Chapter 20 - Simpson County Schools
... a benzene ring. Naming: Carbon atoms are numbered starting at one of the substituted groups. Numbering may be either clockwise or counterclockwise but must be done in the direction that gives the lowest possible numbers to the substituent groups. When the compound is named as a derivative of one o ...
... a benzene ring. Naming: Carbon atoms are numbered starting at one of the substituted groups. Numbering may be either clockwise or counterclockwise but must be done in the direction that gives the lowest possible numbers to the substituent groups. When the compound is named as a derivative of one o ...
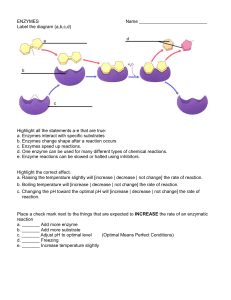
ENZYMES
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
Kinetics of the Selective Reaction of Diazonium Salts with Single
... Current methods of synthesis for carbon nanotubes (CNTs) usually produce heterogeneous mixtures of different nanotube diameters, thus a mixture of electronic properties. Consequently, many techniques have been developed in attempts to separate nanotubes according to their electronic type, w ith vary ...
... Current methods of synthesis for carbon nanotubes (CNTs) usually produce heterogeneous mixtures of different nanotube diameters, thus a mixture of electronic properties. Consequently, many techniques have been developed in attempts to separate nanotubes according to their electronic type, w ith vary ...
Lecture 1
... considering the combination of the softer element with organic group and harder element with fluoride or chloride. *An insoluble product or reactant may change the outcome, e.g.; ...
... considering the combination of the softer element with organic group and harder element with fluoride or chloride. *An insoluble product or reactant may change the outcome, e.g.; ...
Organic - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... dichloromethane we obtained a 76% yield of an approximately 2:l mixture by lH NMR integration). Under these conditions, we obtained no more than traces of the diastereomeric products 5b and 6b, which would arise from the corresponding transition states derived from 4b. The mixture of 5a and 6a could ...
... dichloromethane we obtained a 76% yield of an approximately 2:l mixture by lH NMR integration). Under these conditions, we obtained no more than traces of the diastereomeric products 5b and 6b, which would arise from the corresponding transition states derived from 4b. The mixture of 5a and 6a could ...
The Baylis–Hillman reaction is an organic reaction of an aldehyde
... The MBH reaction of phenyl vinyl ketone with benzaldehyde and DABCO in DMF is not limited to the monoadduct because the MBH adduct reacts with a second molecule of phenyl vinyl ketone in a nucleophilic conjugate addition. ...
... The MBH reaction of phenyl vinyl ketone with benzaldehyde and DABCO in DMF is not limited to the monoadduct because the MBH adduct reacts with a second molecule of phenyl vinyl ketone in a nucleophilic conjugate addition. ...
H1- Functional Groups Theory Sheet Alcohol An alcohol group
... A functional group is a specific group of atoms or bonds that form part of an organic molecule. A certain type of functional group will undergo similar chemical reactions even when attached to different sized molecules; however neighbouring groups may affect this reactivity. A molecule can have mult ...
... A functional group is a specific group of atoms or bonds that form part of an organic molecule. A certain type of functional group will undergo similar chemical reactions even when attached to different sized molecules; however neighbouring groups may affect this reactivity. A molecule can have mult ...
Samantha Landolfa Amy Ryan Section 10 Experiment 9 – Alkenes
... In this experiment, 2-methyl-2-butanol is dehydrated to produce a mixture of two isomers that can be analyzed by gas chromatography. The dehydration of the alcohol is accomplished via an E1 elimination reaction. The rates of reactivity are tertiary > secondary > primary. An E1 reaction is favored wh ...
... In this experiment, 2-methyl-2-butanol is dehydrated to produce a mixture of two isomers that can be analyzed by gas chromatography. The dehydration of the alcohol is accomplished via an E1 elimination reaction. The rates of reactivity are tertiary > secondary > primary. An E1 reaction is favored wh ...
136KB - NZQA
... Two products are formed in this reaction because propene is an asymmetric alkene. When another asymmetric molecule such as hydrogen chloride, HCl, is added to it, there are two possible products. One product is produced in greater quantities (the major product) than the other (minor product). The ru ...
... Two products are formed in this reaction because propene is an asymmetric alkene. When another asymmetric molecule such as hydrogen chloride, HCl, is added to it, there are two possible products. One product is produced in greater quantities (the major product) than the other (minor product). The ru ...
