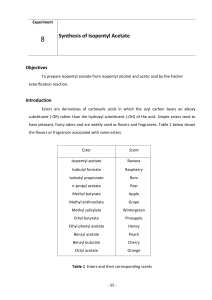
AP Chemistry
... order to make relevant observations and collect data; use the collected data to form conclusions and verify hypotheses; and communicate and compare results and procedures (informally to other experimenters, and also in a formal, written report to the teacher). ...
... order to make relevant observations and collect data; use the collected data to form conclusions and verify hypotheses; and communicate and compare results and procedures (informally to other experimenters, and also in a formal, written report to the teacher). ...
Document
... • Fuels (e.g. the RM1.92 RM2.10 Ron95) are made up mostly of alkanes. In excess oxygen • CnH2n+2 + (1.5n+½)O2 nCO2 + (n+1)H2O ...
... • Fuels (e.g. the RM1.92 RM2.10 Ron95) are made up mostly of alkanes. In excess oxygen • CnH2n+2 + (1.5n+½)O2 nCO2 + (n+1)H2O ...
phenol - Knockhardy
... • the aromatic ring helps weaken the O-H bond and stabilises the resulting anion • it dissolves very slightly in water to form a weak acidic solution C6H5OH(aq) ...
... • the aromatic ring helps weaken the O-H bond and stabilises the resulting anion • it dissolves very slightly in water to form a weak acidic solution C6H5OH(aq) ...
Document
... Because acid chlorides and anhydrides contain good leaving groups, these compounds are very reactive toward nucleophilic substitution by an alcohol, as shown in Equations 7-8. ...
... Because acid chlorides and anhydrides contain good leaving groups, these compounds are very reactive toward nucleophilic substitution by an alcohol, as shown in Equations 7-8. ...
Chapter 16. Biological Reagents
... of glucose-6-phosphate by an enzyme and ATP to fructose 1,6-diphosphate. Show the structure of fructose 1,6-diphosphate. 16.2 The oxidation of ethanol by NAD+ is stereospecific. Only the pro-R hydrogen atom is removed. Which hydrogen atom is the pro-R hydrogen? 16.3 Show a crossed Claisen reaction b ...
... of glucose-6-phosphate by an enzyme and ATP to fructose 1,6-diphosphate. Show the structure of fructose 1,6-diphosphate. 16.2 The oxidation of ethanol by NAD+ is stereospecific. Only the pro-R hydrogen atom is removed. Which hydrogen atom is the pro-R hydrogen? 16.3 Show a crossed Claisen reaction b ...
The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings
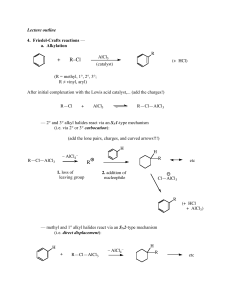
... 1. In FC alkylation, carbocation rearrangements often occur ...
... 1. In FC alkylation, carbocation rearrangements often occur ...
(Z)-Tamoxifen and Tetrasubstituted Alkenes and Dienes via a Regio
... Alkenol 18 was oxidized with Dess-Martin periodinane in CH2Cl2 to give the corresponding unsaturated aldehyde 20 (96%), which was transformed directly with methyl triphenylphosphonium bromide to give diene 21. Selective hydrogenation of the less hindered double bond (10% Pd/C, H2) afforded (Z)-Tamox ...
... Alkenol 18 was oxidized with Dess-Martin periodinane in CH2Cl2 to give the corresponding unsaturated aldehyde 20 (96%), which was transformed directly with methyl triphenylphosphonium bromide to give diene 21. Selective hydrogenation of the less hindered double bond (10% Pd/C, H2) afforded (Z)-Tamox ...
Hydrocarbon - TeacherWeb
... hydrogen atoms, and electrons that are shared among all six carbons in the ring (Draw the structure.) 2. Aromatic Compound: an organic compound that contains a benzene ring ...
... hydrogen atoms, and electrons that are shared among all six carbons in the ring (Draw the structure.) 2. Aromatic Compound: an organic compound that contains a benzene ring ...
Unit F322 - Chains, energy and resources - Visually impaired
... In your answer, you should make clear how each structure fits with the information given above. __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
... In your answer, you should make clear how each structure fits with the information given above. __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
Activation of C–F bonds using Cp*2ZrH2: a
... Examination of a different olefin helps differentiate these pathways. Reaction of 1 with 1,1-difluoromethylenecyclohexane only occurs slowly upon heating to 80 ⬚C. One observes both the monofluoro and the difluoro reduction products, as shown in eqn. (1). This observation is inconsistent with the H/F meta ...
... Examination of a different olefin helps differentiate these pathways. Reaction of 1 with 1,1-difluoromethylenecyclohexane only occurs slowly upon heating to 80 ⬚C. One observes both the monofluoro and the difluoro reduction products, as shown in eqn. (1). This observation is inconsistent with the H/F meta ...
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
... Biological Reactions • Only one substrate molecule at a time is present in the active site of the enzyme where the reaction occurs (necessary reactant groups nearby) • More controlled • More common than laboratory radical reactions ...
... Biological Reactions • Only one substrate molecule at a time is present in the active site of the enzyme where the reaction occurs (necessary reactant groups nearby) • More controlled • More common than laboratory radical reactions ...
Review Chapter 19
... Alcohols are a common organic functional group. The prevalence of this group is in no small part due to its myriad of reaction pathways. Alcohols are weak acids, weak bases, nucleophiles and electrophiles. Sometimes it is necessary to cover over this reactivity to react a group e ...
... Alcohols are a common organic functional group. The prevalence of this group is in no small part due to its myriad of reaction pathways. Alcohols are weak acids, weak bases, nucleophiles and electrophiles. Sometimes it is necessary to cover over this reactivity to react a group e ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.