Carola Lentz Culture The making, unmaking and remaking of an
... ent culture concepts, both of which to this day continue to shape how anthropologists talk about culture. In 1871, Tylor published his magnum opus under the ambiguous title Primitive Culture, which can be read as meaning both primitive culture and the culture of primitives. In Great Britain, at the ...
... ent culture concepts, both of which to this day continue to shape how anthropologists talk about culture. In 1871, Tylor published his magnum opus under the ambiguous title Primitive Culture, which can be read as meaning both primitive culture and the culture of primitives. In Great Britain, at the ...
1 The archaeology of disasters: past and future trends
... to individuals or their property – is all that is essential to the definition of a disaster. In this conception disasters can be placed along a continuum ranging from those with minimal consequences to others with economic and social losses. For archaeology the most critical point is not whether a d ...
... to individuals or their property – is all that is essential to the definition of a disaster. In this conception disasters can be placed along a continuum ranging from those with minimal consequences to others with economic and social losses. For archaeology the most critical point is not whether a d ...
Evolutionary Psychology as of September 15
... It is thus crucial to distinguish between a trait’s being an adaptation and its being adaptive. A trait is an adaptation if it was “‘designed’ by natural selection to solve the specific problems posed by the regularities of the physical, chemical, ecological, informational, and social environments e ...
... It is thus crucial to distinguish between a trait’s being an adaptation and its being adaptive. A trait is an adaptation if it was “‘designed’ by natural selection to solve the specific problems posed by the regularities of the physical, chemical, ecological, informational, and social environments e ...
Philosophical Foundations of ZFEL - Duke University | Center for
... to produce the pattern in our simple model. For example, suppose that each particle represents a population, and each population is moving under the control of selection, but the selective forces on the particles are independent of each other at any given time, and also change independently in time. ...
... to produce the pattern in our simple model. For example, suppose that each particle represents a population, and each population is moving under the control of selection, but the selective forces on the particles are independent of each other at any given time, and also change independently in time. ...
Development, Postmodernism and Aboriginal Policy
... the ―civilized‖ ruled over ―savages‖.10 One media columnist even asserts that our book ―sounds an awful lot like the KKK who [sic] insists they don't want government to hate black people, but that government should love white people more‖.11 But it is necessary to acknowledge that culture and race a ...
... the ―civilized‖ ruled over ―savages‖.10 One media columnist even asserts that our book ―sounds an awful lot like the KKK who [sic] insists they don't want government to hate black people, but that government should love white people more‖.11 But it is necessary to acknowledge that culture and race a ...
Fifteen years of genomewide scans for selection: trends, lessons
... selective events are inherently more difficult to identify. For example, selection on standing variation (Hermisson & Pennings 2005; Przeworski et al. 2005) and selection targeting molecular variants with complex mutational properties (Zhang et al. 2012; Haasl & Paysuer 2013) involve population gene ...
... selective events are inherently more difficult to identify. For example, selection on standing variation (Hermisson & Pennings 2005; Przeworski et al. 2005) and selection targeting molecular variants with complex mutational properties (Zhang et al. 2012; Haasl & Paysuer 2013) involve population gene ...
Genetic Improvement and Crossbreeding in Meat Goats
... can just purchase the right buck, all these things will come true. Right? Wrong. Why? Well, there are a number of reasons. In this first section we will focus on some of those reasons, and perhaps create more reasonable expectations. It is not our business to burst your dreams. What we want to do is ...
... can just purchase the right buck, all these things will come true. Right? Wrong. Why? Well, there are a number of reasons. In this first section we will focus on some of those reasons, and perhaps create more reasonable expectations. It is not our business to burst your dreams. What we want to do is ...
genetic counselling in psychiatry : scope and challenges.
... allele R is not dominant than the phenotype ratio of the offspring on average is (1 dominant): (2 inter mediate): (1 recessive). Law of Independent Assortment: It states that alleles at different loci assort independently of each other. For example, when two homozygous individuals with genotypes say ...
... allele R is not dominant than the phenotype ratio of the offspring on average is (1 dominant): (2 inter mediate): (1 recessive). Law of Independent Assortment: It states that alleles at different loci assort independently of each other. For example, when two homozygous individuals with genotypes say ...
Perspectives on Memetics -Cultural Transmission as a
... required three skills: Making decisions about what to imitate Complex transformations from one point of view to another Production of matching bodily actions ...
... required three skills: Making decisions about what to imitate Complex transformations from one point of view to another Production of matching bodily actions ...
State Your Traits - University of Washington Department of Genome
... first genetic trait from the list, e.g. “I am a PTC taster.” Students who cannot taste PTC sit down. Volunteer reads off next trait: e.g. “I have attached earlobes.” Students with free earlobes sit down. Volunteer continues reading off traits, one at a time, until he is the only student left standin ...
... first genetic trait from the list, e.g. “I am a PTC taster.” Students who cannot taste PTC sit down. Volunteer reads off next trait: e.g. “I have attached earlobes.” Students with free earlobes sit down. Volunteer continues reading off traits, one at a time, until he is the only student left standin ...
signatures of natural selection in the human
... state. By contrast, the traditional definition referred to an allele with a population frequency >1% and <99%. GENETIC DRIFT ...
... state. By contrast, the traditional definition referred to an allele with a population frequency >1% and <99%. GENETIC DRIFT ...
