Circuit Theorems
... TRANSFER THEOREM The maximum power transfer theorem states the following: “A load will receive maximum power from a linear bilateral dc network when its total resistive value is exactly equal to the Thévenin resistance of the network as “seen” by the load.” ...
... TRANSFER THEOREM The maximum power transfer theorem states the following: “A load will receive maximum power from a linear bilateral dc network when its total resistive value is exactly equal to the Thévenin resistance of the network as “seen” by the load.” ...
Written - Rose
... So v4 : v3 2 : 1 , which is consistent with the specification given before. Also we can verify the result using the current divider, which is a parallel-connected resistance circuit. The two resistors can be combine into a since they are in series. For the parallel circuit, the current through one ...
... So v4 : v3 2 : 1 , which is consistent with the specification given before. Also we can verify the result using the current divider, which is a parallel-connected resistance circuit. The two resistors can be combine into a since they are in series. For the parallel circuit, the current through one ...
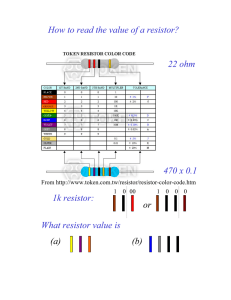
How to read the value of a resistor? 22 ohm 1k resistor:
... How to read the value of a resistor? ...
... How to read the value of a resistor? ...
14.1 Series Circuits
... •I=V/R • You can calculate current (I) if you know voltage and resistance ...
... •I=V/R • You can calculate current (I) if you know voltage and resistance ...
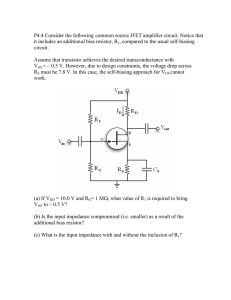
P4.4 Consider the following common source JFET amplifier circuit. Notice... it includes an additional bias resistor, R
... P4.4 Consider the following common source JFET amplifier circuit. Notice that it includes an additional bias resistor, R1, compared to the usual self-biasing circuit. Assume that transistor achieves the desired transconductance with VGS = – 0.5 V. However, due to design constraints, the voltage drop ...
... P4.4 Consider the following common source JFET amplifier circuit. Notice that it includes an additional bias resistor, R1, compared to the usual self-biasing circuit. Assume that transistor achieves the desired transconductance with VGS = – 0.5 V. However, due to design constraints, the voltage drop ...
COMBINED SERIES-PARALLEL CIRCUIT EXAMPLE
... The combination of parallel resistors resulted in equivalent resistances less than any single resistor in the combination, as expected. The voltage across R5 was less than the voltage supplied by the battery, as expected. ...
... The combination of parallel resistors resulted in equivalent resistances less than any single resistor in the combination, as expected. The voltage across R5 was less than the voltage supplied by the battery, as expected. ...
Kirchhoff*s Laws
... In a parallel circuit the charge can take different paths. Therefore the amount of charge at any point… ...
... In a parallel circuit the charge can take different paths. Therefore the amount of charge at any point… ...
OpAmp Output Protection (posted 16 June, 2016)
... resistor R4; though practically the op amp can be protected with a small value of 50 or 100 ohms depending on the output drive capability of the selected device. This method also can be used to verify that as A the voltage between the input terminals also tends to zero. Find V2: ...
... resistor R4; though practically the op amp can be protected with a small value of 50 or 100 ohms depending on the output drive capability of the selected device. This method also can be used to verify that as A the voltage between the input terminals also tends to zero. Find V2: ...
Name - Mr. Nickels
... score of 5 – 4i and Joe has a score of 3 + 2i, what is their total score? (1) 8 + 6i (3) 8 – 6i (2) 8 + 2i (4) 8 – 2i Show that the product of a + bi and its conjugate is a real number. ...
... score of 5 – 4i and Joe has a score of 3 + 2i, what is their total score? (1) 8 + 6i (3) 8 – 6i (2) 8 + 2i (4) 8 – 2i Show that the product of a + bi and its conjugate is a real number. ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.