Activity - OChemOnline
... The models use in this experiment show the correct angles between chemical bonds, but they do not accurately show the relative sizes of atoms or the correct bond lengths. Nevertheless, they help us appreciate: 1) the different possible arrangements of the atoms in a molecule, 2) the different shapes ...
... The models use in this experiment show the correct angles between chemical bonds, but they do not accurately show the relative sizes of atoms or the correct bond lengths. Nevertheless, they help us appreciate: 1) the different possible arrangements of the atoms in a molecule, 2) the different shapes ...
rev1
... 4. Know how to draw the structural formula, the condensed structural formula, the skeletal formula and the line structural formula for any hydrocarbon. 5. Be able to use table 11.2 to identify major families (functional groups) for organic compounds. 6. Know how sp3 hybridization is achieved for car ...
... 4. Know how to draw the structural formula, the condensed structural formula, the skeletal formula and the line structural formula for any hydrocarbon. 5. Be able to use table 11.2 to identify major families (functional groups) for organic compounds. 6. Know how sp3 hybridization is achieved for car ...
Basic definitions for organic chemistry
... ethene, butene ethanoic acid systematic name ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) ...
... ethene, butene ethanoic acid systematic name ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) ...
Organic Molecules
... they are bonded. The condensed structural formula below shows that in 2-methylpropane, there is a branched chain attached to the second carbon atom of the main chain. You can check this by looking at the structural formula in . ...
... they are bonded. The condensed structural formula below shows that in 2-methylpropane, there is a branched chain attached to the second carbon atom of the main chain. You can check this by looking at the structural formula in . ...
Document
... • They add to each other by opening up their carbon to carbon double bonds. • This process is called addition ...
... • They add to each other by opening up their carbon to carbon double bonds. • This process is called addition ...
Chapter 18 Organic Chemistry - American Public University System
... straight chain without any branching—like the ones we have just seen—are called normal alkanes or n-alkanes. • In addition to linking together in straight chains to form the n-alkanes, carbon atoms can form branched structures called branched alkanes. The simplest branched alkane is isobutane. • Iso ...
... straight chain without any branching—like the ones we have just seen—are called normal alkanes or n-alkanes. • In addition to linking together in straight chains to form the n-alkanes, carbon atoms can form branched structures called branched alkanes. The simplest branched alkane is isobutane. • Iso ...
c8h18 isomers
... ♦ The molecules are non-polar or very weakly polar ♦ The forces holding together non-polar molecules are van der Waals forces. These intermolecular forces, which operate only over very small distances, result from induced polarization of the electron clouds in molecules. ♦ Within a family: The large ...
... ♦ The molecules are non-polar or very weakly polar ♦ The forces holding together non-polar molecules are van der Waals forces. These intermolecular forces, which operate only over very small distances, result from induced polarization of the electron clouds in molecules. ♦ Within a family: The large ...
Chemistry Unit 1
... more carbon atoms are solids. Alkanes are nonpolar organic compounds. Weak intermolecular forces called Van der Waal’s forces hold their molecules together. The strength of these forces increases with the ...
... more carbon atoms are solids. Alkanes are nonpolar organic compounds. Weak intermolecular forces called Van der Waal’s forces hold their molecules together. The strength of these forces increases with the ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... NAMING ALDEHYDES • ALDEHYDES ARE NAMED BY REPLACING THE FINAL “E” OF THE NAME OF THE ALKANE WITH THE SAME NUMBER OF CARBONS TO “AL”. • BECAUSE IN ALDEHYDES THE CARBONYL GROUP IS ALWAYS ATTACHED TO THE FIRST CARBON, THERE IS NO NEED TO PLACE A 1 IN FRONT OF THE NAME. • IF THERE ARE SUBSTITUENTS PRES ...
... NAMING ALDEHYDES • ALDEHYDES ARE NAMED BY REPLACING THE FINAL “E” OF THE NAME OF THE ALKANE WITH THE SAME NUMBER OF CARBONS TO “AL”. • BECAUSE IN ALDEHYDES THE CARBONYL GROUP IS ALWAYS ATTACHED TO THE FIRST CARBON, THERE IS NO NEED TO PLACE A 1 IN FRONT OF THE NAME. • IF THERE ARE SUBSTITUENTS PRES ...
ORGANIC NOMENCLATURE
... than B (in A the methyl is up and in B the methyl is down). A and B are not superimposable on one another. To name the two isomers, the left side of the double bond is considered first and the two groups are prioritized based on atomic number (the largest atomic number at the first point of differen ...
