CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES
... carbon in an alkane is bonded to four other atoms (either C or H atoms). If the compound contains a ring in the structure and is composed of only C−C and C−H single bonds, then it is called a cyclic alkane. Alkanes: general formula = CnH2n + 2; all carbons are sp3 hybridized; bond angles = 109.5Ε Cy ...
... carbon in an alkane is bonded to four other atoms (either C or H atoms). If the compound contains a ring in the structure and is composed of only C−C and C−H single bonds, then it is called a cyclic alkane. Alkanes: general formula = CnH2n + 2; all carbons are sp3 hybridized; bond angles = 109.5Ε Cy ...
questions based on high order thinking skill - Entrance
... or ions leacve the lattice site completely some lattice sites are vacant. As a result of this defect the density of the substance decreases, because some atoms leave the structure completely. Q. 9. (a) (b) ...
... or ions leacve the lattice site completely some lattice sites are vacant. As a result of this defect the density of the substance decreases, because some atoms leave the structure completely. Q. 9. (a) (b) ...
questions based on high order thinking skill
... or ions leacve the lattice site completely some lattice sites are vacant. As a result of this defect the density of the substance decreases, because some atoms leave the structure completely. Q. 9. (a) (b) ...
... or ions leacve the lattice site completely some lattice sites are vacant. As a result of this defect the density of the substance decreases, because some atoms leave the structure completely. Q. 9. (a) (b) ...
4.04 Nomenclature and Isomerism in Organic Chemistry
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS - A
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
The Results from a Canadian National Field Trial Comparing 1,8-
... The differences observed between the Israeli and UK research groups regarding 1,2-indanedione formulations and development conditions highlight the need to perform regional field trials in order to be confident that the solutions recommended in Canada are truly the best for that region of the countr ...
... The differences observed between the Israeli and UK research groups regarding 1,2-indanedione formulations and development conditions highlight the need to perform regional field trials in order to be confident that the solutions recommended in Canada are truly the best for that region of the countr ...
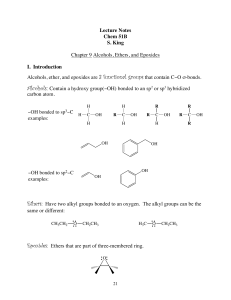
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and
... The mechanism depends on the structure of the alcohol. Under these strongly acidic conditions, both 2° & 3° alcohols undergo an E1 reaction, whereas 1° alcohols go undergo an E2 reaction. All three (1°, 2° and 3°) have the same first step, protonation of the hydroxyl group by the strong acid to make ...
... The mechanism depends on the structure of the alcohol. Under these strongly acidic conditions, both 2° & 3° alcohols undergo an E1 reaction, whereas 1° alcohols go undergo an E2 reaction. All three (1°, 2° and 3°) have the same first step, protonation of the hydroxyl group by the strong acid to make ...
Chemistry.of Organic Compounds
... in this text considerable emphasis is placed on the explanation of physical properties and on the mechanism of organic reactions. Where such material is given, an effort has been made to keep the discussion as simple as possible even at the risk of being quantitatively inaccurate, for "except ye utt ...
... in this text considerable emphasis is placed on the explanation of physical properties and on the mechanism of organic reactions. Where such material is given, an effort has been made to keep the discussion as simple as possible even at the risk of being quantitatively inaccurate, for "except ye utt ...
GCE Chemistry Teachers` Guide
... oxidation number. Candidates should be able to apply the rules for assigning oxidation numbers in order to work out the oxidation number of an element in a compound or ion from its formula. ...
... oxidation number. Candidates should be able to apply the rules for assigning oxidation numbers in order to work out the oxidation number of an element in a compound or ion from its formula. ...
Charles-Adolphe Wurtz
... important influence on the progress of chemistry, and which gave him the clue to the constitution of the vegetable alkaloids (Wurtz, 1848a,b; 1849a,b; 1851). It was also at Dumas laboratory that he com pleted the investigation that he had begun at Giessen on the constitution of the hypophosphites (W ...
... important influence on the progress of chemistry, and which gave him the clue to the constitution of the vegetable alkaloids (Wurtz, 1848a,b; 1849a,b; 1851). It was also at Dumas laboratory that he com pleted the investigation that he had begun at Giessen on the constitution of the hypophosphites (W ...
