Oxidation Reactions of Sugars
... with molecular oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. The carbon atoms in glucose are oxidized. That is, they lose electron and go to a higher oxidation state. The oxygen atoms in molecular oxygen are reduced. That is, they add electrons and go to a lower oxidation state. If we want to represen ...
... with molecular oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. The carbon atoms in glucose are oxidized. That is, they lose electron and go to a higher oxidation state. The oxygen atoms in molecular oxygen are reduced. That is, they add electrons and go to a lower oxidation state. If we want to represen ...
CHEM1102 2014-J-8 June 2014 • Complete the following table
... treatment of attention-deficit disorder. Identify all stereogenic (chiral) centres in methylphenidate by clearly marking each with an asterisk (*) on the structure below. ...
... treatment of attention-deficit disorder. Identify all stereogenic (chiral) centres in methylphenidate by clearly marking each with an asterisk (*) on the structure below. ...
Lecture 3-edited
... Chromium is the 21st most abundant element in Earth's crust with atomic number 24. Naturally occurring chromium composed of three stable isotopes; 52Cr, 53Cr and 54Cr with 52Cr being most abundant. It has an electronic configuration of 3d5 4s1 and exhibits a wide range of oxidation states, where the ...
... Chromium is the 21st most abundant element in Earth's crust with atomic number 24. Naturally occurring chromium composed of three stable isotopes; 52Cr, 53Cr and 54Cr with 52Cr being most abundant. It has an electronic configuration of 3d5 4s1 and exhibits a wide range of oxidation states, where the ...
principle group
... 1) Identify the longest carbon chain containing the sulfhydryl group. Name this chain and add “thiol” to the end (no space). 2) Number the chain so that the carbon connected to the –SH group has the lowest number possible 3) Name and number all of the substituents and place them, in alphabetical ord ...
... 1) Identify the longest carbon chain containing the sulfhydryl group. Name this chain and add “thiol” to the end (no space). 2) Number the chain so that the carbon connected to the –SH group has the lowest number possible 3) Name and number all of the substituents and place them, in alphabetical ord ...
Ch 17 practice assessment w
... how can this be accomplished if they are traveling in a truck through different weather conditions? Also, when you receive your perishable product, how can you be certain that it has not been exposed to unfavorable conditions? It’s simple. You can use equilibrium. In water solutions, the Co 2 ion i ...
... how can this be accomplished if they are traveling in a truck through different weather conditions? Also, when you receive your perishable product, how can you be certain that it has not been exposed to unfavorable conditions? It’s simple. You can use equilibrium. In water solutions, the Co 2 ion i ...
Carboxylic Acid Structure and Chemistry
... C. Nucleophilic Reactions at the Alpha-Carbon Carboxylic acids containing a "good leaving" group at the carbon atom adjacent to the carbonyl (the α-carbon) may be substrates for nucleophilic displacement reactions. The α-carbon atoms in these systems are electron deficient due to their positioning n ...
... C. Nucleophilic Reactions at the Alpha-Carbon Carboxylic acids containing a "good leaving" group at the carbon atom adjacent to the carbonyl (the α-carbon) may be substrates for nucleophilic displacement reactions. The α-carbon atoms in these systems are electron deficient due to their positioning n ...
Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... Esters are reduced to 1° alcohols by reduction with LiAlH4 (but not NaBH4 or catalytic hydrogenation). ...
... Esters are reduced to 1° alcohols by reduction with LiAlH4 (but not NaBH4 or catalytic hydrogenation). ...
Chlorine chemistry representation
... routes: H abstraction from the CHO (45%) and Cl addition to the C=C (55%), based on the OH-oxidation scheme in the MCM. Hence, 45% of MACR is oxidized by Cl as a common aldehyde, while 55% is treated as an alkene species and is summed into the lumped ‘OLEFIN’ ...
... routes: H abstraction from the CHO (45%) and Cl addition to the C=C (55%), based on the OH-oxidation scheme in the MCM. Hence, 45% of MACR is oxidized by Cl as a common aldehyde, while 55% is treated as an alkene species and is summed into the lumped ‘OLEFIN’ ...
supplemenatary material - Royal Society of Chemistry
... sample valve to measure the selectivity as the reaction proceeded. Conversion and regioselectivity in these samples and in the final solution were directly analyzed by GC. Samples were immediately oxidized with KMnO4/ MgSO4 in acetone to convert the aldehydes in the corresponding acids, which where ...
