Electronic Components
... Diodes allow electricity to flow in only one direction. The arrow of the circuit symbol shows the direction in which the current can flow. Diodes are the electrical version of a valve and early diodes were actually called valves. ...
... Diodes allow electricity to flow in only one direction. The arrow of the circuit symbol shows the direction in which the current can flow. Diodes are the electrical version of a valve and early diodes were actually called valves. ...
In a series circuit, every device must function for the circuit to be
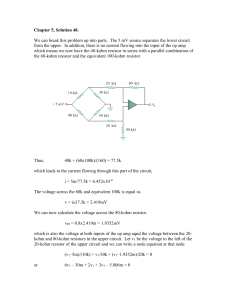
... Remember with series circuit, there is voltage drop across each resistor. To find voltage drop use ohm’s law. ...
... Remember with series circuit, there is voltage drop across each resistor. To find voltage drop use ohm’s law. ...
VOLTAGE STABILITY
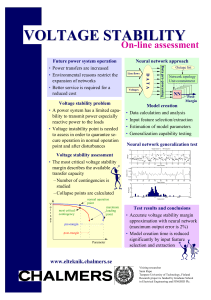
... Test results and conclusions • Accurate voltage stability margin approximation with neural network (maximum output error is 2%) • Model creation time is reduced significantly by input feature selection and extraction ...
... Test results and conclusions • Accurate voltage stability margin approximation with neural network (maximum output error is 2%) • Model creation time is reduced significantly by input feature selection and extraction ...
Physics 4700 HOMEWORK III Due Oct 5
... frequency is f = 700 kHz. The tuner must be able to detect the AM sidebands which are located at ±5 kHz (695 kHz and 705 kHz) from the central frequency. An easy way to achieve the above is to use a series RLC circuit and take VR for the output voltage. The resonant frequency of this circuit is that ...
... frequency is f = 700 kHz. The tuner must be able to detect the AM sidebands which are located at ±5 kHz (695 kHz and 705 kHz) from the central frequency. An easy way to achieve the above is to use a series RLC circuit and take VR for the output voltage. The resonant frequency of this circuit is that ...
Physics 517/617 HOMEWORK III Due July 19
... is f = 700 kHz. The tuner must be able to detect the AM sidebands which are located at ±5 kHz (695 kHz and 705 kHz) from the central frequency. An easy way to achieve the above is to use a series RLC circuit and take VR for the output voltage. The resonant frequency of this circuit is that of the ra ...
... is f = 700 kHz. The tuner must be able to detect the AM sidebands which are located at ±5 kHz (695 kHz and 705 kHz) from the central frequency. An easy way to achieve the above is to use a series RLC circuit and take VR for the output voltage. The resonant frequency of this circuit is that of the ra ...
linalg paper 1
... the basic working of a circuit, the task of analyzing even the simplest of circuits can seem daunting. However, once it is known that you can organize the information into a system of equations that can them be solved by linear algebra the task becomes far less intimidating. The resistor network. Be ...
... the basic working of a circuit, the task of analyzing even the simplest of circuits can seem daunting. However, once it is known that you can organize the information into a system of equations that can them be solved by linear algebra the task becomes far less intimidating. The resistor network. Be ...
Physics 4700 HOMEWORK III Due Feb 22
... frequency is f = 700 kHz. The tuner must be able to detect the AM sidebands which are located at ±5 kHz (695 kHz and 705 kHz) from the central frequency. An easy way to achieve the above is to use a series RLC circuit and take VR for the output voltage. The resonant frequency of this circuit is that ...
... frequency is f = 700 kHz. The tuner must be able to detect the AM sidebands which are located at ±5 kHz (695 kHz and 705 kHz) from the central frequency. An easy way to achieve the above is to use a series RLC circuit and take VR for the output voltage. The resonant frequency of this circuit is that ...
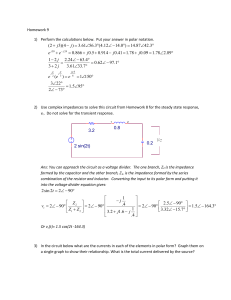
2 sin 2 2 90 1 2.5 90 .4 2 90 2 90 2 90 1.5 164.3 1 3.32 15.7 3.2 1.6
... Ans: You can approach the circuit as a voltage divider. The one branch, Z2 is the impedance formed by the capacitor and the other branch, Z1, is the impedance formed by the series combination of the resistor and inductor. Converting the input to its polar form and putting it into the voltage divider ...
... Ans: You can approach the circuit as a voltage divider. The one branch, Z2 is the impedance formed by the capacitor and the other branch, Z1, is the impedance formed by the series combination of the resistor and inductor. Converting the input to its polar form and putting it into the voltage divider ...
Differentiated Task - science
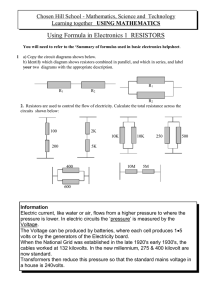
... For the circuit on the right are the pairs of components connected in series or in parallel? ...
... For the circuit on the right are the pairs of components connected in series or in parallel? ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.