New Phenylglycine-Derived Primary Amine Organocatalysts for the
... prepared by a Strecker reaction of benzaldehyde, followed by hydrolysis of the nitrile. This racemate is then resolved by diastereomeric salt formation,[18a] with (+)-(1S)-camphor-10-sulfonic acid being a very effective resolving agent for this compound.[19] Therefore, phenylglycine is particularly ...
... prepared by a Strecker reaction of benzaldehyde, followed by hydrolysis of the nitrile. This racemate is then resolved by diastereomeric salt formation,[18a] with (+)-(1S)-camphor-10-sulfonic acid being a very effective resolving agent for this compound.[19] Therefore, phenylglycine is particularly ...
Rxn Types
... Single Displacement Reactions Not all single displacement reactions that can be written actually happen. The metal or non-metal must be more active than the ion it is replacing. It will depend upon the element’s Activity as ...
... Single Displacement Reactions Not all single displacement reactions that can be written actually happen. The metal or non-metal must be more active than the ion it is replacing. It will depend upon the element’s Activity as ...
Ch 12- 13 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... Addition of water to alkenes: Hydration Alcohol is produced on treatment of the alkene with water in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, such as H2SO4. Markovnikov’s rule can be used to predict the product when water adds to an unsymmetrically substituted alkene. Hydrated alkenes produce alcohol ...
... Addition of water to alkenes: Hydration Alcohol is produced on treatment of the alkene with water in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, such as H2SO4. Markovnikov’s rule can be used to predict the product when water adds to an unsymmetrically substituted alkene. Hydrated alkenes produce alcohol ...
Lectures 32-33 - U of L Class Index
... properties of a pair of enantiomers are identical unless they are in a chiral environment (such as any biological system). Your hands are chiral and can be used as an analogy for enantiomers - left and right hands are mirror images that cannot be superimposed. If you have a right-hand glove, it will ...
... properties of a pair of enantiomers are identical unless they are in a chiral environment (such as any biological system). Your hands are chiral and can be used as an analogy for enantiomers - left and right hands are mirror images that cannot be superimposed. If you have a right-hand glove, it will ...
Postprint
... alkene. The heterocycle bears a group (often phenyl), pointing out of the plane, which generates a large bulk in the plane of the coordinated olefin, trans t the phosphine: the hindered quadrant. The di-aryl phosphine, while large, has only a small portion of its bulk coming out of the plane: the se ...
... alkene. The heterocycle bears a group (often phenyl), pointing out of the plane, which generates a large bulk in the plane of the coordinated olefin, trans t the phosphine: the hindered quadrant. The di-aryl phosphine, while large, has only a small portion of its bulk coming out of the plane: the se ...
Functional Groups: Centers of Reactivity
... Alkanes can be classified into three general classes: straight-chain alkanes, branched alkanes, and cycloalkanes: ...
... Alkanes can be classified into three general classes: straight-chain alkanes, branched alkanes, and cycloalkanes: ...
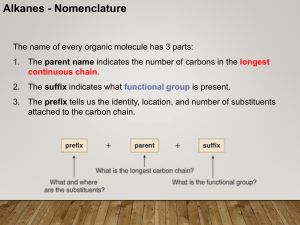
CHEM 210 Nomenclature Lecture 1
... • In the IUPAC system, change the –ane ending of the parent alkane name to the suffix –yne. • Choose the longest continuous chain that contains both atoms of the triple bond and number the chain to give the triple bond the lower number. ...
... • In the IUPAC system, change the –ane ending of the parent alkane name to the suffix –yne. • Choose the longest continuous chain that contains both atoms of the triple bond and number the chain to give the triple bond the lower number. ...
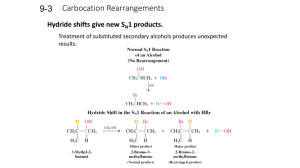
Learning Guide for Chapter 9 - Alkyl Halides I
... surrounds Nu/base, makes it hard to react What kind of solvent do SN1 reactions require? polarity isn't important - reagents are not charged, dissolve easily protic solvent - stabilizes the C+, increases reaction rate What solvents are in the following categories? ...
... surrounds Nu/base, makes it hard to react What kind of solvent do SN1 reactions require? polarity isn't important - reagents are not charged, dissolve easily protic solvent - stabilizes the C+, increases reaction rate What solvents are in the following categories? ...
SPRING 2002 Test 2 1. Which of the following statements is
... 11. For which of the following gaseous reactions will the values of Kp and Kc be the same? A. 2 NO + O2 <=> 2 NO2 B. N2 + 3H2 <=> 2 NH3 C. 2 CO + O2 <=> 2 CO2 D. N2O4 <=> 2 NO2 E. N2 + O2 <=> 2 NO Ans. E 12. Consider the exothermic reaction between N2 and H2 to produce NH3. In order to produce as mu ...
