Circuits and Systems Design Automation of Analog VLSI
... of the real system. The case of small signal situation Basically it is a first order approximation of Taylor expansion ...
... of the real system. The case of small signal situation Basically it is a first order approximation of Taylor expansion ...
Electric Circuits Prentice Hall
... 1. Changing the voltage in a circuit changes the current, but will not change the resistance C. Calculating Ohm’s Law 1. puts the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance into numbers 2. resistance is equal to the voltage divided by the current resistance = voltage current 3. another wa ...
... 1. Changing the voltage in a circuit changes the current, but will not change the resistance C. Calculating Ohm’s Law 1. puts the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance into numbers 2. resistance is equal to the voltage divided by the current resistance = voltage current 3. another wa ...
Parallel Circuits Worksheet File
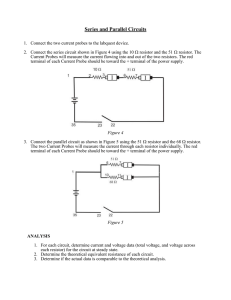
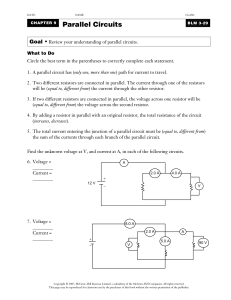
... 1. A parallel circuit has (only one, more than one) path for current to travel. 2. Two different resistors are connected in parallel. The current through one of the resistors will be (equal to, different from) the current through the other resistor. 3. If two different resistors are connected in par ...
... 1. A parallel circuit has (only one, more than one) path for current to travel. 2. Two different resistors are connected in parallel. The current through one of the resistors will be (equal to, different from) the current through the other resistor. 3. If two different resistors are connected in par ...
Electronic Circuits and Devices: ELEE 3455
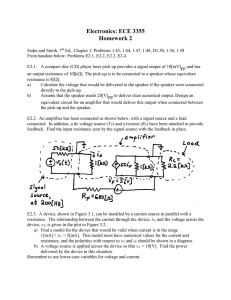
... Assume that the speaker needs 20[V]pp to deliver clear acoustical output. Design an equivalent circuit for an amplifier that would deliver this output when connected between the pick-up and the speaker. E2.2. An amplifier has been connected as shown below, with a signal source and a load connected. ...
... Assume that the speaker needs 20[V]pp to deliver clear acoustical output. Design an equivalent circuit for an amplifier that would deliver this output when connected between the pick-up and the speaker. E2.2. An amplifier has been connected as shown below, with a signal source and a load connected. ...
BBA IInd SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2008-09
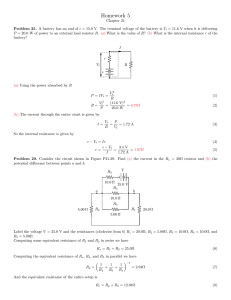
... Calculate the open circuit voltage in the network that have 50 v dc source with series resistance of 38k ohm. Sate the superposition theorem? Is possible to calculate power using this theorem? State the Norton’s theorem along with the process of calculation of Norton’s equivalent resistance with ...
... Calculate the open circuit voltage in the network that have 50 v dc source with series resistance of 38k ohm. Sate the superposition theorem? Is possible to calculate power using this theorem? State the Norton’s theorem along with the process of calculation of Norton’s equivalent resistance with ...
Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 11 – Chapter 25 sec. 4-5
... Fall 2012 Semester Matthew Jones ...
... Fall 2012 Semester Matthew Jones ...
circuits and current review
... 2. What is actually flowing in a current carrying wire? 3. What is an ampere? 4. The resistance of a wire depends on what three factors? 5. Which has more resistance, a thick wire or a thin wire? 6. What is the unit of resistance? of power? 7. State the formula for Ohm’s law. 8. What is grounding, a ...
... 2. What is actually flowing in a current carrying wire? 3. What is an ampere? 4. The resistance of a wire depends on what three factors? 5. Which has more resistance, a thick wire or a thin wire? 6. What is the unit of resistance? of power? 7. State the formula for Ohm’s law. 8. What is grounding, a ...
Title: TCCN: Electrical Circuits I ENGR 2305 Draft Course
... 2. Apply concepts of electric network topology: nodes, branches, and loops to solve circuit problems, including the use of computer simulation. 3. Analyze circuits with ideal, independent, and controlled voltage and current sources. 4. Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage and current laws to the analysis of el ...
... 2. Apply concepts of electric network topology: nodes, branches, and loops to solve circuit problems, including the use of computer simulation. 3. Analyze circuits with ideal, independent, and controlled voltage and current sources. 4. Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage and current laws to the analysis of el ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.