無投影片標題
... Naming with Multiple Halides • If more than one of the same kind of halogen is present, use prefix di, tri, tetra • If there are several different halogens, number them and list them in alphabetical order ...
... Naming with Multiple Halides • If more than one of the same kind of halogen is present, use prefix di, tri, tetra • If there are several different halogens, number them and list them in alphabetical order ...
reactions of organic compounds
... Asymmetrical alkynes follow M.’s rule. when an asymmetrical molecule is added to the triple bond. Note: the halogen is bonded to the carbon around the triple bond that is bonded to the most carbons. The hydrogen is bonded to the carbon around the triple bond that has the most hydrogens. ...
... Asymmetrical alkynes follow M.’s rule. when an asymmetrical molecule is added to the triple bond. Note: the halogen is bonded to the carbon around the triple bond that is bonded to the most carbons. The hydrogen is bonded to the carbon around the triple bond that has the most hydrogens. ...
ALDOL CONDENSATION
... When a mixture of formaldehyde and a non enolizable aldehyde is treated with a strong base, the later is preferentially reduced to alcohol while formaldehyde is oxidized to formic acid. This variant is known as crossed Cannizzaro reaction. E.g. Benzyl alcohol and formic acid are obtained when a ...
... When a mixture of formaldehyde and a non enolizable aldehyde is treated with a strong base, the later is preferentially reduced to alcohol while formaldehyde is oxidized to formic acid. This variant is known as crossed Cannizzaro reaction. E.g. Benzyl alcohol and formic acid are obtained when a ...
Document
... • HYDROLYSIS Reaction of Alkyl Hydrogen Sulfate • Simply Heat the Sulfate in Water • Net Reaction is Markovnikov Addition of H2O to Alkene • Used in One Industrial Ethanol Making Process ...
... • HYDROLYSIS Reaction of Alkyl Hydrogen Sulfate • Simply Heat the Sulfate in Water • Net Reaction is Markovnikov Addition of H2O to Alkene • Used in One Industrial Ethanol Making Process ...
Carbon - Napa Valley College
... Have the same arrangement of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms are different. An example is cis vs trans arrangements across a double bond (cis = large groups are on same side, trans = large groups on opposite side ...
... Have the same arrangement of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms are different. An example is cis vs trans arrangements across a double bond (cis = large groups are on same side, trans = large groups on opposite side ...
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
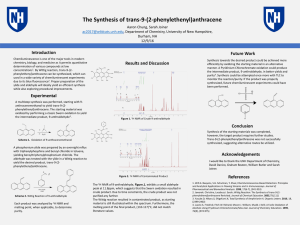
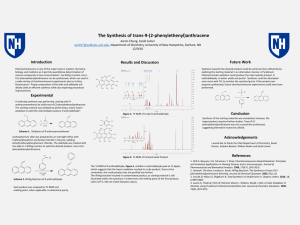
... chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper pre ...
... chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper pre ...
The Synthesis of trans-9-(2
... various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans9-(2-phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper preparation of the ylide and aldehyde will ideally yield an efficient synthesis ...
... various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans9-(2-phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper preparation of the ylide and aldehyde will ideally yield an efficient synthesis ...
UNIT 2 - Glow Blogs
... molecule that confers pharmacological activity (alters biological processes in the body). The structure of a (lead) compound can be altered to give a large number of derivatives. As long as the pharmacophore is retained, there is a good chance these derivatives will be biologically active. ...
... molecule that confers pharmacological activity (alters biological processes in the body). The structure of a (lead) compound can be altered to give a large number of derivatives. As long as the pharmacophore is retained, there is a good chance these derivatives will be biologically active. ...
Organic Chemistry
... • Cyclohexane is one member of a much larger group of saturated hydrocarbons with ring structures called cycloalkanes. • This group includes cyclopropane (C3H6) all the way up to an infinite number of carbons in theory. ...
... • Cyclohexane is one member of a much larger group of saturated hydrocarbons with ring structures called cycloalkanes. • This group includes cyclopropane (C3H6) all the way up to an infinite number of carbons in theory. ...
Organic Chemistry
... selectivity with the result that enzyme-catalyzed reactions invariably give only one of all possible stereoisomers. ...
... selectivity with the result that enzyme-catalyzed reactions invariably give only one of all possible stereoisomers. ...
Chemistry 122 Chapter 9 Ketones and Aldehydes
... • A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated. • A weak nucleophile will attack a carbonyl if it has been protonated, thus increasing its reactivity. • Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones. ...
... • A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated. • A weak nucleophile will attack a carbonyl if it has been protonated, thus increasing its reactivity. • Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones. ...
Drawing Organic Structures Functional Groups Constitutional Isomers
... • Multiple products can be formed if there is more than one ...
... • Multiple products can be formed if there is more than one ...
Exam 1 Solution Key
... The resonance structures illustrate the fact that there is extensive electron delocalization within the conjugate base, which makes the conjugate base exceptionally stable and a “weak base”; therefore, the undissociated acid would have considerable tendency to dissociate, making it a strong acid. ...
... The resonance structures illustrate the fact that there is extensive electron delocalization within the conjugate base, which makes the conjugate base exceptionally stable and a “weak base”; therefore, the undissociated acid would have considerable tendency to dissociate, making it a strong acid. ...
Orbitals
... • If neutral, the nucleophile usually carries a hydrogen atom that can be subsequently eliminated ...
... • If neutral, the nucleophile usually carries a hydrogen atom that can be subsequently eliminated ...
Chapter 2 Study Guides
... ______ 7. atoms held together by covalent bonds ______ 8. composed of different types of atoms ______ 9. composed of one type of atom ...
... ______ 7. atoms held together by covalent bonds ______ 8. composed of different types of atoms ______ 9. composed of one type of atom ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE HYDROCARBONS 1. Name the least
... 23. Explain with equations how to convert ketone into hydrocarbon ( Or How do you convert acetone to propane?) 24. How does benzaldehyde reacts with strong KOH (Or explain with equations how to convert aldehyde containing no alpha-hydrogen to a mixture of sodium salt of the carboxylic acid and alcoh ...
... 23. Explain with equations how to convert ketone into hydrocarbon ( Or How do you convert acetone to propane?) 24. How does benzaldehyde reacts with strong KOH (Or explain with equations how to convert aldehyde containing no alpha-hydrogen to a mixture of sodium salt of the carboxylic acid and alcoh ...
Chapter 2 Key Terms: element, atom, proton, neutron, electron
... hydrogenated fats, trans-fats, phospholipid, amino acid, polypeptide, peptide bond, primary, secondary, alpha helix, beta pleated sheet, tertiary, quaternary structure, R-groups, hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bridges, denaturation, deoxyribonucleic acid, ribonucleic acid Essays: 1. Describe hy ...
... hydrogenated fats, trans-fats, phospholipid, amino acid, polypeptide, peptide bond, primary, secondary, alpha helix, beta pleated sheet, tertiary, quaternary structure, R-groups, hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bridges, denaturation, deoxyribonucleic acid, ribonucleic acid Essays: 1. Describe hy ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.