proteins are associated with inactive regions of chrom ...
... • Methylation (the addition of –CH3) of DNA or histone proteins is associated with the control of gene expression. • Clusters of methylated cytosine nucleotides bind to a protein that prevents activators from binding to DNA. • Methylated histone proteins are associated with inactive regions of chrom ...
Chapter 7A
... polymerase further requires activators that bind to upstream enhancer sequences for initiation. As shown in Fig. 7.4, these "enhancer binding proteins" (e.g., NtrC) contact s54-RNA polymerase by looping of the DNA between them. The mechanism of transcription activation by s54-RNA polymerase is simil ...
... polymerase further requires activators that bind to upstream enhancer sequences for initiation. As shown in Fig. 7.4, these "enhancer binding proteins" (e.g., NtrC) contact s54-RNA polymerase by looping of the DNA between them. The mechanism of transcription activation by s54-RNA polymerase is simil ...
401Lecture8Sp2013post
... modular proteins composed of a DNA binding domain and an activation domain • Repressors inhibit transcription and are modular proteins composed of a DNA binding domain and a repressor domain • Both repressor and activators recruit other proteins to affect gene expression • A cell must produce the sp ...
... modular proteins composed of a DNA binding domain and an activation domain • Repressors inhibit transcription and are modular proteins composed of a DNA binding domain and a repressor domain • Both repressor and activators recruit other proteins to affect gene expression • A cell must produce the sp ...
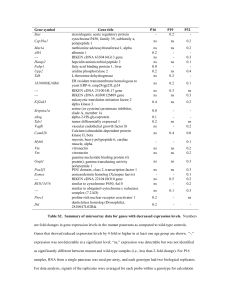
Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
6.4 Gene Regulation - Ms. Franklin`s Classroom
... When lactose is present in the E.coli’s environment, a protein must bind to the CAP binding site to increase the production of enzymes, if there is a lack of lactose in the environment transcription o the genes must be inhibited. The lacI is a regulator gene which codes for a protein that acts as an ...
... When lactose is present in the E.coli’s environment, a protein must bind to the CAP binding site to increase the production of enzymes, if there is a lack of lactose in the environment transcription o the genes must be inhibited. The lacI is a regulator gene which codes for a protein that acts as an ...
AP gene regulation
... produce the enzymes (proteins) that digest lactose all of the time. No, only when the environment requires it. – Most prokaryotic controls are transcriptional controls ...
... produce the enzymes (proteins) that digest lactose all of the time. No, only when the environment requires it. – Most prokaryotic controls are transcriptional controls ...
Judgement Statement – 2012
... inducer is present (lactose) it binds to the repressor and inactivates it / causes it to move off the operator site. The operator region is open, RNA polymerase can now bind to the promotor and transcription happens. Lactose digesting enzymes can be made. As the lactose is removed / broken down the ...
... inducer is present (lactose) it binds to the repressor and inactivates it / causes it to move off the operator site. The operator region is open, RNA polymerase can now bind to the promotor and transcription happens. Lactose digesting enzymes can be made. As the lactose is removed / broken down the ...
Schedule
... inducer is present (lactose) it binds to the repressor and inactivates it / causes it to move off the operator site. The operator region is open, RNA polymerase can now bind to the promotor and transcription happens. Lactose digesting enzymes can be made. As the lactose is removed / broken down the ...
... inducer is present (lactose) it binds to the repressor and inactivates it / causes it to move off the operator site. The operator region is open, RNA polymerase can now bind to the promotor and transcription happens. Lactose digesting enzymes can be made. As the lactose is removed / broken down the ...
ppt
... • Not all genes are active in all cells • Not all genes in a given cell are activated all the time • There MUST be some way to control when a gene is turned "on" or "off" • The activation of a gene results in transcription (mRNA made) which in turn results in the formation of a protein • Chromosomes ...
... • Not all genes are active in all cells • Not all genes in a given cell are activated all the time • There MUST be some way to control when a gene is turned "on" or "off" • The activation of a gene results in transcription (mRNA made) which in turn results in the formation of a protein • Chromosomes ...