SIGNATURES OF NATURAL SELECTION IN THE HUMAN GENOME
... state. By contrast, the traditional definition referred to an allele with a population frequency >1% and <99%. GENETIC DRIFT ...
... state. By contrast, the traditional definition referred to an allele with a population frequency >1% and <99%. GENETIC DRIFT ...
Books by Margaret Mead, Reissued with New Introductions for the
... Margaret Mead accomplished this remarkable feat not once but several times, beginning with Coming of Age in Samoa. It details her historic journey to American Samoa, taken where she was just twenty-three, where she did her first fieldwork. Here, for the first time, she presented to the public the id ...
... Margaret Mead accomplished this remarkable feat not once but several times, beginning with Coming of Age in Samoa. It details her historic journey to American Samoa, taken where she was just twenty-three, where she did her first fieldwork. Here, for the first time, she presented to the public the id ...
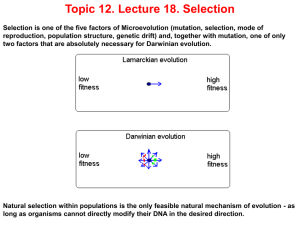
L18Selection
... We can define (natural) selection as differential reproduction of individuals within a population - an unavoidable consequence of variation in fitness, efficiency of reproduction. Fitness depends on viability, mating success (with sex), fecundity, and longevity. Usually, fitness of an individual ca ...
... We can define (natural) selection as differential reproduction of individuals within a population - an unavoidable consequence of variation in fitness, efficiency of reproduction. Fitness depends on viability, mating success (with sex), fecundity, and longevity. Usually, fitness of an individual ca ...
Reprint
... In the early years of the twentieth century, the Danish biologist Wilhelm Johannsen laid the conceptual foundations of modern genetics and evolutionary biology by differentiating the phenotype—the traits expressed by an organism—from the genotype—the “sequestered” library of hereditary information t ...
... In the early years of the twentieth century, the Danish biologist Wilhelm Johannsen laid the conceptual foundations of modern genetics and evolutionary biology by differentiating the phenotype—the traits expressed by an organism—from the genotype—the “sequestered” library of hereditary information t ...
s - Universidad Politécnica de Madrid
... (Genetics) • The entire combination of genes: genotype • A genotype is expressed as a phenotype • Alleles can be either dominant or recessive • Dominant alleles will always express from the genotype to the phenotype • Recessive alleles can survive in the population for many generations, without bein ...
... (Genetics) • The entire combination of genes: genotype • A genotype is expressed as a phenotype • Alleles can be either dominant or recessive • Dominant alleles will always express from the genotype to the phenotype • Recessive alleles can survive in the population for many generations, without bein ...
Experimental design II: artificial selection
... This artificial selection experiment on 6-week body weight mice (carried out over 30 generations in the upward and 24 generations in the downward direction) demonstrates how the intensity of selection (proportion selected) predicts the response to selection. Natural selection opposing artificial sel ...
... This artificial selection experiment on 6-week body weight mice (carried out over 30 generations in the upward and 24 generations in the downward direction) demonstrates how the intensity of selection (proportion selected) predicts the response to selection. Natural selection opposing artificial sel ...
ARTIFACTS AS DOMESTICATED KINDS OF PRACTICES Sergio F
... Psychologists study phenomena at a level of abstraction that allows such phenomena to be detached from the (cultural) context in which they take place. Such an assumption leads to a division of labor in which anthropology describes the content of human experience while psychology aim to characterize ...
... Psychologists study phenomena at a level of abstraction that allows such phenomena to be detached from the (cultural) context in which they take place. Such an assumption leads to a division of labor in which anthropology describes the content of human experience while psychology aim to characterize ...
Lecture 3: (Part 1) Natural selection
... - various forms of selection that lead to the active maintenance of genetic variation in natural populations. - alleles are said to be “balanced” because a stable equilibrium state is reached. - if allele frequencies are perturbed from this equilibrium, selection will return them back to that state. ...
... - various forms of selection that lead to the active maintenance of genetic variation in natural populations. - alleles are said to be “balanced” because a stable equilibrium state is reached. - if allele frequencies are perturbed from this equilibrium, selection will return them back to that state. ...
phenotypic correlations - Watson et al (v91)
... familiar in cognitive learning systems. These include formation of a distributed associative memory that can ‘store’ and ‘recall’ multiple phenotypes that have been selected in the past, recreate complete adult phenotypic patterns accurately from partial or corrupted embryonic phenotypes, and ‘gener ...
... familiar in cognitive learning systems. These include formation of a distributed associative memory that can ‘store’ and ‘recall’ multiple phenotypes that have been selected in the past, recreate complete adult phenotypic patterns accurately from partial or corrupted embryonic phenotypes, and ‘gener ...
- SlideBoom
... perspective . . . Meaning that different aspects of human experience are seen as interrelated and non-reducible. You cannot study politics in isolation from family structures or economics in isolation from cultural values. • Anthropologists have a “multi-field” approach – incorporating cultural and ...
... perspective . . . Meaning that different aspects of human experience are seen as interrelated and non-reducible. You cannot study politics in isolation from family structures or economics in isolation from cultural values. • Anthropologists have a “multi-field” approach – incorporating cultural and ...