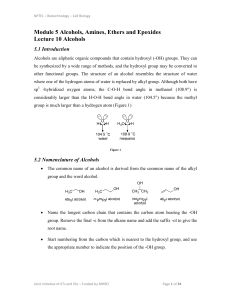
Chemistry 3.5 - CashmereChemistry
... Pour this into a pear shaped flask Carefully add 5mls of concentrated HCl Place a condenser on top of the flask and secure it in a retort stand with a water bath. Then warm the solution until a solid forms. Cool the solution to room temperature by placing the flask in a cold water bath ie a 250ml be ...
... Pour this into a pear shaped flask Carefully add 5mls of concentrated HCl Place a condenser on top of the flask and secure it in a retort stand with a water bath. Then warm the solution until a solid forms. Cool the solution to room temperature by placing the flask in a cold water bath ie a 250ml be ...
RES15_c2_wp
... 2. The structures of phenol and other phenols 3. The acidic properties of phenol, i.e. with sodium and sodium hydroxide 4. The explanation of the acidic properties of phenol – in terms of the delocalisation of oxygen’s lone pairs 5. The reaction of phenol with bromine 6. The explanation of phenol’s ...
... 2. The structures of phenol and other phenols 3. The acidic properties of phenol, i.e. with sodium and sodium hydroxide 4. The explanation of the acidic properties of phenol – in terms of the delocalisation of oxygen’s lone pairs 5. The reaction of phenol with bromine 6. The explanation of phenol’s ...
CHAPTER V Fischer-Tropsch Syncrude
... the carbon number distribution from C3 to C12, while the second α-value (α2) describes the distribution of the C20 and heavier fraction.(4) This seems to be a mathematical convenience, since the α-value seems to slowly increase with chain length. Some attribute this to short chain olefin incorporati ...
... the carbon number distribution from C3 to C12, while the second α-value (α2) describes the distribution of the C20 and heavier fraction.(4) This seems to be a mathematical convenience, since the α-value seems to slowly increase with chain length. Some attribute this to short chain olefin incorporati ...
Molecular orbital approach to substituent effects in amine
... of P by PO, formation and desorption before atomic P forms. In a recent study by Smentkowski et al.1° catalytic decomposition of D M M P was observed on Mo(l10) above 898 K in a 2:l 0,-DMMP molecular beam without accumulation of P or C on the surface. The Mo(l10) surface formed a stable oxide layer ...
... of P by PO, formation and desorption before atomic P forms. In a recent study by Smentkowski et al.1° catalytic decomposition of D M M P was observed on Mo(l10) above 898 K in a 2:l 0,-DMMP molecular beam without accumulation of P or C on the surface. The Mo(l10) surface formed a stable oxide layer ...
Handout V
... While comparing cyclohexanamine and aniline, aniline is a weak base because the lone pair can be delocalized into the benzene ring (Figure 7). In order for the lone pair to be fully conjugated with the benzene ring, the nitrogen would have to be sp2 hybridized with the lone pair in the p-orbital. Th ...
... While comparing cyclohexanamine and aniline, aniline is a weak base because the lone pair can be delocalized into the benzene ring (Figure 7). In order for the lone pair to be fully conjugated with the benzene ring, the nitrogen would have to be sp2 hybridized with the lone pair in the p-orbital. Th ...
ALKANE ALKYL HALIDE Halogenation of Alkanes
... E2 mechanism (write on back of card) only works with 2o and 3o alkyl halides with 2o alkyl halides, use (CH3)3COK to avoid SN2 reactions must have a strong base (usually alkoxide ) constitutional isomers may form if more than one ! hydrogen is available anti elimination: when both carbons are stereo ...
... E2 mechanism (write on back of card) only works with 2o and 3o alkyl halides with 2o alkyl halides, use (CH3)3COK to avoid SN2 reactions must have a strong base (usually alkoxide ) constitutional isomers may form if more than one ! hydrogen is available anti elimination: when both carbons are stereo ...
Module 5 Reactions with Miscellaneous Reagents
... Alkenes react with NBS in dry CCl4 under reflux conditions to give allyl bromide. The reaction is initiated by light or peroxide. Although a number of reagents are available for bromination of allylic C-H bond of alkenes, NBS is most commonly used. The reaction is called Wohl-Zigler bromination. For ...
... Alkenes react with NBS in dry CCl4 under reflux conditions to give allyl bromide. The reaction is initiated by light or peroxide. Although a number of reagents are available for bromination of allylic C-H bond of alkenes, NBS is most commonly used. The reaction is called Wohl-Zigler bromination. For ...
The Effects of Ozone on Compounds in Epicuticular Waxes in Plant
... ozonized product were analyzed using 1H NMR, 13C NMR, CRAFT NMR, HSQC NMR and HPLC-QToF-MS. We found that the 1-octadecanol, oleanolic acid, quercetin and ferulic acid all showed evidence of reaction with ozone; however, the complexity of the spectra has made it difficult to deduce possible structur ...
... ozonized product were analyzed using 1H NMR, 13C NMR, CRAFT NMR, HSQC NMR and HPLC-QToF-MS. We found that the 1-octadecanol, oleanolic acid, quercetin and ferulic acid all showed evidence of reaction with ozone; however, the complexity of the spectra has made it difficult to deduce possible structur ...