... 11. For which of the following gaseous reactions will the values of Kp and Kc be the same? A. 2 NO + O2 <=> 2 NO2 B. N2 + 3H2 <=> 2 NH3 C. 2 CO + O2 <=> 2 CO2 D. N2O4 <=> 2 NO2 E. N2 + O2 <=> 2 NO Ans. E 12. Consider the exothermic reaction between N2 and H2 to produce NH3. In order to produce as mu ...
Oxidation of Alcohols
... Reduction of alehydes, ketones, esters, and carboxylic acids (Chapter 15.2 - 15.3) Reaction of epoxides with Grignard Reagents (Chapter 15.4) ...
... Reduction of alehydes, ketones, esters, and carboxylic acids (Chapter 15.2 - 15.3) Reaction of epoxides with Grignard Reagents (Chapter 15.4) ...
IB Chemistry
... • Effect on volatility of the different functional groups is summarized as: haloalkane>aldehyde> ketone> alcohol> carboxylic acid • Solubility in water is increased by the presence of functional groups like alcohols, carboxylic acids and amines as these can all form hydrogen bonds. • Aldehydes, keto ...
... • Effect on volatility of the different functional groups is summarized as: haloalkane>aldehyde> ketone> alcohol> carboxylic acid • Solubility in water is increased by the presence of functional groups like alcohols, carboxylic acids and amines as these can all form hydrogen bonds. • Aldehydes, keto ...
Today Electrochemistry electrons moving about equilibrium with a
... electrons are moving between different chemical species 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) ...
... electrons are moving between different chemical species 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) ...
Today Electrochemistry electrons moving about equilibrium with a
... If we imagine this breaking up it would make! Mg2+ and O2-! So the "oxidation state" of Mg is 2+! the "oxidation state" of O is 2-! How will we figure it out for other molecules?! There are rules.! ...
... If we imagine this breaking up it would make! Mg2+ and O2-! So the "oxidation state" of Mg is 2+! the "oxidation state" of O is 2-! How will we figure it out for other molecules?! There are rules.! ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... Recall that nucleophilic hydride sources are boron or aluminum-based, while NaH is used almost exclusively as a base (not as a nucleophile) ...
... Recall that nucleophilic hydride sources are boron or aluminum-based, while NaH is used almost exclusively as a base (not as a nucleophile) ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 32) A nitrile can be made by dehydrating an amide. However, for this reaction to occur, the amide must be: A) secondary. B) primary. C) part of a lactam. D) N-methylated. E) tertiary. SHORT ANSWER. ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 32) A nitrile can be made by dehydrating an amide. However, for this reaction to occur, the amide must be: A) secondary. B) primary. C) part of a lactam. D) N-methylated. E) tertiary. SHORT ANSWER. ...
CHEM_01A_ExptD_Copper_Cycle_F14
... Clean all glassware used for the experiment before leaving the laboratory. Place all solutions/precipitates/solids in the appropriate waste container. Wash your hands before leaving the lab room. ...
... Clean all glassware used for the experiment before leaving the laboratory. Place all solutions/precipitates/solids in the appropriate waste container. Wash your hands before leaving the lab room. ...
Chem 216 H W13 Notes - Dr. Masato Koreeda Thin
... (1) UV lamp – The UV lamp in the lab emits UV light having the 254 nm wavelength. The silica gel TLC plates we use have an inorganic fluorescent agent (<0.5%) impregnated into the adsorbent layer. When illuminated with an ultraviolet (UV) lamp, the absorbent then glows the pale green or blue colored ...
... (1) UV lamp – The UV lamp in the lab emits UV light having the 254 nm wavelength. The silica gel TLC plates we use have an inorganic fluorescent agent (<0.5%) impregnated into the adsorbent layer. When illuminated with an ultraviolet (UV) lamp, the absorbent then glows the pale green or blue colored ...
in a Chemical Reactor - Max-Planck
... We are currently working to identify the best conditions for obtaining cyclohexanol in this way. Here, too, we are faced with the problem that cyclohexene and formic acid are not particularly mutually soluble. However, what they do form under certain conditions is an azeotrope – a mixture in which t ...
... We are currently working to identify the best conditions for obtaining cyclohexanol in this way. Here, too, we are faced with the problem that cyclohexene and formic acid are not particularly mutually soluble. However, what they do form under certain conditions is an azeotrope – a mixture in which t ...
Document
... Addition, Substitution, and Elimination Reactions Addition reactions, substitution reactions, and elimination reactions are the three main types of organic reactions. Most organic reactions can be classified as one of these three types. Addition Reactions In an addition reaction, atoms are added to ...
... Addition, Substitution, and Elimination Reactions Addition reactions, substitution reactions, and elimination reactions are the three main types of organic reactions. Most organic reactions can be classified as one of these three types. Addition Reactions In an addition reaction, atoms are added to ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.