... than B (in A the methyl is up and in B the methyl is down). A and B are not superimposable on one another. To name the two isomers, the left side of the double bond is considered first and the two groups are prioritized based on atomic number (the largest atomic number at the first point of differen ...
Organic Chemistry - St Mary's College, Wallasey
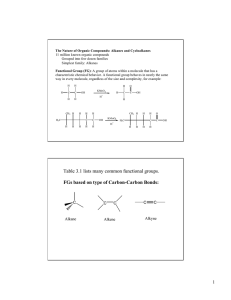
... • What about organic molecules that have different bonds? • We call families of different types of bonded atoms FUNCTIONAL GROUPS • An example is the –OH group or alcohol group. ...
... • What about organic molecules that have different bonds? • We call families of different types of bonded atoms FUNCTIONAL GROUPS • An example is the –OH group or alcohol group. ...
organic chemistry
... Arabic numeric prefix) and the kind of substituent (by its name). The position of a substituent on the chain is indicated by the lowest number possible. The number precedes the name of the substituent. When there are two or more substituents of a given kind, use prefixes to indicate the number of ...
... Arabic numeric prefix) and the kind of substituent (by its name). The position of a substituent on the chain is indicated by the lowest number possible. The number precedes the name of the substituent. When there are two or more substituents of a given kind, use prefixes to indicate the number of ...
ch 1: organic chemistry
... compared to a carboxylic the functional group is similar but is missing the OH group i.e. the –OH is replaced by an –OR group therefore esters are less polar, less soluble in water and have lower melting and boiling points than their parent acids acidity of carboxylic acids is from the H on ...
... compared to a carboxylic the functional group is similar but is missing the OH group i.e. the –OH is replaced by an –OR group therefore esters are less polar, less soluble in water and have lower melting and boiling points than their parent acids acidity of carboxylic acids is from the H on ...
Topic 20 IB Chemistry Definitions
... Chemistry: Definitions Topic 20 – Organic Chemistry Chiral center: ...
... Chemistry: Definitions Topic 20 – Organic Chemistry Chiral center: ...
Document
... Also called - London forces, instantaneous dipole - induced dipole interactions and dispersion forces. When noble gases are cooled sufficiently they will condense. This shows that there must be some forces acting between the atoms. These forces are called van der Waals' forces. The random motion of ...
... Also called - London forces, instantaneous dipole - induced dipole interactions and dispersion forces. When noble gases are cooled sufficiently they will condense. This shows that there must be some forces acting between the atoms. These forces are called van der Waals' forces. The random motion of ...
NOMENCLATURE VI This exercise covers the basics of organic
... Aromatic compounds contain one or more aromatic rings. For this class an aromatic ring will be indicated by a ring of six carbon atoms connected by alternating single and double bonds (resonating) or a six membered ring with a circle in it. Aromatic compounds are not limited to six membered rings, b ...
... Aromatic compounds contain one or more aromatic rings. For this class an aromatic ring will be indicated by a ring of six carbon atoms connected by alternating single and double bonds (resonating) or a six membered ring with a circle in it. Aromatic compounds are not limited to six membered rings, b ...
Molecular Orbitals - Calderglen High School
... previously met the familiar homologous series of alkanes, alkenes, cycloalkanes and alkynes. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons which fit the general formula CnH-2n+2. This means that every carbon atom in an alkane molecule will have 4 single covalent bonds and as we have previously studied have the ...
... previously met the familiar homologous series of alkanes, alkenes, cycloalkanes and alkynes. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons which fit the general formula CnH-2n+2. This means that every carbon atom in an alkane molecule will have 4 single covalent bonds and as we have previously studied have the ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... 1. Determine the longest continuous chain of carbon. (Parent chain) 2. Number carbons in parent chain. Do this by starting at the end that gives the attached groups the smallest number. 3. Add numbers to the names of the attached groups to identify their position. Numbers become prefixes to the name ...
... 1. Determine the longest continuous chain of carbon. (Parent chain) 2. Number carbons in parent chain. Do this by starting at the end that gives the attached groups the smallest number. 3. Add numbers to the names of the attached groups to identify their position. Numbers become prefixes to the name ...
Functional groups and homologous series
... drawing organic structures. The skeletal formula showing just the carbon atoms without the hydrogen atoms is not acceptable except for benzene (see below). However, unless specifically asked, Lewis structures showing all the valence electrons are not necessary. The bonding must be clearly indicated. ...
