- Department of Biosystems Science and
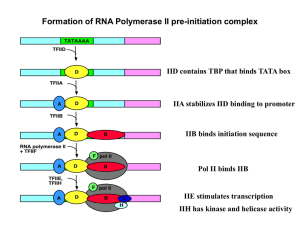
... co-chaperones such as Pih1 and Tah1, takes part in the stepwise assembly of these complexes, including RNA polymerase II. ...
... co-chaperones such as Pih1 and Tah1, takes part in the stepwise assembly of these complexes, including RNA polymerase II. ...
... 26. (12 pts) Please do one of the following two choices: Choice A: You haven’t eaten in a while but your liver has been actively metabolizing, consuming ATP. You then have a large influx of glucose due to eating lunch. i) What will happen to glycogen levels in the liver cell? Describe the regulatory ...
On the Nucleotide Sequence of Yeast Tyrosine Transfer RNA
... between the two RNAs. The left-hand loop and the "lump" between the right-hand and lower limbs show variations in both size and nucleotide composition, either of which an enzyme could probably use to recognize which tRNA it was about to aminoacylate. The G :U base pair in the upper stem might be imp ...
... between the two RNAs. The left-hand loop and the "lump" between the right-hand and lower limbs show variations in both size and nucleotide composition, either of which an enzyme could probably use to recognize which tRNA it was about to aminoacylate. The G :U base pair in the upper stem might be imp ...
Automatic identification of topic boundaries in
... For Nucleotide Sequences, the submenu items displayed are: Statistics, Restriction sites, Tandem repeats and BLAST. The Statistics option displays different measures like; the nucleotide base count, codon count and molecular weight of the sequence. Restriction site analysis: Restriction enzymes (RE) ...
... For Nucleotide Sequences, the submenu items displayed are: Statistics, Restriction sites, Tandem repeats and BLAST. The Statistics option displays different measures like; the nucleotide base count, codon count and molecular weight of the sequence. Restriction site analysis: Restriction enzymes (RE) ...
Translation tRNA is a link between the mRNA and the polypeptide
... After attachment to 5’end the complex is called initiation complex. It can scan the RNA. Leader sequences in eukaryotes are long – up to 100 or more bp, have structures – hairpins and other. eIF-4A and eIF-4B. eIF-4A and possible eIF-4B have helicase activity and are able to break intramolecular bas ...
... After attachment to 5’end the complex is called initiation complex. It can scan the RNA. Leader sequences in eukaryotes are long – up to 100 or more bp, have structures – hairpins and other. eIF-4A and eIF-4B. eIF-4A and possible eIF-4B have helicase activity and are able to break intramolecular bas ...
Annex 1
... (iv) "amino acids" are those L-amino acids commonly found in naturally occurring proteins and are listed in paragraph 48, table 3. Those amino acid sequences containing at least one D-amino acid are not intended to be embraced by this definition. Any amino acid sequence that contains post-translatio ...
... (iv) "amino acids" are those L-amino acids commonly found in naturally occurring proteins and are listed in paragraph 48, table 3. Those amino acid sequences containing at least one D-amino acid are not intended to be embraced by this definition. Any amino acid sequence that contains post-translatio ...
Can the Origin of the Genetic Code Be Explained - BIO
... proteins recognizes a specific amino acid and the specific anticodons it binds to within the code. They then bind amino acids to the tRNA that bears the corresponding anticodon. Thus, instead of the code reducing to a simple set of stereochemical affinities, biochemists have found a functionally int ...
... proteins recognizes a specific amino acid and the specific anticodons it binds to within the code. They then bind amino acids to the tRNA that bears the corresponding anticodon. Thus, instead of the code reducing to a simple set of stereochemical affinities, biochemists have found a functionally int ...
Counting Small RNA in Pathogenic Bacteria
... key insights into how messenger RNA (mRNA) are produced,1 the regulatory role of long noncoding RNA,2 and determination of cell fate by spatial patterning. One key method used to obtain single cell expression data is singlemolecule fluorescence hybridization (smFISH), a technique first introduced for ...
... key insights into how messenger RNA (mRNA) are produced,1 the regulatory role of long noncoding RNA,2 and determination of cell fate by spatial patterning. One key method used to obtain single cell expression data is singlemolecule fluorescence hybridization (smFISH), a technique first introduced for ...
this lecture as PDF here
... c. Repression of the phage genome - A phage coded protein, called a repressor, is made which binds to a particular site on the phage DNA, called the operator, and shuts off transcription of most phage genes EXCEPT the repressor gene. The result is a stable repressed phage genome which is integrated ...
... c. Repression of the phage genome - A phage coded protein, called a repressor, is made which binds to a particular site on the phage DNA, called the operator, and shuts off transcription of most phage genes EXCEPT the repressor gene. The result is a stable repressed phage genome which is integrated ...
