ch4_L1_i
... without passing through any intermediate node more than once Kirchhoff’s first (or current) law: at a circuit node, the current flowing into the node equals the current flowing out (charge is conserved) Kirchhoff’s second (or voltage) law: around a circuit loop, the sum of the voltages equal zero (e ...
... without passing through any intermediate node more than once Kirchhoff’s first (or current) law: at a circuit node, the current flowing into the node equals the current flowing out (charge is conserved) Kirchhoff’s second (or voltage) law: around a circuit loop, the sum of the voltages equal zero (e ...
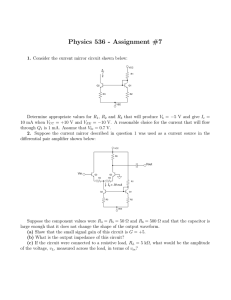
Resistance Across Cubic Network
... In this network, the points B, D, and E are equivalent, i.e., all of them have the same voltage, namely exactly one resistance drop down from the voltage at point A. Thus, we may connect these three points together by wires BD, DE, and BE without changing anything. Similarly, the points F, H, and C ...
... In this network, the points B, D, and E are equivalent, i.e., all of them have the same voltage, namely exactly one resistance drop down from the voltage at point A. Thus, we may connect these three points together by wires BD, DE, and BE without changing anything. Similarly, the points F, H, and C ...
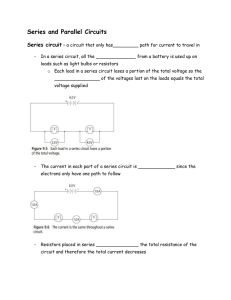
Series and Parallel Circuits
... Voltage Divider: Series circuits are thought of as voltage dividers. They can produce a voltage of desired magnitude. ...
... Voltage Divider: Series circuits are thought of as voltage dividers. They can produce a voltage of desired magnitude. ...
ENG 220
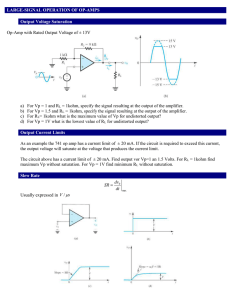
... 20. Be able to calculate the Total Current load of an op-amp output with negative feedback. 21. Be able to determine the input network of a non-inverting op-amp so that the gain would be the same as a given inverting configuration. 22. Be able to determine the node voltages of a resistor/voltage sou ...
... 20. Be able to calculate the Total Current load of an op-amp output with negative feedback. 21. Be able to determine the input network of a non-inverting op-amp so that the gain would be the same as a given inverting configuration. 22. Be able to determine the node voltages of a resistor/voltage sou ...
ECE1250F14_PracticeEx1p2soln
... SOL'N: a) Because the problem says nothing about what method of solution must be used, we might use any of the tools studied thus far: Ohm's law, KVL, KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special confi ...
... SOL'N: a) Because the problem says nothing about what method of solution must be used, we might use any of the tools studied thus far: Ohm's law, KVL, KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special confi ...
FN-Series and Parallel Circuits
... Loads that are in parallel have the _______________ voltage since it doesn’t matter which path is taken, all potential energy is lost before returning to the battery ...
... Loads that are in parallel have the _______________ voltage since it doesn’t matter which path is taken, all potential energy is lost before returning to the battery ...
P517/617 Lec1, P1 Some Definitions: I Q
... Can use matrix methods to solve these equations: V = RI, with V and I column vectors and R a matrix (3x3). If we have n (n = 3 here) linearly independent equations then the determinant of R ≠ 0. See any decent book on ...
... Can use matrix methods to solve these equations: V = RI, with V and I column vectors and R a matrix (3x3). If we have n (n = 3 here) linearly independent equations then the determinant of R ≠ 0. See any decent book on ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.