... drawing organic structures. The skeletal formula showing just the carbon atoms without the hydrogen atoms is not acceptable except for benzene (see below). However, unless specifically asked, Lewis structures showing all the valence electrons are not necessary. The bonding must be clearly indicated. ...
Organic Chemistry 145 CHEM
... -With an ordinary nickel or platinum catalyst, alkynes are hydrogenated all the way to alkanes. - However, a special palladium catalyst (called Lindlar’s catalyst) can control hydrogen addition so that only one mole of hydrogen adds. In this case, the product is a cis alkene. ...
... -With an ordinary nickel or platinum catalyst, alkynes are hydrogenated all the way to alkanes. - However, a special palladium catalyst (called Lindlar’s catalyst) can control hydrogen addition so that only one mole of hydrogen adds. In this case, the product is a cis alkene. ...
Organic Chemistry
... • in addition polymerisation, the simple units (ethene) which join together are called monomers • that unsaturated hydrocarbons differ from saturated hydrocarbons in structure and reaction with bromine water Describe an homologous series in more detail: • e.g. they can be represented by a general fo ...
... • in addition polymerisation, the simple units (ethene) which join together are called monomers • that unsaturated hydrocarbons differ from saturated hydrocarbons in structure and reaction with bromine water Describe an homologous series in more detail: • e.g. they can be represented by a general fo ...
Waste Disposal
... or alcohols, under controlled conditions in an inert gas atmosphere. This is best carried out by carefully adding only small quantities of the aluminum alkyl solution to an excess of water or alcohol, under efficient agitation. The reactivity of solvolyzing agents increases in the following order: B ...
... or alcohols, under controlled conditions in an inert gas atmosphere. This is best carried out by carefully adding only small quantities of the aluminum alkyl solution to an excess of water or alcohol, under efficient agitation. The reactivity of solvolyzing agents increases in the following order: B ...
Workshop #1 Part 1. Organic Chemistry Nomenclature
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
Chapter 13 - U of L Class Index
... contain single bonds to oxygen atoms or sulphur atoms. Structure of Alcohols and Thiols. In an alcohol, a hydroxyl group (-OH) replaces a hydrogen atom in an alkane. In a phenol, a hydroxyl group is attached to an aromatic ring. Thiols are similar to alcohols except that thiols contain a sulfhydryl ...
... contain single bonds to oxygen atoms or sulphur atoms. Structure of Alcohols and Thiols. In an alcohol, a hydroxyl group (-OH) replaces a hydrogen atom in an alkane. In a phenol, a hydroxyl group is attached to an aromatic ring. Thiols are similar to alcohols except that thiols contain a sulfhydryl ...
Functional Group Handout
... another carbon. The nitrogen atom of a tertiary amide is bonded to the carbonyl carbon and two other carbons. Cyclic amides are called lactams. Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acids. O ...
... another carbon. The nitrogen atom of a tertiary amide is bonded to the carbonyl carbon and two other carbons. Cyclic amides are called lactams. Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acids. O ...
Alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical name that also has other meanings), is a saturated hydrocarbon. Alkanes consist only of hydrogen and carbon atoms and all bonds are single bonds. Alkanes (technically, always acyclic or open-chain compounds) have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2. For example, Methane is CH4, in which n=1 (n being the number of Carbon atoms). Alkanes belong to a homologous series of organic compounds in which the members differ by a molecular mass of 14.03u (mass of a methanediyl group, —CH2—, one carbon atom of mass 12.01u, and two hydrogen atoms of mass ≈1.01u each). There are two main commercial sources: petroleum (crude oil) and natural gas.Each carbon atom has 4 bonds (either C-H or C-C bonds), and each hydrogen atom is joined to a carbon atom (H-C bonds). A series of linked carbon atoms is known as the carbon skeleton or carbon backbone. The number of carbon atoms is used to define the size of the alkane e.g., C2-alkane.An alkyl group, generally abbreviated with the symbol R, is a functional group or side-chain that, like an alkane, consists solely of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms, for example a methyl or ethyl group.The simplest possible alkane (the parent molecule) is methane, CH4. There is no limit to the number of carbon atoms that can be linked together, the only limitation being that the molecule is acyclic, is saturated, and is a hydrocarbon. Waxes include examples of larger alkanes where the number of carbons in the carbon backbone is greater than about 17, above which the compounds are solids at standard ambient temperature and pressure (SATP).Alkanes are not very reactive and have little biological activity. All alkanes are colourless and odourless. Alkanes can be viewed as a molecular tree upon which can be hung the more biologically active/reactive portions (functional groups) of the molecule.