IB:Enthalpy Review Questions
... a. Calculate the value of ∆H0 for the above reaction and state what information the sign of ∆H0 provides about this reaction. b. Calculate ∆S0 for the reaction and state the meaning of the sign of ∆S0 obtained. c. Identify a thermodynamic function that can be used to predict reaction spontaneity, at ...
... a. Calculate the value of ∆H0 for the above reaction and state what information the sign of ∆H0 provides about this reaction. b. Calculate ∆S0 for the reaction and state the meaning of the sign of ∆S0 obtained. c. Identify a thermodynamic function that can be used to predict reaction spontaneity, at ...
CH 2
... 3. The positions of substituent groups are specified by numbering the longest chain of carbon atoms sequentially, starting at the end closest to the branching. H3C1 ...
... 3. The positions of substituent groups are specified by numbering the longest chain of carbon atoms sequentially, starting at the end closest to the branching. H3C1 ...
Packet #7- Chemical Reactions
... represent substances in symbol equations. Molecular formulas show the number of each type of atom in a molecule, while displayed formulas show the atoms and bonds in a molecule. Reactions and compounds New substances are formed by chemical reactions. When elements react together to form compounds th ...
... represent substances in symbol equations. Molecular formulas show the number of each type of atom in a molecule, while displayed formulas show the atoms and bonds in a molecule. Reactions and compounds New substances are formed by chemical reactions. When elements react together to form compounds th ...
Cis/Trans
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1qGPWdm2M lI • The most common type of reaction for alkenes is addition: • general pattern – alkene + AB ---> see board ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1qGPWdm2M lI • The most common type of reaction for alkenes is addition: • general pattern – alkene + AB ---> see board ...
CHM 222: Organic Chemistry III
... 2. Do you expect hyperconjugation to be important in stabilization of alkyloxonium ions? (e.g. ROH 2+ or R2OH+) Explain your answer with respect to the orbitals involved. No. There are no empty orbitals on the oxygen atom. The oxygen is formally positive but has a complete octet of electrons surroun ...
... 2. Do you expect hyperconjugation to be important in stabilization of alkyloxonium ions? (e.g. ROH 2+ or R2OH+) Explain your answer with respect to the orbitals involved. No. There are no empty orbitals on the oxygen atom. The oxygen is formally positive but has a complete octet of electrons surroun ...
Reactions of Alkenes
... This reaction proceeds via a concerted electrophilic addition generating an osmate ester, which is hydrolyzed to a syn diol by hydrogen peroxide, which also reoxidizes the osmium catalyst. The two C-O bonds are formed at the same time with the cyclic ester, and the oxygen atoms are added at the same ...
... This reaction proceeds via a concerted electrophilic addition generating an osmate ester, which is hydrolyzed to a syn diol by hydrogen peroxide, which also reoxidizes the osmium catalyst. The two C-O bonds are formed at the same time with the cyclic ester, and the oxygen atoms are added at the same ...
Hydrocarbons - msottchemistry
... Reactivity of Hydrocarbons • Alkanes are generally less reactive than alkenes or alkynes • Aromatic compounds are more reactive than alkanes, but less reactive than alkenes and alkynes. ...
... Reactivity of Hydrocarbons • Alkanes are generally less reactive than alkenes or alkynes • Aromatic compounds are more reactive than alkanes, but less reactive than alkenes and alkynes. ...
Slide 1
... Most amino acids found on Earth appear in only one of two possible mirror-image forms, called enantiomers or optical isomers. Non-superimposable ...
... Most amino acids found on Earth appear in only one of two possible mirror-image forms, called enantiomers or optical isomers. Non-superimposable ...
CHEMISTRY
... The name noble gas indicates their high stability. Reactions involving noble gas are really very unusual. Each electron has a specific energy and occupies a particular shell around the nucleus. External shells containing 8 electrons are particularly stable, like noble gases. Compounds are formed by ...
... The name noble gas indicates their high stability. Reactions involving noble gas are really very unusual. Each electron has a specific energy and occupies a particular shell around the nucleus. External shells containing 8 electrons are particularly stable, like noble gases. Compounds are formed by ...
