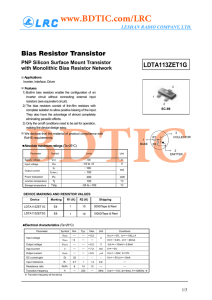
Bias Resistor Transistor LDTA113ZET1G PNP Silicon Surface Mount Transistor
... with Monolithic Bias Resistor Network ...
... with Monolithic Bias Resistor Network ...
N45 Electricity 1 20Q
... 18. Calculate the energy used by a 12V kettle in 2minutes if it draws 3A from it’s supply. ...
... 18. Calculate the energy used by a 12V kettle in 2minutes if it draws 3A from it’s supply. ...
Modelling Electricity
... What is current, voltage and resistance? Current – the flow of electrons around the circuit Voltage – driving force which pushes the current around Resistance – anything in the circuit which slows the flow down ...
... What is current, voltage and resistance? Current – the flow of electrons around the circuit Voltage – driving force which pushes the current around Resistance – anything in the circuit which slows the flow down ...
Lecture_1
... of the resistance of the load. (i.e., they have zero internal resistance.) However, real voltage sources have an internal non-zero resistance and the voltage delivered depends upon the resistance of the load. Ideal Current sources supply a fixed current I independent of the resistance of the load. ( ...
... of the resistance of the load. (i.e., they have zero internal resistance.) However, real voltage sources have an internal non-zero resistance and the voltage delivered depends upon the resistance of the load. Ideal Current sources supply a fixed current I independent of the resistance of the load. ( ...
Node Voltage with Thevenin Equivalent
... the currents and voltages from the values obtained from your Analysis and that measured on the modified circuit of the original experiment. ...
... the currents and voltages from the values obtained from your Analysis and that measured on the modified circuit of the original experiment. ...
File
... Most residential and commerical circuits are parallel. •The voltage across all loads in parallel circuits is the same. If you use an appliance it will not use up voltage for a different appliance • Current increases as each path becomes closed. The current in the appliance closest to the source will ...
... Most residential and commerical circuits are parallel. •The voltage across all loads in parallel circuits is the same. If you use an appliance it will not use up voltage for a different appliance • Current increases as each path becomes closed. The current in the appliance closest to the source will ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.