GRIGNARD REAGENTS
... by sp2 (C) – sp3 (C) overlap. A third σ bond connects the C carbonyl carbon to the oxygen atom by by sp2 (C) –2p (O) overlap. The π bond is formed by 2p(C) – 2p(O) overlap. Carbonyl groups are flat. The π electrons are above and below the trigonal plane formed by the sp2 orbitals of the carbonyl car ...
... by sp2 (C) – sp3 (C) overlap. A third σ bond connects the C carbonyl carbon to the oxygen atom by by sp2 (C) –2p (O) overlap. The π bond is formed by 2p(C) – 2p(O) overlap. Carbonyl groups are flat. The π electrons are above and below the trigonal plane formed by the sp2 orbitals of the carbonyl car ...
Alkene Addition Reactions
... The rate-‐determining step of the reaction is the formation of a carbocation, which represents the most stable on the immediate double bond. The order of carbocation stability is 3o > 2o > 1o. ...
... The rate-‐determining step of the reaction is the formation of a carbocation, which represents the most stable on the immediate double bond. The order of carbocation stability is 3o > 2o > 1o. ...
III. ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Reactions
... substitution reactions occur one step at a time; therefore, two substitutions cannot (and do not) take place at the same time (ex. bromine is diatomic, meaning two atoms of bromine are available for a substitution; however, each bromine gets added to a separate hydrocarbon, yielding a HBr molecule i ...
... substitution reactions occur one step at a time; therefore, two substitutions cannot (and do not) take place at the same time (ex. bromine is diatomic, meaning two atoms of bromine are available for a substitution; however, each bromine gets added to a separate hydrocarbon, yielding a HBr molecule i ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... what type and how many reactants are present. We can use a generalized equation to represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis ...
... what type and how many reactants are present. We can use a generalized equation to represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis ...
File
... Identify one isomer that will react with aqueous sodium hydroxide almost exclusively by an SN2 mechanism. Draw the mechanism for this reaction using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs. Include the structural formulas of the transition state and the organic product. ...
... Identify one isomer that will react with aqueous sodium hydroxide almost exclusively by an SN2 mechanism. Draw the mechanism for this reaction using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs. Include the structural formulas of the transition state and the organic product. ...
File - TGHS Level 3 Chemistry
... aldehydes except the double bond is not at the end of a carbon chain Their names have ‘–one’ as a suffix e.g. propanone, butanone… The smaller ketones are the same as aldehydes. They are liquids because of their polar bonding The smaller molecules (below hexanone) are soluble in water Ketones are go ...
... aldehydes except the double bond is not at the end of a carbon chain Their names have ‘–one’ as a suffix e.g. propanone, butanone… The smaller ketones are the same as aldehydes. They are liquids because of their polar bonding The smaller molecules (below hexanone) are soluble in water Ketones are go ...
chemistry 1000 - U of L Class Index
... Of course, there will be a variety of different ways to achieve each desired connection – hence the use of the generic X in place of heteroatoms in many synthons. Functional group interchanges (FGI) allow for alternate approaches using the same bond-set. These alternate approaches are not always as ...
... Of course, there will be a variety of different ways to achieve each desired connection – hence the use of the generic X in place of heteroatoms in many synthons. Functional group interchanges (FGI) allow for alternate approaches using the same bond-set. These alternate approaches are not always as ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... Typical for alkenes and alkynes Markovnikov´s rule: the more positive part of the agent is attached to the carbon atom (of the double bond) with the greatest number of hydrogens: ...
... Typical for alkenes and alkynes Markovnikov´s rule: the more positive part of the agent is attached to the carbon atom (of the double bond) with the greatest number of hydrogens: ...
Chem 30A Final Exam
... 1. Draw valid Lewis structures for the simplest compounds of the second row elements (except for Li) with flourine including lone pair electrons. Indicate the valence (i.e. # of bonds), the central atom geometry, and the approximate bond angles in each case. Also indicate when there is an exception ...
... 1. Draw valid Lewis structures for the simplest compounds of the second row elements (except for Li) with flourine including lone pair electrons. Indicate the valence (i.e. # of bonds), the central atom geometry, and the approximate bond angles in each case. Also indicate when there is an exception ...
Chemistry 160 Th 13 Mar 2008 In-Class Worksheet A. Each of the
... In order to create a double bond, the carbons overlap their p orbitals, which are perpendicular to the sigma bond formed between the carbons. The reason that no rotation can occur between the carbons is that rotation would break the contact between the p orbitals, thus destroying the pi bond that ac ...
... In order to create a double bond, the carbons overlap their p orbitals, which are perpendicular to the sigma bond formed between the carbons. The reason that no rotation can occur between the carbons is that rotation would break the contact between the p orbitals, thus destroying the pi bond that ac ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.