Ch 13 kinetics
... More than a balanced chemical equation, a reaction mechanism ________________________________________ . Provides a detailed picture of how a reaction occurs. Elementary step: Any process that occurs ____________________________________________________________________ Makes either ___________________ ...
... More than a balanced chemical equation, a reaction mechanism ________________________________________ . Provides a detailed picture of how a reaction occurs. Elementary step: Any process that occurs ____________________________________________________________________ Makes either ___________________ ...
Ryoji Noyori - Nobel Lecture
... Most importantly, in 1956, S. Akabori at Osaka reported that metallic Pd drawn on silk catalyzes asymmetric (heterogeneous) hydrogenation of oximes and oxazolones[13]. This pioneering work, though not effective synthetically, was already well known throughout Japan. In 1968, two years after our asym ...
... Most importantly, in 1956, S. Akabori at Osaka reported that metallic Pd drawn on silk catalyzes asymmetric (heterogeneous) hydrogenation of oximes and oxazolones[13]. This pioneering work, though not effective synthetically, was already well known throughout Japan. In 1968, two years after our asym ...
Mechanism of Autoxidative Degradation of Cellulose
... In aqueous solutions, molecular oxygen is a fairly good oxidizing agent. During the reaction, oxygen may be reduced to water by one-electron transfer in four successive stages giving rise to intermediate products, namely, superoxide (HOO/O2ˉ), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl radicals (HO). The ...
... In aqueous solutions, molecular oxygen is a fairly good oxidizing agent. During the reaction, oxygen may be reduced to water by one-electron transfer in four successive stages giving rise to intermediate products, namely, superoxide (HOO/O2ˉ), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl radicals (HO). The ...
Chapter 6: Chemical Equilibrium
... 9. The reaction, Q + 2 SO3(g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) is endothermic. Predict what will happen if the temperature is increased. a. Kc remains the same b. Kc decreases c. the pressure decreases d. more SO3(g) is produced * e. Kc increases T increase, reaction will shift to right side and Kc increase 10. Con ...
... 9. The reaction, Q + 2 SO3(g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) is endothermic. Predict what will happen if the temperature is increased. a. Kc remains the same b. Kc decreases c. the pressure decreases d. more SO3(g) is produced * e. Kc increases T increase, reaction will shift to right side and Kc increase 10. Con ...
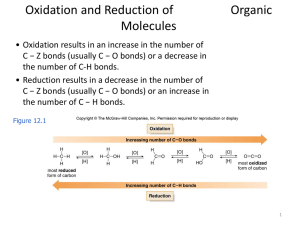
Classifying Chemical Reactions by What Atoms Do
... must gain or lose electrons (of course, if one atom loses electrons, another must accept them). Atoms that lose electrons are being oxidized, atoms that gain electrons are being reduced. ...
... must gain or lose electrons (of course, if one atom loses electrons, another must accept them). Atoms that lose electrons are being oxidized, atoms that gain electrons are being reduced. ...
Guide_to_Life_in_Orgo_Ib
... given atom. Convert a stereoview into a conventional drawing of a molecule using wedged, dashed, and normal lines. Identify the number of covalent bonds an atom forms to reach an octet. Given a molecular or ionic formula, draw a Lewis and line-bond structure. Describe electron sharing according to v ...
... given atom. Convert a stereoview into a conventional drawing of a molecule using wedged, dashed, and normal lines. Identify the number of covalent bonds an atom forms to reach an octet. Given a molecular or ionic formula, draw a Lewis and line-bond structure. Describe electron sharing according to v ...
rev2
... 2. Know that aldehydes and ketones are functional isomers (constitutional isomers that involve having different functional groups) 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes an ...
... 2. Know that aldehydes and ketones are functional isomers (constitutional isomers that involve having different functional groups) 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes an ...
Electrophilic Additions: Alkenes Addition of Hydrogen Halides
... In a regioselective reaction, one constitutional isomer is the major or the only product. I: early transition state (Like reactants) ...
... In a regioselective reaction, one constitutional isomer is the major or the only product. I: early transition state (Like reactants) ...
F Practice Test #2 Solutions
... A) The equilibrium constant is independent of temperature. B) The value of the equilibrium constant for a given reaction mixture is the same regardless of the direction from which equilibrium is attained. C) A system that is disturbed from an equilibrium condition responds in such a way as to restor ...
... A) The equilibrium constant is independent of temperature. B) The value of the equilibrium constant for a given reaction mixture is the same regardless of the direction from which equilibrium is attained. C) A system that is disturbed from an equilibrium condition responds in such a way as to restor ...
Organometallics II
... formula C11H22O, are formed in the reaction of methyl lithium with 3-(R)-tertbutylcyclohexanone. These two alcohols are ...
... formula C11H22O, are formed in the reaction of methyl lithium with 3-(R)-tertbutylcyclohexanone. These two alcohols are ...
Experiment 11 CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... example above, Zn would be listed above Cu. In the case of single replacement reactions, hydrogen acts like a metal. Only the most active metals will replace hydrogen from water at room temperature. M(s) ...
... example above, Zn would be listed above Cu. In the case of single replacement reactions, hydrogen acts like a metal. Only the most active metals will replace hydrogen from water at room temperature. M(s) ...
Reactions of Alcohols - John Carroll University
... synthesis, however, dehydrogenation is not practical, and cost is not as large a factor as it would be in industry. Most labs would have chromium trioxide or sodium dichromate available, and the chromic acid oxidation would be simple. PCC and the Swern oxidation would also work, although these reage ...
... synthesis, however, dehydrogenation is not practical, and cost is not as large a factor as it would be in industry. Most labs would have chromium trioxide or sodium dichromate available, and the chromic acid oxidation would be simple. PCC and the Swern oxidation would also work, although these reage ...
Alkene - Synthesis
... E1 Dehydrohalogenation 2° or 3° alkyl halides requires a good ionizing solvent: alcohol or water. no strong nucleophile or base Rearrangements can occur. ...
... E1 Dehydrohalogenation 2° or 3° alkyl halides requires a good ionizing solvent: alcohol or water. no strong nucleophile or base Rearrangements can occur. ...
Isomerism Guide
... Synthesis of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid) LACTIC ACID can be formed from ethanal in a two stage process. 1. Nucleophilic addition of hydrogen cyanide to ethanal 2 Hydrolysis of the nitrile group ...
... Synthesis of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid) LACTIC ACID can be formed from ethanal in a two stage process. 1. Nucleophilic addition of hydrogen cyanide to ethanal 2 Hydrolysis of the nitrile group ...
C 3 H 8 (g) - Ms Critchley`s Lab
... • Using a calorimeter for a combustion reaction or or other reaction can often give the ΔHr directly (think about the spirit burners and copper sulphate experiments you have done). • Bond enthalpies can also be used to estimate ΔHr ...
... • Using a calorimeter for a combustion reaction or or other reaction can often give the ΔHr directly (think about the spirit burners and copper sulphate experiments you have done). • Bond enthalpies can also be used to estimate ΔHr ...
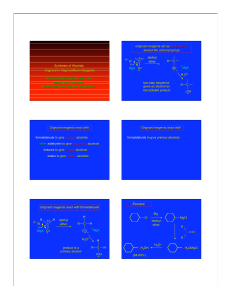
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.