View/Open
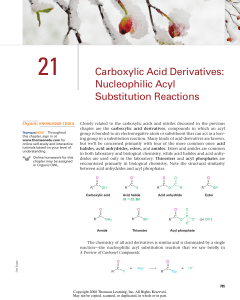
... group is similar to the way they affect the reactivity of an aromatic ring toward electrophilic substitution (Section 16.5). A chlorine substituent, for example, inductively withdraws electrons from an acyl group in the same way that it withdraws electrons from and thus deactivates an aromatic ring. ...
... group is similar to the way they affect the reactivity of an aromatic ring toward electrophilic substitution (Section 16.5). A chlorine substituent, for example, inductively withdraws electrons from an acyl group in the same way that it withdraws electrons from and thus deactivates an aromatic ring. ...
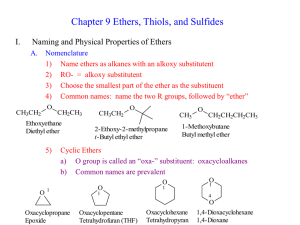
Ch 9 Lecture 2
... Ether Synthesis through Solvolysis of Haloalkanes or other Electrophiles 1) Solvolysis = nucleophilic substitution by solvent 2) Alcoholysis = solvolysis when solvent = ROH 3) Simple SN1 conditions can give complex ethers by solvolysis Br ...
... Ether Synthesis through Solvolysis of Haloalkanes or other Electrophiles 1) Solvolysis = nucleophilic substitution by solvent 2) Alcoholysis = solvolysis when solvent = ROH 3) Simple SN1 conditions can give complex ethers by solvolysis Br ...
Full-Text PDF
... electron-rich aromatic compounds. The relatively higher acid lability of these groups when compared with the naked benzyl group is due to the stability of the carbocation formed in the removal process [22]. In this regard, electron-rich aromatic aldehydes, which can be easily transformed into hydrox ...
... electron-rich aromatic compounds. The relatively higher acid lability of these groups when compared with the naked benzyl group is due to the stability of the carbocation formed in the removal process [22]. In this regard, electron-rich aromatic aldehydes, which can be easily transformed into hydrox ...
No Slide Title
... loss of a water molecule to generate a carbocation (carbonium ion) a bromide ion behaves as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation ...
... loss of a water molecule to generate a carbocation (carbonium ion) a bromide ion behaves as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation ...
The alcohols
... loss of a water molecule to generate a carbocation (carbonium ion) a bromide ion behaves as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation ...
... loss of a water molecule to generate a carbocation (carbonium ion) a bromide ion behaves as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation ...
Solvent and Temperature Effects on the Reduction and Amination
... noboranes in organic chemistry have been scarcely studied. The methods to synthesize aminoboranes include reduction of corresponding (amino)dihaloboranes5 and thermally induced dehydrogenation of secondary amine-borane adducts (R1R2HN:BH3).6 It was recently shown, however, that monomeric (dialkylami ...
... noboranes in organic chemistry have been scarcely studied. The methods to synthesize aminoboranes include reduction of corresponding (amino)dihaloboranes5 and thermally induced dehydrogenation of secondary amine-borane adducts (R1R2HN:BH3).6 It was recently shown, however, that monomeric (dialkylami ...
Title The Cyanide-Ion Cleavage of Organic Disulfides
... reaction are summarized in Table 4. It is expected that alkyl aryl sulfides would be derived from aryl thiocyanates. Thus, aryl thiocyanates were found to react with alcohols in the presence of cyanide ion to give alkyl aryl sulfides. The reaction conditions and the yields of alkyl aryl sulfides are ...
... reaction are summarized in Table 4. It is expected that alkyl aryl sulfides would be derived from aryl thiocyanates. Thus, aryl thiocyanates were found to react with alcohols in the presence of cyanide ion to give alkyl aryl sulfides. The reaction conditions and the yields of alkyl aryl sulfides are ...
CHM 235 Course Outline and Homework in McMurry (6th ed.)
... Polar reactions (electrophile, nucleophile) Curved arrow formalism (“arrow-pushing”) to show reaction mechanisms Thermodynamics (Go = Ho - TSo) (exergonic, endergonic, exothermic, endothermic) Bond dissociation energies (Ho = energy used to break bonds–energy gained by making bonds) En ...
... Polar reactions (electrophile, nucleophile) Curved arrow formalism (“arrow-pushing”) to show reaction mechanisms Thermodynamics (Go = Ho - TSo) (exergonic, endergonic, exothermic, endothermic) Bond dissociation energies (Ho = energy used to break bonds–energy gained by making bonds) En ...
Heterogeneously Catalyzed Reactions with - RWTH
... are derived from vegetable, animal and marine sources and often are by-products in the production of vegetable proteins or fibers and animal and marine proteins. Fats of all types have been used throughout the ages as foods, fuels, lubricants, and starting materials for other chemicals. This wide ut ...
... are derived from vegetable, animal and marine sources and often are by-products in the production of vegetable proteins or fibers and animal and marine proteins. Fats of all types have been used throughout the ages as foods, fuels, lubricants, and starting materials for other chemicals. This wide ut ...
000217986-Tajbakhsh_et_al_
... silylethers, a,b-unsaturated carbonyl compounds and esters. The reactions were performed in diethyl ether at room temperature or under reflux, and the yields of the corresponding alcohols were excellent. The selective reduction of aldehydes in the presence of ketones and complete regioselectivity in ...
... silylethers, a,b-unsaturated carbonyl compounds and esters. The reactions were performed in diethyl ether at room temperature or under reflux, and the yields of the corresponding alcohols were excellent. The selective reduction of aldehydes in the presence of ketones and complete regioselectivity in ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.