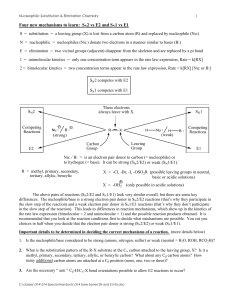
Four new mechanisms to learn: SN2 vs E2 and SN1 vs E1
... SN1 and E1 reactions are multistep reactions and also compete with one another. Both of these reactions begin with the same rate-limiting step of carbocation formation from an R-X compound. Carbocations (R+) are very reactive electron deficient carbon intermediates that typically follow one of three ...
... SN1 and E1 reactions are multistep reactions and also compete with one another. Both of these reactions begin with the same rate-limiting step of carbocation formation from an R-X compound. Carbocations (R+) are very reactive electron deficient carbon intermediates that typically follow one of three ...
Chapter 6 Chemical reactions Classification And Mass Relationships
... • When two things have different sizes you can't get equal numbers by taking equal weights. For example since one grape weighs less than one cabbage, one pound of each will have different numbers. • The same is true for atoms or molecules of different substances. Equal numbers hydrogen and glucose m ...
... • When two things have different sizes you can't get equal numbers by taking equal weights. For example since one grape weighs less than one cabbage, one pound of each will have different numbers. • The same is true for atoms or molecules of different substances. Equal numbers hydrogen and glucose m ...
Name __KEY____________ Per. ______ Polarity and
... (hold onto/ let go of) their electrons. For any two elements that share a chemical bond, we can calculate the difference in electronegativity by _subtracting_ (multiplying/ subtracting/ adding) their electronegativity values that we can get from a table. In our textbook there is a table on page 177. ...
... (hold onto/ let go of) their electrons. For any two elements that share a chemical bond, we can calculate the difference in electronegativity by _subtracting_ (multiplying/ subtracting/ adding) their electronegativity values that we can get from a table. In our textbook there is a table on page 177. ...
Organometallic Chemistry
... reaction for C-C bond formation, it is often accompanied by competing side reactions such as enolization, reduction, or aldol condensation of the carbonyl substrate. • Organomagnesium compounds can act not only as nucleophiles, but also as bases • It can convert ketones with enolizable hydrogens to ...
... reaction for C-C bond formation, it is often accompanied by competing side reactions such as enolization, reduction, or aldol condensation of the carbonyl substrate. • Organomagnesium compounds can act not only as nucleophiles, but also as bases • It can convert ketones with enolizable hydrogens to ...
Methylcyclohexane + bromine and heat = 1-bromo-1
... **It was announced during the exam that you can start with methylcyclohexene. If you started all the way from methylcyclohexane, you got an additional 2 points. Hopefully, by now, everyone knows that a simple two-step process can convert an alkane to an alkene (E1 or E2). Methylcyclohexane + bromine ...
... **It was announced during the exam that you can start with methylcyclohexene. If you started all the way from methylcyclohexane, you got an additional 2 points. Hopefully, by now, everyone knows that a simple two-step process can convert an alkane to an alkene (E1 or E2). Methylcyclohexane + bromine ...
Asymmetric Glycine Enolate Aldol Reactions
... H, NH), 3.85-4.60 (m,3 H, NCHCH,), 2.88 (m,2 H, PhCH,); I3C reaction mixture was stirred at 0 OC for an additional 15 min and then N M R (22.5 MHz, CDCI,) d 159.9, 136.0, 129.1, 128.8, 127.0, 69.4, 53.6, quenched by the addition of 0.56 mL of water, 0.56 mL of aqueous 15% 41; [aID+4.9' (EtOH, c 1.10 ...
... H, NH), 3.85-4.60 (m,3 H, NCHCH,), 2.88 (m,2 H, PhCH,); I3C reaction mixture was stirred at 0 OC for an additional 15 min and then N M R (22.5 MHz, CDCI,) d 159.9, 136.0, 129.1, 128.8, 127.0, 69.4, 53.6, quenched by the addition of 0.56 mL of water, 0.56 mL of aqueous 15% 41; [aID+4.9' (EtOH, c 1.10 ...
Grignard-syn-12-ques
... Diethyl ether is most often used solvent. Tetrahydrofuran is also used. ...
... Diethyl ether is most often used solvent. Tetrahydrofuran is also used. ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.