3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and
... share two carbon atoms (the bridgehead carbons, C1 and C6) and a common bond Two isomeric forms of decalin: trans fused or cis fused In cis-decalin hydrogen atoms at the bridgehead carbons are on the same face of the rings In trans-decalin, the bridgehead hydrogens are on ...
... share two carbon atoms (the bridgehead carbons, C1 and C6) and a common bond Two isomeric forms of decalin: trans fused or cis fused In cis-decalin hydrogen atoms at the bridgehead carbons are on the same face of the rings In trans-decalin, the bridgehead hydrogens are on ...
Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acid
... nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positive charge on carbonyl carbon. Greater positive charge means greater reactivity. Electron releasing power of two alkyl groups in ketones is more than one in aldehyde. Therefore positive charge is reduced in ketones as compared to aldehydes. Thus ketone ...
... nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positive charge on carbonyl carbon. Greater positive charge means greater reactivity. Electron releasing power of two alkyl groups in ketones is more than one in aldehyde. Therefore positive charge is reduced in ketones as compared to aldehydes. Thus ketone ...
Application of IBX Method for the Synthesis of Ketones from
... changed into its chloride. Then the acid chloride reacts with an organometallic reagent or gives a FriedelCrafts type reaction in the presence of Lewis acids. These methods are very useful for most aliphatic acid halides and good yields can be obtained in this way. However, if this method is used fo ...
... changed into its chloride. Then the acid chloride reacts with an organometallic reagent or gives a FriedelCrafts type reaction in the presence of Lewis acids. These methods are very useful for most aliphatic acid halides and good yields can be obtained in this way. However, if this method is used fo ...
Triruthenium and triosmium carbonyl clusters containing chiral
... As we could not get crystals of the osmium compounds 7 and 8 suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis, their structures (Scheme 3) were assigned on the basis of TLC elution rates. Using the same eluent, compounds 5 and 7 moved on their TLC plates faster than their diastereoisomers 6 and 8, respective ...
... As we could not get crystals of the osmium compounds 7 and 8 suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis, their structures (Scheme 3) were assigned on the basis of TLC elution rates. Using the same eluent, compounds 5 and 7 moved on their TLC plates faster than their diastereoisomers 6 and 8, respective ...
Bonding Web Practice Trupia - Trupia
... 42. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. Each molecule listed below is formed by sharing electrons between atoms when the atoms within the molecule are bonded together. Molecule A: Cl2 Molecule B: CCl4 Molecule C: NH3 Explain why NH3 has stronger intermolecular forces ...
... 42. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. Each molecule listed below is formed by sharing electrons between atoms when the atoms within the molecule are bonded together. Molecule A: Cl2 Molecule B: CCl4 Molecule C: NH3 Explain why NH3 has stronger intermolecular forces ...
© John Congleton, Orange Coast College Organic Chemistry 220
... Be able to predict whether a reaction will proceed via o SN1 and E1 o S N2 o SN2 and E2 o E2 What makes a good nucleophile? What makes a good base? What makes a good leaving group? What is meant by high and low polarizability? Allylic bromination Understand, be able to predict, and be able to comple ...
... Be able to predict whether a reaction will proceed via o SN1 and E1 o S N2 o SN2 and E2 o E2 What makes a good nucleophile? What makes a good base? What makes a good leaving group? What is meant by high and low polarizability? Allylic bromination Understand, be able to predict, and be able to comple ...
CHAP 1 - NCERT books
... walls. Calcium hydroxide reacts slowly with the carbon dioxide in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate on the walls. Calcium carbonate is formed after two to three days of white washing and gives a shiny finish to the walls. It is interesting to note that the chemical formula for marble is ...
... walls. Calcium hydroxide reacts slowly with the carbon dioxide in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate on the walls. Calcium carbonate is formed after two to three days of white washing and gives a shiny finish to the walls. It is interesting to note that the chemical formula for marble is ...
Reaction Rate review questions
... Show that the sum of the two steps in the reaction mechanism is the same as the overall equation for the reaction. What is the rate-determining step? Explain. First step is the slowest so it is the rate determining step. Identify any intermediates or catalysts. F is an intermediate, no catalyst. Pre ...
... Show that the sum of the two steps in the reaction mechanism is the same as the overall equation for the reaction. What is the rate-determining step? Explain. First step is the slowest so it is the rate determining step. Identify any intermediates or catalysts. F is an intermediate, no catalyst. Pre ...
Synthesis Explorer
... Aldehydes and ketones can be distinguished by using either Fehling’s solution or Tollens’ reagent. Aldehydes give a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide when warmed with Fehling’s solution, while ketones do not react. Similarly aldehydes produce a silver mirror on the inside of the test tube when warm ...
... Aldehydes and ketones can be distinguished by using either Fehling’s solution or Tollens’ reagent. Aldehydes give a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide when warmed with Fehling’s solution, while ketones do not react. Similarly aldehydes produce a silver mirror on the inside of the test tube when warm ...
