Document
... present investigation and data from the literature relative to the composition of comb waxes reveals a general similarity between the latter and propolis waxes, although notable differences are apparent as to the relative proportions of some constituents. This observation suggests that propolis waxe ...
... present investigation and data from the literature relative to the composition of comb waxes reveals a general similarity between the latter and propolis waxes, although notable differences are apparent as to the relative proportions of some constituents. This observation suggests that propolis waxe ...
File
... 14 Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question. A significant contribution to atmospheric carbon dioxide levels comes from the thermal decomposition of limestone, in the manufacture of cement and of lime for agricultural purposes. Cement works roast 1000 million tonnes of limestone per year ...
... 14 Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question. A significant contribution to atmospheric carbon dioxide levels comes from the thermal decomposition of limestone, in the manufacture of cement and of lime for agricultural purposes. Cement works roast 1000 million tonnes of limestone per year ...
CH3
... Much less POLAR than alcohols Slightly soluble in water More soluble than alkane Lower melting point (MP) and boiling point (BP) than water • Chemically inert • ALL are very flammable ...
... Much less POLAR than alcohols Slightly soluble in water More soluble than alkane Lower melting point (MP) and boiling point (BP) than water • Chemically inert • ALL are very flammable ...
Zn(BH4)2/Al2O3: A new synthetic method for the efficient
... reduction reactions being performed under different conditions, i.e., the reductions were performed with 1 molar amounts of Zn(BH4)2 at room temperature in the presence of 1 molar amounts of neutral Al2O3 in THF (Table II, entry 2). The utility of this reducing system was further explored with the r ...
... reduction reactions being performed under different conditions, i.e., the reductions were performed with 1 molar amounts of Zn(BH4)2 at room temperature in the presence of 1 molar amounts of neutral Al2O3 in THF (Table II, entry 2). The utility of this reducing system was further explored with the r ...
Ch. 6 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the Imperial College (UK) and at Harvard University (USA). He joined the Department of Chemistry at the University of Gu ...
... Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the Imperial College (UK) and at Harvard University (USA). He joined the Department of Chemistry at the University of Gu ...
Organic Chemistry
... alkynes, hydroxide ion is not a strong enough base to convert a terminal alkyne to an alkyne anion HC CH + OH pKa 25 W(eaker acid) ...
... alkynes, hydroxide ion is not a strong enough base to convert a terminal alkyne to an alkyne anion HC CH + OH pKa 25 W(eaker acid) ...
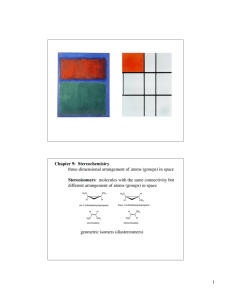
Three-dimensional Arrangement Of Atoms
... Addition of HBr to a chiral alkene: reactions of a chiral reactant with an achiral reagent gives diastereomeric products which may or may not be formed in equal amounts. The intermediate carbocation is asymmetric, therefore attack of Br- from the top or bottom faces may not be equally probable. The ...
... Addition of HBr to a chiral alkene: reactions of a chiral reactant with an achiral reagent gives diastereomeric products which may or may not be formed in equal amounts. The intermediate carbocation is asymmetric, therefore attack of Br- from the top or bottom faces may not be equally probable. The ...
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18
... Dipole-dipole interactions are the main intermolecular force holding ketones and aldehydes in the liquid phase. The dipole-dipole interaction is strong because of the high dipole moment attributable to the carbonyl group, giving ketones and aldehydes higher boiling points than hydrocarbons. However, ...
... Dipole-dipole interactions are the main intermolecular force holding ketones and aldehydes in the liquid phase. The dipole-dipole interaction is strong because of the high dipole moment attributable to the carbonyl group, giving ketones and aldehydes higher boiling points than hydrocarbons. However, ...
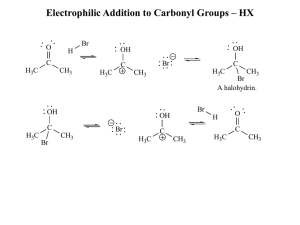
Electrophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups – HX
... Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups: Enolate and Aldol Reactions • This reaction is known as the aldol reaction. It takes an aldehyde and converts it into an alcohol (while extending the carbon chain). • If an aldol reaction is worked up under acidic conditions, an E2 reaction will follow, giv ...
... Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups: Enolate and Aldol Reactions • This reaction is known as the aldol reaction. It takes an aldehyde and converts it into an alcohol (while extending the carbon chain). • If an aldol reaction is worked up under acidic conditions, an E2 reaction will follow, giv ...
LIPIDS
... Lipids are insoluble in polar solvents (water) Lipids are soluble in the non-polar solvents (benzene and carbon tetrachloride) ...
... Lipids are insoluble in polar solvents (water) Lipids are soluble in the non-polar solvents (benzene and carbon tetrachloride) ...
23.2 Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... What do mouthwash, perfume, and hairspray have in common? • They all contain an alcohol of some type. • An alcohol is an organic compound with an —OH group. ...
... What do mouthwash, perfume, and hairspray have in common? • They all contain an alcohol of some type. • An alcohol is an organic compound with an —OH group. ...
iNTRODUCTiON TO ORGANiC COMPOUNDS
... and flavors of fruits. Oil of wintergreen and aspirin are esters. Esters can be considered to be derivatives of carboxylic acids. The functional group of esters looks similar to the carboxyl group of acids, except that the hydrogen atom on the hydroxy group is replaced with an organic group such as ...
... and flavors of fruits. Oil of wintergreen and aspirin are esters. Esters can be considered to be derivatives of carboxylic acids. The functional group of esters looks similar to the carboxyl group of acids, except that the hydrogen atom on the hydroxy group is replaced with an organic group such as ...
Hydrocarbons Note
... The characteristics of organic compounds (boiling point, odour, reactivity etc.) depend on the composition and arrangement of atoms. For example the properties of alkanes depend greatly on the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain due to the increased strength of the van der Waal attractio ...
... The characteristics of organic compounds (boiling point, odour, reactivity etc.) depend on the composition and arrangement of atoms. For example the properties of alkanes depend greatly on the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain due to the increased strength of the van der Waal attractio ...
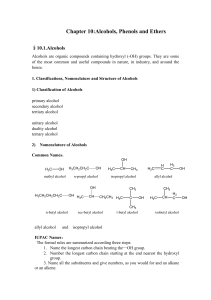
Chapter 7. Alcohols, Thiols, Phenols, Ethers
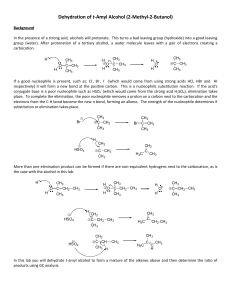
... CH3CH2CH2COOH, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH H2SO4 Secondary alcohols are easily converted to ketones. Further oxidation of the ketone occurs only under very harsh conditions. The mechanism of the oxidation involves formation of a chromate (VI) ester of the alcohol followed by loss of chromous (IV) acid. Tertiary ...
... CH3CH2CH2COOH, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH H2SO4 Secondary alcohols are easily converted to ketones. Further oxidation of the ketone occurs only under very harsh conditions. The mechanism of the oxidation involves formation of a chromate (VI) ester of the alcohol followed by loss of chromous (IV) acid. Tertiary ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.