19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
... Selectivity with LiAlH4 and NaBH4 • NaBH4 is less reactive and hence more selective than LiAlH4 • LiAlH4 reacts with alkyl halides, alkyl tosylates, and nitro groups, but NaBH4 does not ...
... Selectivity with LiAlH4 and NaBH4 • NaBH4 is less reactive and hence more selective than LiAlH4 • LiAlH4 reacts with alkyl halides, alkyl tosylates, and nitro groups, but NaBH4 does not ...
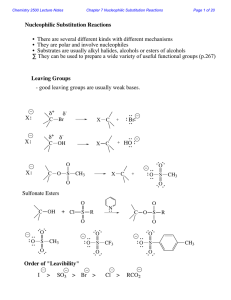
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
... Two mechanisms apply to most substitution reactions: SN1 and SN2 SN1: Substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular SN2: Substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular Which mechanism applies depends on the structure of your substrate. ...
... Two mechanisms apply to most substitution reactions: SN1 and SN2 SN1: Substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular SN2: Substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular Which mechanism applies depends on the structure of your substrate. ...
Answers and Solutions to Text Problems
... obtained by a lipid bilayer of glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids along with proteins and carbohydrates. Some molecules flow by simple diffusion through the membrane, while others flow by facilitated transport via integral proteins that extend through the membrane. ...
... obtained by a lipid bilayer of glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids along with proteins and carbohydrates. Some molecules flow by simple diffusion through the membrane, while others flow by facilitated transport via integral proteins that extend through the membrane. ...
Biochemistry - ChemGod.com
... Fructose is a ketose. It’s structure is similar to aldoses (like glucose) but it is a ketone in the linear representation rather than an aldehyde. Notice: Fructose is a structural isomer of glucose! ...
... Fructose is a ketose. It’s structure is similar to aldoses (like glucose) but it is a ketone in the linear representation rather than an aldehyde. Notice: Fructose is a structural isomer of glucose! ...
barker_rg
... The tendency of an unsymmetrical anhydride to disproportionate into the twocomponent simple anhydrides often makes isolation impossible or at least difficult. This behavior greatly complicates the purification and determination of physical constants and frequently requires immediate use after prepar ...
... The tendency of an unsymmetrical anhydride to disproportionate into the twocomponent simple anhydrides often makes isolation impossible or at least difficult. This behavior greatly complicates the purification and determination of physical constants and frequently requires immediate use after prepar ...
Chapter 4 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... (1) Thionyl Chloride: We can treat alcohols with boiling thionyl chloride (SOCl2) to convert the alcohol to an alkyl chloride. This method is considerably milder than using concentrated hydrochloric acid and is useful when the molecule contains sensitive functional groups that would react with the s ...
... (1) Thionyl Chloride: We can treat alcohols with boiling thionyl chloride (SOCl2) to convert the alcohol to an alkyl chloride. This method is considerably milder than using concentrated hydrochloric acid and is useful when the molecule contains sensitive functional groups that would react with the s ...
CH 3
... 1.3Ao. C-H bond is also shorter than ethene, which is shorter than ethane, because in ethyne it is overlap between an sp orbital and a s-orbital of H to give the s-bond. The23/05/2017 bonding electrons reside closer to the C-nucleus, and so ...
... 1.3Ao. C-H bond is also shorter than ethene, which is shorter than ethane, because in ethyne it is overlap between an sp orbital and a s-orbital of H to give the s-bond. The23/05/2017 bonding electrons reside closer to the C-nucleus, and so ...
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... 44) As the molar mass of these alcohols increases, the water solubility decreases. This occurs because the polarity of the hydroxyl group, which is the reason for the interaction with the polar water molecules, becomes less important as the size of the nonpolar hydrocarbon portion of the molecule in ...
... 44) As the molar mass of these alcohols increases, the water solubility decreases. This occurs because the polarity of the hydroxyl group, which is the reason for the interaction with the polar water molecules, becomes less important as the size of the nonpolar hydrocarbon portion of the molecule in ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.