Basic IUPAC Nomenclature V
... to indicate the number. (di-, tri-, tetra-) these prefixes do not count towards alphabetical order unless they are part of a branched substituent. 6) Indicate stereochemistry using cis- or trans- prefixes for disubstituted rings or R,S labels for multiply substituted rings and straight chains. Stere ...
... to indicate the number. (di-, tri-, tetra-) these prefixes do not count towards alphabetical order unless they are part of a branched substituent. 6) Indicate stereochemistry using cis- or trans- prefixes for disubstituted rings or R,S labels for multiply substituted rings and straight chains. Stere ...
Synthesis_of_Organometallic_Compounds
... • less application in organic synthesis than palladium compounds, probably because their chemistry is more complicated. ...
... • less application in organic synthesis than palladium compounds, probably because their chemistry is more complicated. ...
Unit 8 Test Review
... Dimensional Analysis – A method of treating units as algebraic quantities, which can be cancelled. ...
... Dimensional Analysis – A method of treating units as algebraic quantities, which can be cancelled. ...
Chapter 4 Alkanes
... • The maximum number of possible constitutional isomers increases dramatically as the number of carbon atoms in the alkane increases. For example, there are 75 possible isomers for an alkane having 10 carbon atoms, but 366,319 possible isomers for one having 20 carbons. • The suffix “ane” identifie ...
... • The maximum number of possible constitutional isomers increases dramatically as the number of carbon atoms in the alkane increases. For example, there are 75 possible isomers for an alkane having 10 carbon atoms, but 366,319 possible isomers for one having 20 carbons. • The suffix “ane” identifie ...
Chapter 1 Review, pages 72–77
... 37. (a) The compound on the right, benzoic acid, has two polar groups—a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group—located close together, adding polarity to the molecule, which contributes to its solubility in water. However, the non-polar ring makes benzoic acid less soluble. Consequently, benzoic acid ...
... 37. (a) The compound on the right, benzoic acid, has two polar groups—a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group—located close together, adding polarity to the molecule, which contributes to its solubility in water. However, the non-polar ring makes benzoic acid less soluble. Consequently, benzoic acid ...
Chemical Reactions - Johnston County Schools
... Substances other than hydrocarbons can also combust. However, you may not be able to tell whether it’s combustion from the chemical equation alone. Remember that combustion must have O2 as a reactant and must release (exothermic) heat and light energy. Reactions with O2.mov ...
... Substances other than hydrocarbons can also combust. However, you may not be able to tell whether it’s combustion from the chemical equation alone. Remember that combustion must have O2 as a reactant and must release (exothermic) heat and light energy. Reactions with O2.mov ...
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH)
... • Although entropy favors product formation in dehydration (i.e., one molecule of reactant forms two molecules of product), enthalpy does not, since the bonds broken in the reactant are stronger than the and bonds formed in the products. ...
... • Although entropy favors product formation in dehydration (i.e., one molecule of reactant forms two molecules of product), enthalpy does not, since the bonds broken in the reactant are stronger than the and bonds formed in the products. ...
Final Study Guide
... amines using common and IUPAC names; draw the condensed structures given the names. Describe the boiling points and solubility of amines; write equations for the neutralization of amines. Identify heterocyclic amines; distinguish between the types of heterocyclic amines. Write the amide products of ...
... amines using common and IUPAC names; draw the condensed structures given the names. Describe the boiling points and solubility of amines; write equations for the neutralization of amines. Identify heterocyclic amines; distinguish between the types of heterocyclic amines. Write the amide products of ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 1. Background and Properties
... on the alkyl chain relative to the carboxyl carbonyl group. • Nitriles: Simple acyclic nitriles are named by adding nitrile as a suffix to the name of the corresponding alkane (same number of carbon atoms). Chain numbering begins with the nitrile carbon . Commonly, the oic acid or ic acid ending of ...
... on the alkyl chain relative to the carboxyl carbonyl group. • Nitriles: Simple acyclic nitriles are named by adding nitrile as a suffix to the name of the corresponding alkane (same number of carbon atoms). Chain numbering begins with the nitrile carbon . Commonly, the oic acid or ic acid ending of ...
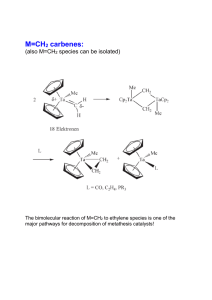
Steric protection of alkylidene is not needed:
... - complex should be well-accessible for alkenes (low coordination of 4 => free coordination site) - X should NOT be O (dimer formation) but NR with large R group - other substituents should be electron-withdrawing (important for alkene coordination) ...
... - complex should be well-accessible for alkenes (low coordination of 4 => free coordination site) - X should NOT be O (dimer formation) but NR with large R group - other substituents should be electron-withdrawing (important for alkene coordination) ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... bonded to the same oxygen atom, R–O–R • Diethyl ether is used industrially as a solvent • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether • Thiols (R–S–H) and sulfides (R–S–R) are sulfur (for oxygen) analogs of alcohols and ethers ...
... bonded to the same oxygen atom, R–O–R • Diethyl ether is used industrially as a solvent • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether • Thiols (R–S–H) and sulfides (R–S–R) are sulfur (for oxygen) analogs of alcohols and ethers ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.