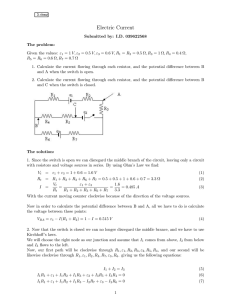
Electric Current
... 1. Calculate the current flowing through each resistor, and the potential difference between B and A when the switch is open. 2. Calculate the current flowing through each resistor, and the potential difference between B and C when the switch is closed. ...
... 1. Calculate the current flowing through each resistor, and the potential difference between B and A when the switch is open. 2. Calculate the current flowing through each resistor, and the potential difference between B and C when the switch is closed. ...
Current, Voltage and resistance
... Voltage is measured as a difference in potential between two points. Thus a voltmeter must be connected in parallel and used to measure the difference in potential across a device. If a cell supplies 23 coulombs of charge with 776 J of energy, what is its voltage? ...
... Voltage is measured as a difference in potential between two points. Thus a voltmeter must be connected in parallel and used to measure the difference in potential across a device. If a cell supplies 23 coulombs of charge with 776 J of energy, what is its voltage? ...
S R 1 2
... A simple first order RC circuit can approximate an integrator or a differentiator, which, respectively, are circuits which have as an output the time integral or time differential of an input signal. 1. Consider the circuit: ...
... A simple first order RC circuit can approximate an integrator or a differentiator, which, respectively, are circuits which have as an output the time integral or time differential of an input signal. 1. Consider the circuit: ...
Millmans Theorem - Wintec Learning
... It permits any number of parallel branches consisting of voltage sources and impedances to be reduced to a single equivalent voltage source and equivalent impedance. Such multibranch circuits are frequently encountered in both electronics and power applications ...
... It permits any number of parallel branches consisting of voltage sources and impedances to be reduced to a single equivalent voltage source and equivalent impedance. Such multibranch circuits are frequently encountered in both electronics and power applications ...
PPT
... • A 120VAC switch that can be controlled via a home wireless network. o Handle loads up to 15A at 120V. o The switch module needs to be able to fit inside a standard wall receptacle box and be able to be inserted through a hole smaller than a standard switch cover. ...
... • A 120VAC switch that can be controlled via a home wireless network. o Handle loads up to 15A at 120V. o The switch module needs to be able to fit inside a standard wall receptacle box and be able to be inserted through a hole smaller than a standard switch cover. ...
Electricity Review
... Resistance: the material property that makes it hard to push an electron through a wire Power: the rate at which energy is used up. The more power, the brighter a light bulb. ...
... Resistance: the material property that makes it hard to push an electron through a wire Power: the rate at which energy is used up. The more power, the brighter a light bulb. ...
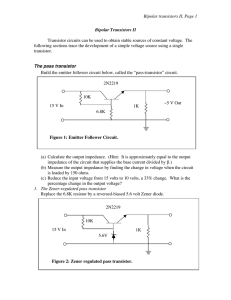
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer. Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with tw ...
... “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer. Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with tw ...
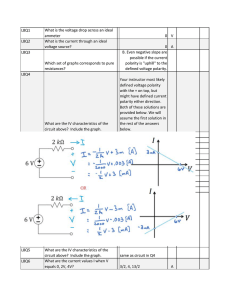
L8Q1 What is the voltage drop across an ideal ammeter 0 V L8Q2
... Considering the three choices for circuit #2 - a 3mA current source, a 3kΩ resistor, or a combination with IV characteristics I(mA)=(1/3)*V - 3, what is the operating point when the 2 su-circuits are connected? Which sub-circuit supplies the power? ...
... Considering the three choices for circuit #2 - a 3mA current source, a 3kΩ resistor, or a combination with IV characteristics I(mA)=(1/3)*V - 3, what is the operating point when the 2 su-circuits are connected? Which sub-circuit supplies the power? ...
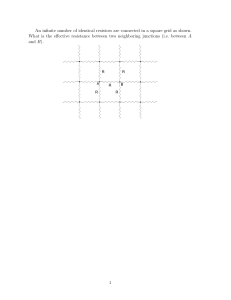
An infinite number of identical resistors are connected in a square
... An infinite number of identical resistors are connected in a square grid as shown. What is the effective resistance between two neighboring junctions (i.e. between A and B). ...
... An infinite number of identical resistors are connected in a square grid as shown. What is the effective resistance between two neighboring junctions (i.e. between A and B). ...
The solution to Homework Assignment #0
... 1) Give a Boolean expression for the detection of overflow in addition of two binary numbers in terms of specific bits of the numbers. The numbers are each 8 bits with one bit being the sign bit, in 2's complement form ...
... 1) Give a Boolean expression for the detection of overflow in addition of two binary numbers in terms of specific bits of the numbers. The numbers are each 8 bits with one bit being the sign bit, in 2's complement form ...
Document
... • - input = inverting • + input = non-inverting • used as an inverting amplifier or a comparator • An analog device ...
... • - input = inverting • + input = non-inverting • used as an inverting amplifier or a comparator • An analog device ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.