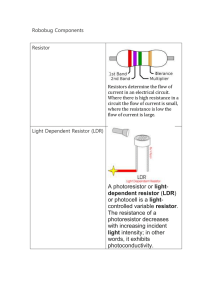
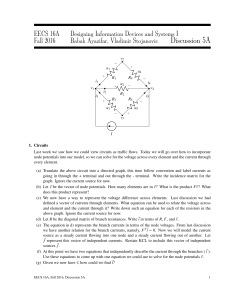
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING
... 6. An understanding of the natural and step responses of RL and RC circuits. (a, e) 7. An understanding of the natural and step responses of RLC circuits. (a, e) 8. An understanding of phasors and an ability to determine the sinusoidal steady-state response of linear circuits. (a, e) 9. An ability t ...
... 6. An understanding of the natural and step responses of RL and RC circuits. (a, e) 7. An understanding of the natural and step responses of RLC circuits. (a, e) 8. An understanding of phasors and an ability to determine the sinusoidal steady-state response of linear circuits. (a, e) 9. An ability t ...
Electricity Packet
... Review the proper method of connecting an ammeter in a circuit. Connecting it incorrectly may result in broken equipment. Measure the current flowing out of the battery, and after each resistor. (Like with the last lab, this may require rearranging the circuit with different wires. Make sure you are ...
... Review the proper method of connecting an ammeter in a circuit. Connecting it incorrectly may result in broken equipment. Measure the current flowing out of the battery, and after each resistor. (Like with the last lab, this may require rearranging the circuit with different wires. Make sure you are ...
Providing Power Supply and Communication Lines
... The Sendyne SFP10x family of current, voltage and temperature measurement ICs is designed to be used in high voltage battery and power systems. Current measurements across a shunt can be performed at either the high or low side of the power system. For current measurements, the IC uses a dedicated o ...
... The Sendyne SFP10x family of current, voltage and temperature measurement ICs is designed to be used in high voltage battery and power systems. Current measurements across a shunt can be performed at either the high or low side of the power system. For current measurements, the IC uses a dedicated o ...
1 - Marine Institute
... b) Write them using phasor notation. c) Calculate the RMS resultant of the two voltages. (82.6VRMS) ...
... b) Write them using phasor notation. c) Calculate the RMS resultant of the two voltages. (82.6VRMS) ...
Series and Parallel - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... • There are multiple pathways for the electrons to travel • The current is not the same at all the points in the circuit but initial current and final current must equal. ...
... • There are multiple pathways for the electrons to travel • The current is not the same at all the points in the circuit but initial current and final current must equal. ...
Unit 10 (Electricity) - Ms. Voit`s Physics Wiki
... Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Redraw the circuit with its equivalent resistance. Find the current through the battery. Using ohm’s law, find the current through and voltage drop across each resistor. (6A, 4A & 8V, 1.33A & 8V, 6.67A & 8V) V = 8 volts s ...
... Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Redraw the circuit with its equivalent resistance. Find the current through the battery. Using ohm’s law, find the current through and voltage drop across each resistor. (6A, 4A & 8V, 1.33A & 8V, 6.67A & 8V) V = 8 volts s ...
Resonance in RLC Circuits ~
... Theory: A resonant circuit, also called a tuned circuit consists of an inductor and a capacitor together with a voltage or current source. It is one of the most important circuits used in electronics. For example, a resonant circuit, in one of its many forms, allows us to select a desired radio or t ...
... Theory: A resonant circuit, also called a tuned circuit consists of an inductor and a capacitor together with a voltage or current source. It is one of the most important circuits used in electronics. For example, a resonant circuit, in one of its many forms, allows us to select a desired radio or t ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.