Calculating Percent Yield
... (Friedel-Crafts Alkylation) that incorporates the effect of substitution of the aromatic ring into the experiment. Students will prepare the product the first week of the experiment. During the second week, students will analyze the products by TLC analysis and melting point determination. In additi ...
... (Friedel-Crafts Alkylation) that incorporates the effect of substitution of the aromatic ring into the experiment. Students will prepare the product the first week of the experiment. During the second week, students will analyze the products by TLC analysis and melting point determination. In additi ...
full size
... group (methanal, the simplest, has two). ¾The group is somewhat more polar than ethers, but like ethers it cannot donate a hydrogen bond to itself. Thus aldehydes are less volatile (higher boiling) than alkanes or ethers but are more volatile than alcohols or carboxylic acids. They are slightly less ...
... group (methanal, the simplest, has two). ¾The group is somewhat more polar than ethers, but like ethers it cannot donate a hydrogen bond to itself. Thus aldehydes are less volatile (higher boiling) than alkanes or ethers but are more volatile than alcohols or carboxylic acids. They are slightly less ...
Lecture 15
... 1st Half Reaction: NAD+ + H+ + 2e- --> NADH E°’ = -0.320V 2nd Half Reaction (Note: Its reversed!): FADH2 --> FAD + 2H+ + 2eE°’ = +0.219V E°’= –0.320V + +0.219V ...
... 1st Half Reaction: NAD+ + H+ + 2e- --> NADH E°’ = -0.320V 2nd Half Reaction (Note: Its reversed!): FADH2 --> FAD + 2H+ + 2eE°’ = +0.219V E°’= –0.320V + +0.219V ...
stereochemistry of internucleotide bond formation by the h
... stereoselectivity during condensing agents-promoted formation of an internucleotidic bond1,2. The activation of ribonucleoside H-phosphonates of type 1 with pivaloyl chloride yields two diastereomers (A and B, Fig. 1) of mixed anhydrides 2. These isomers have to exist in a rapid equilibrium to regen ...
... stereoselectivity during condensing agents-promoted formation of an internucleotidic bond1,2. The activation of ribonucleoside H-phosphonates of type 1 with pivaloyl chloride yields two diastereomers (A and B, Fig. 1) of mixed anhydrides 2. These isomers have to exist in a rapid equilibrium to regen ...
Identification of Aldehydes and Ketones
... with ammonium hydroxide in the presence of NaOH solution. Aldehydes show + ve result with this reagent because the reaction between them involves the oxidation of the aldehyde to the corresponding carboxylic acid & the reduction of the silver ions from this reagent to silver element in the form of ...
... with ammonium hydroxide in the presence of NaOH solution. Aldehydes show + ve result with this reagent because the reaction between them involves the oxidation of the aldehyde to the corresponding carboxylic acid & the reduction of the silver ions from this reagent to silver element in the form of ...
Whited Lit Discussion - M-L Multiple Bonds and FLPs
... the importance of orbital cooperation in small-molecule activation. What is the DewarChatt-Duncanson (DCD) model? Draw a simplified diagram for the molecular-orbital interactions in the DCD model. Why is it important to have both filled and empty d orbitals cooperating in the DCD model? 2) Frustrate ...
... the importance of orbital cooperation in small-molecule activation. What is the DewarChatt-Duncanson (DCD) model? Draw a simplified diagram for the molecular-orbital interactions in the DCD model. Why is it important to have both filled and empty d orbitals cooperating in the DCD model? 2) Frustrate ...
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015
... Chiral starting material gives racemic mixture of enantiomeric products ...
... Chiral starting material gives racemic mixture of enantiomeric products ...
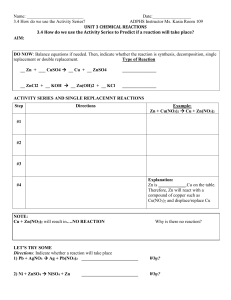
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... Zn is ____________ Cu on the table. Therefore, Zn will react with a ...
... Zn is ____________ Cu on the table. Therefore, Zn will react with a ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 3. Which of the following statements about catalysts is false? a. A catalyst will speed up the rate of a reaction. b. Catalysts are used in very many commercially important chemical reactions. c. Catalytic converters are examples of heterogeneous catalysts. d. A catalyst can cause a nonspontaneous r ...
... 3. Which of the following statements about catalysts is false? a. A catalyst will speed up the rate of a reaction. b. Catalysts are used in very many commercially important chemical reactions. c. Catalytic converters are examples of heterogeneous catalysts. d. A catalyst can cause a nonspontaneous r ...
Chapter 26 Functional Groups and Organic Reactions
... aliphatic alcohols used in laboratories, clinics, and industry –Isopropyl alcohol (2-propanol) is rubbing alcohol; used as antiseptic, and a base for perfume, creams, lotions, and other cosmetics Ethylene glycol (1,2-ethanediol) commonly sold as antifreeze ...
... aliphatic alcohols used in laboratories, clinics, and industry –Isopropyl alcohol (2-propanol) is rubbing alcohol; used as antiseptic, and a base for perfume, creams, lotions, and other cosmetics Ethylene glycol (1,2-ethanediol) commonly sold as antifreeze ...
Chemistry B11 Chapters 16-18 Amines, aldehydes, ketones and
... charge and oxygen obtains the partial negative charge). 3. There is only the dipole-dipole interaction between the molecules and there is no possibility for hydrogen bonding. 4. They have lower boiling points than amines and alcohols. 5. They are soluble in water (form hydrogen bonds with water - th ...
... charge and oxygen obtains the partial negative charge). 3. There is only the dipole-dipole interaction between the molecules and there is no possibility for hydrogen bonding. 4. They have lower boiling points than amines and alcohols. 5. They are soluble in water (form hydrogen bonds with water - th ...
Chapter 22/23-Organic Chemistry
... 5. Draw and name all possible products for this reaction (there are two): (It will be helpful to first draw the full structural formula of the alkane.) CH3CH2CH3 + Br2 ...
... 5. Draw and name all possible products for this reaction (there are two): (It will be helpful to first draw the full structural formula of the alkane.) CH3CH2CH3 + Br2 ...
Chapter 12 –Part 2 Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds with
... t Grignard reagents cannot be made from halides which contain ...
... t Grignard reagents cannot be made from halides which contain ...
Lecture 13a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... used in Chem 30CL because of its high reactivity!) • Solvent: DMSO (cannot be used in Chem 30CL), PTC conditions, solid state reaction • An one-pot reaction is not advisable here because the reactants, the intermediate and the product are very difficult to separate from each other (anhydrous ZnI2 is ...
... used in Chem 30CL because of its high reactivity!) • Solvent: DMSO (cannot be used in Chem 30CL), PTC conditions, solid state reaction • An one-pot reaction is not advisable here because the reactants, the intermediate and the product are very difficult to separate from each other (anhydrous ZnI2 is ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. ...
Chapter 14 Chemical Reactions
... 14.1 Balancing chemical equations A balanced chemical equation has the same number of each type of atom on the product side and the reactant side. To balance the equation, we add another water molecule to the product side and add another oxygen molecule to the reactant side. We can practice b ...
... 14.1 Balancing chemical equations A balanced chemical equation has the same number of each type of atom on the product side and the reactant side. To balance the equation, we add another water molecule to the product side and add another oxygen molecule to the reactant side. We can practice b ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.