* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Information - Chosen Hill School
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Electromigration wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
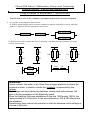
Chosen Hill School - Mathematics, Science and Technology Learning together USING MATHEMATICS Using Formula in Electronics 1 RESISTORS You will need to refer to the ‘Summary of formulas used in basic electronics helpsheet. 1 a) Copy the circuit diagrams shown below. b) Identify which diagram shows resistors combined in parallel, and which in series, and label your two diagrams with the appropriate description. R1 R1 R2 R2 2. Resistors are used to control the flow of electricity. Calculate the total resistance across the circuits shown below: 100 2K 10K 200 10K 250 500 5K 400 10M 5M 600 Information Electric current, like water or air, flows from a higher pressure to where the pressure is lower. In electric circuits the ‘pressure’ is measured by the Voltage. The Voltage can be produced by batteries, where each cell produces 15 volts or by the generators of the Electricity board. When the National Grid was established in the late 1920's early 1930's, the cables worked at 132 kilovolts. In the new millennium, 275 & 400 kilovolt are now standard. Transformers then reduce this pressure so that the standard mains voltage in a house is 240volts. Ohm’s Law, is a relationship discovered between the current, the voltage and the resistance, discovered in 1827 by Georg Simon Ohm. He discovered that the voltage drop (change in pressure) across a resistance was given by the formula V = IR (where I is the current measured in amps and R is the value of the resistance, measured in Ohms). The Current (flow of electricity) is constant throughout a circuit in series. When a circuit is in parallel, the sum of the currents in the ‘parallel channels’ must equal the current in the single channel eg x x+y y +12V +12V 600 +15V + 9V 5K 5K 600 10K 750 500 5K 0V 0V 0V 0V 450 550 +3V 3 4 350 0V + 6V 1K 0V a) b) c) d) e) Rearrange the formula to make I the subject of the formula Calculate the total resistance across each of the circuits shown above Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the current flowing through each of the circuits shown above Rearrange the formula to make R the subject of the formula A Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a device that gives off light when an electrical current passes through. It has limitations in that it can get damaged if the current exceeds 20 mA. Write down an inequality that must be satisfied by these conditions f) What size resistor must be used to run the diode off a 9V battery in order to guarantee the current never exceeds 20mA Use Ohms Law to show that the total resistance of two resistors in series is given by R = R 1 + R2 R1R2 but that the total resistance, when the resistors are in parallel, is given by R= R1 R2 R1R2 5 Show that R = is equivalent to the formula 1 = 1 + 1 R R1 R2 R1 R2