Arenes test - A-Level Chemistry
... Describe how benzene could be converted into nitrobenzene. State the reagents and conditions, give a balanced equation for each stage and show the structure of the product. ...
... Describe how benzene could be converted into nitrobenzene. State the reagents and conditions, give a balanced equation for each stage and show the structure of the product. ...
Week 6 Solutions - Brown University Wiki
... is carbon number 4 as it already has three bonds to carbon. If the alcohol oxygen made a bond with carbon 4, it would form the ring system in the product. But how do we make a bond with carbon 4? So far, we have seem bonds formed between electrophiles and nucleophiles. Since oxygen has lone pairs, i ...
... is carbon number 4 as it already has three bonds to carbon. If the alcohol oxygen made a bond with carbon 4, it would form the ring system in the product. But how do we make a bond with carbon 4? So far, we have seem bonds formed between electrophiles and nucleophiles. Since oxygen has lone pairs, i ...
Synthesis of Ligands for the Functionalization of Magnetic
... The initial tests of the Mukaiyama-Aldol reaction provide valuable insight into the use of reusable catalysts. All three reactions are analyzed by 1H NMR. The NMR of the reaction with no ligand shows no product being made. This supports the necessity of the ligand in catalyzing the reaction. The NMR ...
... The initial tests of the Mukaiyama-Aldol reaction provide valuable insight into the use of reusable catalysts. All three reactions are analyzed by 1H NMR. The NMR of the reaction with no ligand shows no product being made. This supports the necessity of the ligand in catalyzing the reaction. The NMR ...
chapter 8 lecture
... • The reason that stronger bases are needed for this dehydrohalogenation is that the transition state for the second elimination reaction includes partial cleavage of the C—H bond. In this case however, the carbon atom is sp2 hybridized and sp2 hybridized C—H bonds are stronger than sp3 hybridized ...
... • The reason that stronger bases are needed for this dehydrohalogenation is that the transition state for the second elimination reaction includes partial cleavage of the C—H bond. In this case however, the carbon atom is sp2 hybridized and sp2 hybridized C—H bonds are stronger than sp3 hybridized ...
A Biocatalytic Henry Reaction-The Hydroxynitrile Lyase from Hevea
... have to await results from proper kinetics experiments, the reduced yield obtained for the addition of [1,1-D2]nitroethane to benzaldehyde already indicates the existence of a kinetic isotope effect and suggests the deprotonation of the nitroalkane to be the rate-limiting step. In contrast, in the H ...
... have to await results from proper kinetics experiments, the reduced yield obtained for the addition of [1,1-D2]nitroethane to benzaldehyde already indicates the existence of a kinetic isotope effect and suggests the deprotonation of the nitroalkane to be the rate-limiting step. In contrast, in the H ...
PowerPoint 簡報 - Solon City Schools
... The Functional Groups The properties of different biological molecules depend on certain characteristic groupings of atoms called functional groups. The names of the six most important functional groups are: – Hydroxyl – Carbonyl –Aldehydes – Ketones – Carboxyl – Amino – Sulfhydryl – Phosphate ...
... The Functional Groups The properties of different biological molecules depend on certain characteristic groupings of atoms called functional groups. The names of the six most important functional groups are: – Hydroxyl – Carbonyl –Aldehydes – Ketones – Carboxyl – Amino – Sulfhydryl – Phosphate ...
- University at Albany
... Factors influencing what products are formed Substrate/steric effects Strength of nucleophile vs. basicity of ...
... Factors influencing what products are formed Substrate/steric effects Strength of nucleophile vs. basicity of ...
슬라이드 1
... Subsequent studies have found improved ligands, including tri-2-furylphsophine and triphenylarsine. Aryl-aryl coupling rates are increased by the presence of ...
... Subsequent studies have found improved ligands, including tri-2-furylphsophine and triphenylarsine. Aryl-aryl coupling rates are increased by the presence of ...
TM - Intro to Organi..
... – Octane (C8H18) – a fuel used for automobile combustion – Dodecadecane (C20H42) – solid wax used for making candles and as a lubricant All of these are straight-chained hydrocarbons (CnH2n+2). ...
... – Octane (C8H18) – a fuel used for automobile combustion – Dodecadecane (C20H42) – solid wax used for making candles and as a lubricant All of these are straight-chained hydrocarbons (CnH2n+2). ...
Organic Chemistry Review
... Hydrocarbon: an organic compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen. Isomer: compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. Unsaturated compound: an organic compound with one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. Saturated compound: an organic compound ...
... Hydrocarbon: an organic compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen. Isomer: compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. Unsaturated compound: an organic compound with one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. Saturated compound: an organic compound ...
Section 07 - Section Practice Exam II Solutions
... donating methyl group will help to stabilize the carbocation, explaining why the reaction is faster for X=Me versus X=H. In the case of X=OMe, the inductive effect (oxygen is electronegative and electron withdrawing) appears to predominate over the resonance effect. This is easily explained by the s ...
... donating methyl group will help to stabilize the carbocation, explaining why the reaction is faster for X=Me versus X=H. In the case of X=OMe, the inductive effect (oxygen is electronegative and electron withdrawing) appears to predominate over the resonance effect. This is easily explained by the s ...
- Fairview High School
... Key point: Rotation is impossible around a double bond. (Would require breaking pi bond) ...
... Key point: Rotation is impossible around a double bond. (Would require breaking pi bond) ...
Mechanism of Aldol Condensation
... Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis, providing a good way to form carbon– carbon bonds. For example, the Robinson annulation reaction sequence features an aldol condensation; the Wieland-Miescher ketone product is an important starting material for many organic syntheses. Aldol co ...
... Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis, providing a good way to form carbon– carbon bonds. For example, the Robinson annulation reaction sequence features an aldol condensation; the Wieland-Miescher ketone product is an important starting material for many organic syntheses. Aldol co ...
Exam 2 review sheet
... reactions of carboxylic acids: to acyl chlorides, to acid anhydrides, to esters/lactones (mechanism for Fischer esterification); to amides: direct addition of carboxylic acid plus amine is usually unproductive; relative reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives: acid chloride > anhydride > ester > a ...
... reactions of carboxylic acids: to acyl chlorides, to acid anhydrides, to esters/lactones (mechanism for Fischer esterification); to amides: direct addition of carboxylic acid plus amine is usually unproductive; relative reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives: acid chloride > anhydride > ester > a ...
Chapter 7
... • The slow step, RDS, is the second step, the formation of the carbocation • This explains the order of reactivity with the tertiary alcohol reacting easiest, due to the tertiary carbocation being the most stable. ...
... • The slow step, RDS, is the second step, the formation of the carbocation • This explains the order of reactivity with the tertiary alcohol reacting easiest, due to the tertiary carbocation being the most stable. ...
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
... We’ve already seen one reaction which organic chemists would consider to be a reduction reaction – the nucleophilic addition of hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced ...
... We’ve already seen one reaction which organic chemists would consider to be a reduction reaction – the nucleophilic addition of hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced ...
Asymmetric induction

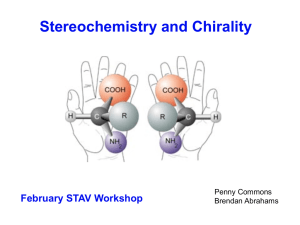
Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.