EXPERIMENT III PREPARATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF
... The cobaltIII system is chosen due to the highly colored isomers, i.e. purple and brown, both of which can be prepared at different temperatures. According to the possible straining of the C-N-C bond angle in the IDA2- ligand, the trans(mer) isomer can be expected to be rather unstable and a reasona ...
... The cobaltIII system is chosen due to the highly colored isomers, i.e. purple and brown, both of which can be prepared at different temperatures. According to the possible straining of the C-N-C bond angle in the IDA2- ligand, the trans(mer) isomer can be expected to be rather unstable and a reasona ...
OS-FGI Lecture2
... The trick to achieving selective substitution (i.e. allylic bromination) is to know that the addition of Br• to the alkene is reversible whereas the allylic H-abstraction is effectively irreversible. A high concentration of Br2 favours the addition product by trapping out the intermediate radical A. ...
... The trick to achieving selective substitution (i.e. allylic bromination) is to know that the addition of Br• to the alkene is reversible whereas the allylic H-abstraction is effectively irreversible. A high concentration of Br2 favours the addition product by trapping out the intermediate radical A. ...
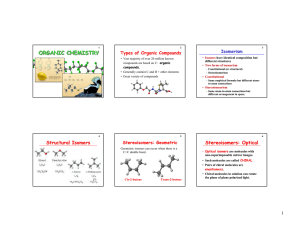
chemistry 30 / unit c chemical changes of organic compounds
... b) - containing only one type of functional group (with multiple bonds categorized as a functional group) eg: pent - 2- ene / and including simple halogenated hydrocarbons eg: 2 - chloropentane alchols – eg: pentan -2-ol / carboxylic acids – eg: pentanoic acid / and esters – eg : methylpropanoate c) ...
... b) - containing only one type of functional group (with multiple bonds categorized as a functional group) eg: pent - 2- ene / and including simple halogenated hydrocarbons eg: 2 - chloropentane alchols – eg: pentan -2-ol / carboxylic acids – eg: pentanoic acid / and esters – eg : methylpropanoate c) ...
Lecture Resource ()
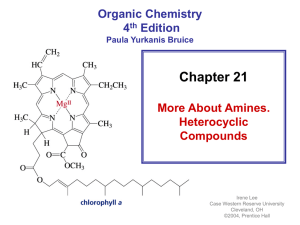
... • Some amines are heterocyclic compounds (or heterocycles) • Most drugs, vitamins, and many other natural products are heterocycles • A natural product is a compound synthesized by a plant or an animal ...
... • Some amines are heterocyclic compounds (or heterocycles) • Most drugs, vitamins, and many other natural products are heterocycles • A natural product is a compound synthesized by a plant or an animal ...
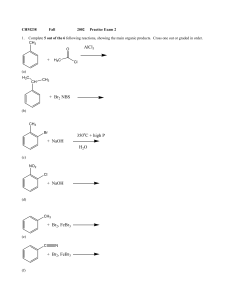
+ NaOH 350 C + high P H2O + H3C AlCl3 + NaOH + Br2, FeBr3
... Starting with toluene, design syntheses, providing the correct reagents for the following transformations. Both processes can be accomplished with 2 steps, but there is more than one correct answer for each. Assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated. OH O CH3 ...
... Starting with toluene, design syntheses, providing the correct reagents for the following transformations. Both processes can be accomplished with 2 steps, but there is more than one correct answer for each. Assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated. OH O CH3 ...
Chemistry 1
... 4. Camels store the fat tristearin (C57H110O6) in the hump. Besides being a source of energy, the fat is a source of water for the camel because when the fat is burned, the following reaction occurs: 2 C57H110O6 (s) + 163 O2 (g) 114 CO2 (g) + 110 H2O (l) a) Determine the molar mass of tristearin. ...
... 4. Camels store the fat tristearin (C57H110O6) in the hump. Besides being a source of energy, the fat is a source of water for the camel because when the fat is burned, the following reaction occurs: 2 C57H110O6 (s) + 163 O2 (g) 114 CO2 (g) + 110 H2O (l) a) Determine the molar mass of tristearin. ...
Bimolecular reactions of the chromium
... insertion into C-H and C-C bonds. Besides the investigation of the reactivity of bare metal ions, a study of the modification of the reactivity of the central metal ions of mrdinatively unsaturated metal complexes by the ligands is a major field of research in metal-organic chemistry.2 Usually the c ...
... insertion into C-H and C-C bonds. Besides the investigation of the reactivity of bare metal ions, a study of the modification of the reactivity of the central metal ions of mrdinatively unsaturated metal complexes by the ligands is a major field of research in metal-organic chemistry.2 Usually the c ...
Organic Chemistry
... developed by E.J. Corey, starts with the target molecule and splices it to pieces according to known reactions. The pieces, or the proposed precursors, receive the same treatment, until available and ideally inexpensive starting materials are reached. Then, the retrosynthesis is written in the oppo ...
... developed by E.J. Corey, starts with the target molecule and splices it to pieces according to known reactions. The pieces, or the proposed precursors, receive the same treatment, until available and ideally inexpensive starting materials are reached. Then, the retrosynthesis is written in the oppo ...
Enzymatic synthesis of sialic acid derivative by immobilized lipase
... MTCC-4713 and gradually declined thereafter (Kanwar et al., 2007). In addition, Yang et al. (2011) reported that the quality of poly(oleic diacid-co-glycerol) was high when the reaction catalyzed by Novozym 435 in a vacuum (10 mmHg) system for 6 h. Therefore, after considering these findings, a react ...
... MTCC-4713 and gradually declined thereafter (Kanwar et al., 2007). In addition, Yang et al. (2011) reported that the quality of poly(oleic diacid-co-glycerol) was high when the reaction catalyzed by Novozym 435 in a vacuum (10 mmHg) system for 6 h. Therefore, after considering these findings, a react ...
Elucidation of Mechanisms and Selectivities of Metal
... between the alkyl group and the Ir/ligand moiety) are responsible for the experimentally observed selectivity. We found furthermore that the difference between C(sp2)−H and C(sp3)−H borylation is mainly due to the different reactivities of the intermediates resulting from the C−H oxidative addition. D ...
... between the alkyl group and the Ir/ligand moiety) are responsible for the experimentally observed selectivity. We found furthermore that the difference between C(sp2)−H and C(sp3)−H borylation is mainly due to the different reactivities of the intermediates resulting from the C−H oxidative addition. D ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.