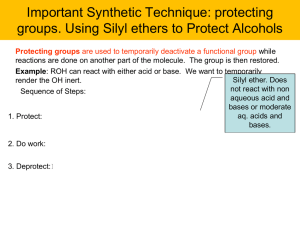
E30 ENANTIOMERS - CHIRALITY IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... No bonds are broken when one conformation is converted into another. For example, the following structures represent two of the many possible conformational isomers of ethane. These conformational isomers rapidly interconvert at room temperature and individual isomers cannot be isolated. Ethane may ...
... No bonds are broken when one conformation is converted into another. For example, the following structures represent two of the many possible conformational isomers of ethane. These conformational isomers rapidly interconvert at room temperature and individual isomers cannot be isolated. Ethane may ...
Lecture 1: Key Concepts in Stereoselective Synthesis
... Carbene ligands bind more strongly to the metal than electron-rich phosphines. Their strong -donating and weak -accepting properties make the metal center more electron-rich relative to the analogous metal complex with phosphine ligand (compare metal complexes for alkene metathesis). Therefore the ...
... Carbene ligands bind more strongly to the metal than electron-rich phosphines. Their strong -donating and weak -accepting properties make the metal center more electron-rich relative to the analogous metal complex with phosphine ligand (compare metal complexes for alkene metathesis). Therefore the ...
2. ACTIVATION OF CARBOXYL GROUPS IN
... By proper choice of the substituents R1, R 2 and R 3 it was possible to limit the reaction of the triamide with nucleophiles to one of the three carboxyl groups. l o o This selective reaction has been utilised by Wasserman the synthesis of macrolide lactones of peptides. ...
... By proper choice of the substituents R1, R 2 and R 3 it was possible to limit the reaction of the triamide with nucleophiles to one of the three carboxyl groups. l o o This selective reaction has been utilised by Wasserman the synthesis of macrolide lactones of peptides. ...
Controlling Rate - Lesmahagow High School
... Lead and its compounds are poisons of transition metal catalysts. This is why unleaded petrol must be used in cars with catalytic converters. Arsenic and its compounds are also common poisons. Catalysts can also be made ineffective by side-reactions. E.g. the iron catalyst used in the Haber Process ...
... Lead and its compounds are poisons of transition metal catalysts. This is why unleaded petrol must be used in cars with catalytic converters. Arsenic and its compounds are also common poisons. Catalysts can also be made ineffective by side-reactions. E.g. the iron catalyst used in the Haber Process ...
Edexcel GCE - The Student Room
... (ii) On the graph above, sketch a line to show the trend of atomic radii across Period 3. Justify any differences and similarities with the trend across Period 2. ...
... (ii) On the graph above, sketch a line to show the trend of atomic radii across Period 3. Justify any differences and similarities with the trend across Period 2. ...
Exam 2 review sheet
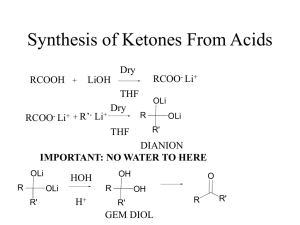
... preparation of aldehydes and ketones: (a) oxidation of alcohols; (b) F-C acylation; (c) ozonolysis (review); (d) reduction of esters or acyl chlorides with specialized hydride reagents LiAlH(OtBu)3 or DIBAL-H to form aldehydes five nucleophilic reactions of aldehyde/ketone: relative reactivity of al ...
... preparation of aldehydes and ketones: (a) oxidation of alcohols; (b) F-C acylation; (c) ozonolysis (review); (d) reduction of esters or acyl chlorides with specialized hydride reagents LiAlH(OtBu)3 or DIBAL-H to form aldehydes five nucleophilic reactions of aldehyde/ketone: relative reactivity of al ...
Le Chatelier`s Principle Notes
... If more Fe3+ is added to the reaction, what will happen? According to Le Châtelier's Principle, the system will react to minimize the stress. Since Fe3+ is on the reactant side of this reaction, the rate of the forward reaction will increase in order to "use up" the additional reactant. This will ca ...
... If more Fe3+ is added to the reaction, what will happen? According to Le Châtelier's Principle, the system will react to minimize the stress. Since Fe3+ is on the reactant side of this reaction, the rate of the forward reaction will increase in order to "use up" the additional reactant. This will ca ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... In general, simple alcohols like methanol and ethanol are not used in the formation of acetals (particularly from less-reactive ketones!) The main reason is entropy - you’ve got to get three molecules together to form one - that’s not so good! The very common way around this is to use a glycol - eth ...
... In general, simple alcohols like methanol and ethanol are not used in the formation of acetals (particularly from less-reactive ketones!) The main reason is entropy - you’ve got to get three molecules together to form one - that’s not so good! The very common way around this is to use a glycol - eth ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.