Molecular Characterization of a Hamster Oviduct
... entire mature form of the bovine oviduct-specific glycoprotein [21]. A search of the GenBank database revealed high sequence homology between baboon and bovine oviductspecific glycoproteins but not with cDNA and other previously sequenced proteins. Northern blotting analysis using the baboon cDNA cl ...
... entire mature form of the bovine oviduct-specific glycoprotein [21]. A search of the GenBank database revealed high sequence homology between baboon and bovine oviductspecific glycoproteins but not with cDNA and other previously sequenced proteins. Northern blotting analysis using the baboon cDNA cl ...
Crystal Structures of Two Viral IRES RNA Domains Bound to the
... normal growth under physiological conditions as well as responses to internal or external stresses. Viruses do not have their own translation apparatus and have to use the host’s ribosome to synthesize their viral proteins. During viral infections, host cells down-regulate capdependent initiation as ...
... normal growth under physiological conditions as well as responses to internal or external stresses. Viruses do not have their own translation apparatus and have to use the host’s ribosome to synthesize their viral proteins. During viral infections, host cells down-regulate capdependent initiation as ...
HMW glutenin subunits in multiploid Aegilops species: composition
... Ae. juvenalis. ) In two of the four species analyzed, the presence of the subunits possessing an electrophoretic mobility similar to, or larger than, that of the 1Dx2.2 subunit was observed. However, it was not known if these subunits were encoded by the D genome component in the relevant Aegilops s ...
... Ae. juvenalis. ) In two of the four species analyzed, the presence of the subunits possessing an electrophoretic mobility similar to, or larger than, that of the 1Dx2.2 subunit was observed. However, it was not known if these subunits were encoded by the D genome component in the relevant Aegilops s ...
BI 112 Instructor: Waite Exam #4 Study Guide Cell Membrane
... Know that the process of the information encoding by DNA being copied into mRNA is called transcription; know the steps of transcription and what happens at each step; know the enzyme complex involved in transcription is called RNA polymerase ...
... Know that the process of the information encoding by DNA being copied into mRNA is called transcription; know the steps of transcription and what happens at each step; know the enzyme complex involved in transcription is called RNA polymerase ...
The KIebsieIIa pneumoniae cytochrome bd
... they require a source of low-potential reductant (between -400 and -500 mV at p H 7) as well as a minimum of 16 moles of ATP per mole of N, fixed (see Hill, 1992). The ability to fix N, is widely distributed amongst obligate anaerobic, facultative anaerobic and obligate aerobic prokaryotes (Young, 1 ...
... they require a source of low-potential reductant (between -400 and -500 mV at p H 7) as well as a minimum of 16 moles of ATP per mole of N, fixed (see Hill, 1992). The ability to fix N, is widely distributed amongst obligate anaerobic, facultative anaerobic and obligate aerobic prokaryotes (Young, 1 ...
Slide 1
... high level of annotation (such as the description of the function of a protein, its domains structure, post-translational modifications, variants, etc.) ...
... high level of annotation (such as the description of the function of a protein, its domains structure, post-translational modifications, variants, etc.) ...
Cloning and functional expression of invertebrate connexins from
... connexin-like sequences and failed to identify any innexin sequences [8]. However, this cursory analysis did not show any data on sequence alignments, provide any figures of molecular phylogeny, discuss gene structure, or most importantly, demonstrate that the connexin-like sequences encoded proteins ...
... connexin-like sequences and failed to identify any innexin sequences [8]. However, this cursory analysis did not show any data on sequence alignments, provide any figures of molecular phylogeny, discuss gene structure, or most importantly, demonstrate that the connexin-like sequences encoded proteins ...
Odyssey of Agrobacterium T-DNA.
... charged ssDNA, thereby allowing its translocation through the channel of the nuclear pore. In addition, in vitro studies of nuclear import of the T-DNA complexes showed its dependence on cytosolic import factors such as importin a and Ran protein, thus indicating that this process follows the so-cal ...
... charged ssDNA, thereby allowing its translocation through the channel of the nuclear pore. In addition, in vitro studies of nuclear import of the T-DNA complexes showed its dependence on cytosolic import factors such as importin a and Ran protein, thus indicating that this process follows the so-cal ...
Akashi_Gojobori.PNAS02
... biosynthesis requires diversion of chemical intermediates from different locations in the fueling reaction pathways of central metabolism. Energy, in the form of high-energy phosphate bonds (‘‘⬃P’’) and reducing power (‘‘H’’), is lost through diversion of intermediates from fueling reactions and fur ...
... biosynthesis requires diversion of chemical intermediates from different locations in the fueling reaction pathways of central metabolism. Energy, in the form of high-energy phosphate bonds (‘‘⬃P’’) and reducing power (‘‘H’’), is lost through diversion of intermediates from fueling reactions and fur ...