Biochemistry 462a - Enzymes Extra Questions
... twice as fast for every 10o rise in temperature. This is true for enzymes up to a certain temperature at which point the reaction no longer occurs. 6. Assuming they have equal affinity for the enzyme, why would a noncompetitive inhibitor be a more effective drug than a competitive inhibitor? 7. Why ...
... twice as fast for every 10o rise in temperature. This is true for enzymes up to a certain temperature at which point the reaction no longer occurs. 6. Assuming they have equal affinity for the enzyme, why would a noncompetitive inhibitor be a more effective drug than a competitive inhibitor? 7. Why ...
Organometallic Organometallic Chemistry
... Valence shells of a MT can accommodate 18 electrons: 2 in each of the five d orbitals (10 in total); 2 in each of the three p orbitals (6 in total); and 2 in the s orbital. Combination of these atomic orbitals with ligand orbitals: 9 MOs which are either metal-ligand bonding or non-bonding. (There a ...
... Valence shells of a MT can accommodate 18 electrons: 2 in each of the five d orbitals (10 in total); 2 in each of the three p orbitals (6 in total); and 2 in the s orbital. Combination of these atomic orbitals with ligand orbitals: 9 MOs which are either metal-ligand bonding or non-bonding. (There a ...
Types of Chemical Reactions (rxns.)
... Writing Total Ionic Equations Once you write the molecular equation (synthesis, decomposition, etc.), you should check for reactants and products that are soluble or ...
... Writing Total Ionic Equations Once you write the molecular equation (synthesis, decomposition, etc.), you should check for reactants and products that are soluble or ...
Numina PowerPoint Presentation
... Inorganic Chemistry Charles Ward, Department of Chemistry David White, Department of Chemistry James Reeves, Department of Chemistry Ron Vetter, Department of Computer Science Gabriel Lugo, Department of Mathematics and Statistics Russ Herman, Department of Mathematics and Statistics Prentice-Hall a ...
... Inorganic Chemistry Charles Ward, Department of Chemistry David White, Department of Chemistry James Reeves, Department of Chemistry Ron Vetter, Department of Computer Science Gabriel Lugo, Department of Mathematics and Statistics Russ Herman, Department of Mathematics and Statistics Prentice-Hall a ...
PowerPoint **
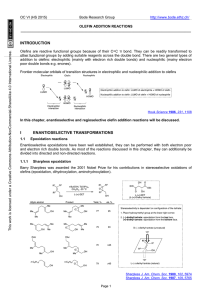
... α, β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds with a leaving group in the β position are susceptible to addition-elimination reactions. ...
... α, β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds with a leaving group in the β position are susceptible to addition-elimination reactions. ...
Yearly Lesson Plan 2007
... 2.3 Analysing alkenes state what alkene is, deduce the molecular formulae of the first nine alkenes, deduce the general formula of alkenes, name the first nine alkenes, draw the structural formulae for the first nine straight-chain alkenes, relate changes in physical properties with inc ...
... 2.3 Analysing alkenes state what alkene is, deduce the molecular formulae of the first nine alkenes, deduce the general formula of alkenes, name the first nine alkenes, draw the structural formulae for the first nine straight-chain alkenes, relate changes in physical properties with inc ...
Organometallic Compounds
... The next slides recall the diversity of nucleophiles that may be used. Observe that there is limited opportunity of creating new C-C bonds, welding together two R groups. We seem to be somewhat lacking in simple carbon based nucleophiles. ...
... The next slides recall the diversity of nucleophiles that may be used. Observe that there is limited opportunity of creating new C-C bonds, welding together two R groups. We seem to be somewhat lacking in simple carbon based nucleophiles. ...
26th IChO Theory Problem No
... Sulfur forms many different compounds with oxygen and halogens (sulfur as the central atom). These compounds are mainly molecular, and many are easily hydrolysed in water. a) Write Lewis structures for the molecules SCl2, SO3, SO2ClF, SF4, and SBrF5. Show all non-bonding electrons. b) Carefully draw ...
... Sulfur forms many different compounds with oxygen and halogens (sulfur as the central atom). These compounds are mainly molecular, and many are easily hydrolysed in water. a) Write Lewis structures for the molecules SCl2, SO3, SO2ClF, SF4, and SBrF5. Show all non-bonding electrons. b) Carefully draw ...
The Chemistry of Alkyl Halides - Welcome to people.pharmacy
... In a stereospecific reaction with a given stereochemistry—anti-elimination, in this case—a diastereomeric product requires a diastereomeric starting material (either enantiomer). The easiest path to the answer is to convert the starting material in Eq. 9.40a into its diastereomer by the interchange ...
... In a stereospecific reaction with a given stereochemistry—anti-elimination, in this case—a diastereomeric product requires a diastereomeric starting material (either enantiomer). The easiest path to the answer is to convert the starting material in Eq. 9.40a into its diastereomer by the interchange ...
Polymers
... A process in which small molecules called monomers join together into large molecules consisting of repeating units. ...
... A process in which small molecules called monomers join together into large molecules consisting of repeating units. ...
CH 102 Laboratory 7 Ester Synthesis and Smells
... behind. Naturally this procedure will not work if the ester also has a low boiling point. Since esters can be formed from a wide variety of acids and alcohols it is not surprising that there is a very large number of possible esters. For example, consider the reaction of the five simplest alcohols w ...
... behind. Naturally this procedure will not work if the ester also has a low boiling point. Since esters can be formed from a wide variety of acids and alcohols it is not surprising that there is a very large number of possible esters. For example, consider the reaction of the five simplest alcohols w ...
Chapter23
... Ethanol is the intoxicating substance in alcoholic beverages. It is a depressant that can be fatal if taken in large doses at once. Denatured alcohol is ethanol with an added substance (CH4OH or wood alcohol) to make it toxic (poisonous). 4. Addition Reactions - Addition reactions of alkenes are an ...
... Ethanol is the intoxicating substance in alcoholic beverages. It is a depressant that can be fatal if taken in large doses at once. Denatured alcohol is ethanol with an added substance (CH4OH or wood alcohol) to make it toxic (poisonous). 4. Addition Reactions - Addition reactions of alkenes are an ...
Silica supported zinc chloride catalyzed acetylation of amines
... (Ref. 19) have also been reported. Literature survey revealed that the application of inorganic solids especially zeolites have recently received considerable attention due to their unique physical and chemical properties. H-FER20 has been reported for the acetylation of alcohols and phenols under s ...
... (Ref. 19) have also been reported. Literature survey revealed that the application of inorganic solids especially zeolites have recently received considerable attention due to their unique physical and chemical properties. H-FER20 has been reported for the acetylation of alcohols and phenols under s ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.