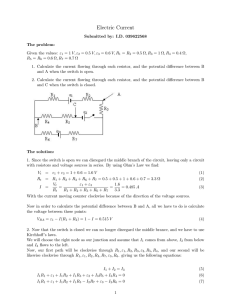
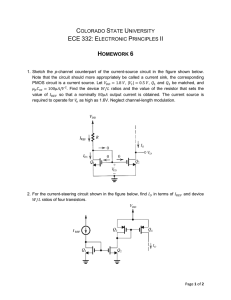
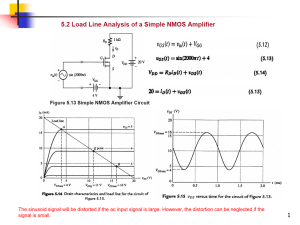
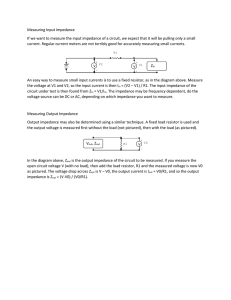
Lecture 1-4 Summary file
... law. For example a linear resistor has a linear voltage vs current relationship which passes through the origin (V = R I). A linear inductor has a linear flux vs current relationshipwhich passes through the origin (φ = k I) and a linear capacitor has a linear charge vs voltage relationship which pas ...
... law. For example a linear resistor has a linear voltage vs current relationship which passes through the origin (V = R I). A linear inductor has a linear flux vs current relationshipwhich passes through the origin (φ = k I) and a linear capacitor has a linear charge vs voltage relationship which pas ...
Physics 536 - Assignment #1
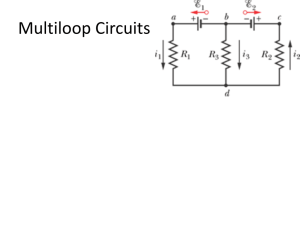
... Nevertheless, it can still be analyzed as a three-loop circuit from which the current flowing through the voltage source can be calculated. (a) Write down the 3×3 matrix equation which can be solved to determine the vector of currents in the three loops. (b) Using Kramer’s rule, express the current ...
... Nevertheless, it can still be analyzed as a three-loop circuit from which the current flowing through the voltage source can be calculated. (a) Write down the 3×3 matrix equation which can be solved to determine the vector of currents in the three loops. (b) Using Kramer’s rule, express the current ...
Document
... Ohm’s Law • Voltage results in current flow • More voltage = more current • Resistance opposes current flow • More resistance = less current ...
... Ohm’s Law • Voltage results in current flow • More voltage = more current • Resistance opposes current flow • More resistance = less current ...
Parallel Circuits Test
... 27. A circuit consists of two resistors in parallel with each other. R1 = 60 ohms and R2 = 120 ohms. The circuit has 10 volts applied. An ammeter, placed to read total current is reading .17 amps. What is the problem with the circuit? a. There is no problem b. R1 is open c. R2 is open d. A ...
... 27. A circuit consists of two resistors in parallel with each other. R1 = 60 ohms and R2 = 120 ohms. The circuit has 10 volts applied. An ammeter, placed to read total current is reading .17 amps. What is the problem with the circuit? a. There is no problem b. R1 is open c. R2 is open d. A ...
EGM 180 Take Home Quiz 1
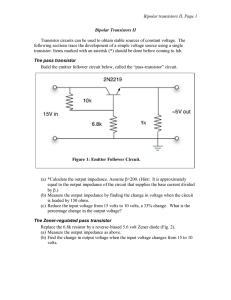
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.