... sample valve to measure the selectivity as the reaction proceeded. Conversion and regioselectivity in these samples and in the final solution were directly analyzed by GC. Samples were immediately oxidized with KMnO4/ MgSO4 in acetone to convert the aldehydes in the corresponding acids, which where ...
File
... 25 CH3CH2COCH2CH3 reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form an organic product called a cyanohydrin. Which feature applies to the cyanohydrin product? A ...
... 25 CH3CH2COCH2CH3 reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form an organic product called a cyanohydrin. Which feature applies to the cyanohydrin product? A ...
Theoretical Competition - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... In order to gain information about the kinetics of this reaction, it is possible to titrate S2O32- with iodine solution from time to time. The following procedure is convenient. 2.00 mL of the thiosulphate solution, which is used in the experiment, need 12.2 mL of iodine solution with c = 5.00·10-3 ...
... In order to gain information about the kinetics of this reaction, it is possible to titrate S2O32- with iodine solution from time to time. The following procedure is convenient. 2.00 mL of the thiosulphate solution, which is used in the experiment, need 12.2 mL of iodine solution with c = 5.00·10-3 ...
19-Oct
... How many kJ of energy are released when 23.7 g of hydrogen are reacted with excess chlorine to form hydrogen chloride. ...
... How many kJ of energy are released when 23.7 g of hydrogen are reacted with excess chlorine to form hydrogen chloride. ...
NOMENCLATURE VI This exercise covers the basics of organic
... or a six membered ring with a circle in it. Aromatic compounds are not limited to six membered rings, but only such materials will be a part of this discussion. In most of the cases examined here, the IUPAC names are the same as the common names. The simplest aromatic presented here is benzene (C6H6 ...
... or a six membered ring with a circle in it. Aromatic compounds are not limited to six membered rings, but only such materials will be a part of this discussion. In most of the cases examined here, the IUPAC names are the same as the common names. The simplest aromatic presented here is benzene (C6H6 ...
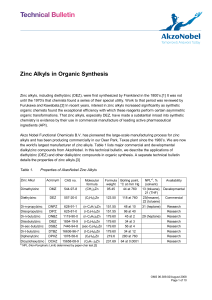
Zinc Alkyls in Organic Synthesis
... Reactions of Other Zinc Alkyls Dimethylzinc (DMZ) has been used in similar ways as DEZ in organic reactions. Because DMZ is highly volatile (bp 44°C), accurate addition of the reagent into the reaction mixture can be difficult. When the reaction mixture is not cooled to a low temperature, a portion ...
... Reactions of Other Zinc Alkyls Dimethylzinc (DMZ) has been used in similar ways as DEZ in organic reactions. Because DMZ is highly volatile (bp 44°C), accurate addition of the reagent into the reaction mixture can be difficult. When the reaction mixture is not cooled to a low temperature, a portion ...
Rapid and Efficient Functionalized Ionic Liquid-Catalyzed
... “task-specific ionic liquids” (TSILs) has been introduced to describe such ILs and they have been applied to various organic reactions as environmentally preferable solvents, reagents, or catalysts [5–9]. Aldol reactions are an effective means of forming C–C bonds and the products of α,β-unsaturated ...
... “task-specific ionic liquids” (TSILs) has been introduced to describe such ILs and they have been applied to various organic reactions as environmentally preferable solvents, reagents, or catalysts [5–9]. Aldol reactions are an effective means of forming C–C bonds and the products of α,β-unsaturated ...
Honors Chemistry
... : a species that appears in some steps but not in the overall reaction. It is relatively short lived. So, in the above example, H2I is the reaction intermediate. ...
... : a species that appears in some steps but not in the overall reaction. It is relatively short lived. So, in the above example, H2I is the reaction intermediate. ...
Give reasons for the following.(one mark each)
... 13. SN2 reaction always proceeds with inversion of configuration. 14. The order of reactivity of alkyl halides for SN2 is 1o> 2o>3o 15. The order of reactivity of alkyl halides for SN1 is 3o> 2o>1o 16. Even trace amounts of water has to be removed from Grignards reagent . 17. Haloarenes/ aryl halide ...
... 13. SN2 reaction always proceeds with inversion of configuration. 14. The order of reactivity of alkyl halides for SN2 is 1o> 2o>3o 15. The order of reactivity of alkyl halides for SN1 is 3o> 2o>1o 16. Even trace amounts of water has to be removed from Grignards reagent . 17. Haloarenes/ aryl halide ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.