The First Chiral Organometallic Triangle for Asymmetric Catalysis
... bisignate band corresponding to naphthyl π f π* transitions and two minor bands due to the other two lower energy π f π* transitions (Figure 1). CD spectra of 1-4 exhibited these three bands similar to L1-4, but with red-shifts in energy and higher intensities. Interestingly, a new intense CD band a ...
... bisignate band corresponding to naphthyl π f π* transitions and two minor bands due to the other two lower energy π f π* transitions (Figure 1). CD spectra of 1-4 exhibited these three bands similar to L1-4, but with red-shifts in energy and higher intensities. Interestingly, a new intense CD band a ...
Part I Carbohydrate Auxiliaries - Wiley-VCH
... (modified Strecker reaction) are fundamental carbon–carbon bond-forming processes [3], which are efficient methods for preparing α-amino acids (Scheme 1.1). In 1987 Kunz and coworkers first reported pivaloyl protected d-galactosyl amine 3 as a very useful tool for asymmetric aminonitrile syntheses [4]. ...
... (modified Strecker reaction) are fundamental carbon–carbon bond-forming processes [3], which are efficient methods for preparing α-amino acids (Scheme 1.1). In 1987 Kunz and coworkers first reported pivaloyl protected d-galactosyl amine 3 as a very useful tool for asymmetric aminonitrile syntheses [4]. ...
Carbonyl Compounds I. Aldehydes and Ketones
... In this and succeeding chapters we describe the chemistry of these compounds with the intent of emphasizing the similarities that exist between them. The differences turn out to be more in degree than in kind. Even so, it is convenient to discuss aldehydes and ketones separately from carboxylic acid ...
... In this and succeeding chapters we describe the chemistry of these compounds with the intent of emphasizing the similarities that exist between them. The differences turn out to be more in degree than in kind. Even so, it is convenient to discuss aldehydes and ketones separately from carboxylic acid ...
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES I. NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION TO …
... apart easily (remember the “unfavorable” equilibrium?), the modified substrate can dissociate from the enzyme and return to the ...
... apart easily (remember the “unfavorable” equilibrium?), the modified substrate can dissociate from the enzyme and return to the ...
cleavage of methyl ethers with iodotrimethylsilane
... prepared by the procedure described in the following paragraph. The submitters have used chlorotrimethylsilane purchased from Aldrich Chemical Company, Inc., and Silar Laboratories, Inc. (10 Alplaus Road, Scotia, New York 12302) either as supplied or after distillation from calcium hydride. No appre ...
... prepared by the procedure described in the following paragraph. The submitters have used chlorotrimethylsilane purchased from Aldrich Chemical Company, Inc., and Silar Laboratories, Inc. (10 Alplaus Road, Scotia, New York 12302) either as supplied or after distillation from calcium hydride. No appre ...
Some uses of mischmetall in organic synthesis
... cases. More unexpectedly, the diol was obtained with ε-caprolactone in excellent yield in the absence of nickel diiodide (entry 3). It was thus anticipated that esters should behave like this unstrained lactone. This was confirmed: good yields in tertiary alcohols were obtained in both procedures (e ...
... cases. More unexpectedly, the diol was obtained with ε-caprolactone in excellent yield in the absence of nickel diiodide (entry 3). It was thus anticipated that esters should behave like this unstrained lactone. This was confirmed: good yields in tertiary alcohols were obtained in both procedures (e ...
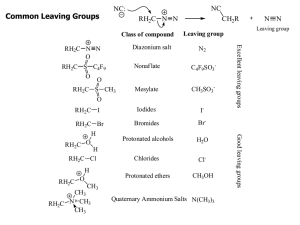
Common Leaving Groups
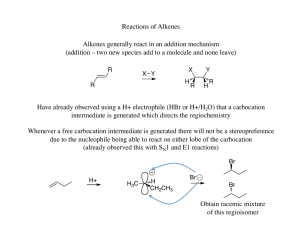
... E1 vs. E2 vs. SN1 vs. SN2 - Summary •As a general rule, elimination reactions can always compete with substitution reactions. We can, however, alter the reaction conditions to favour one process over another. •To favour E1 over SN1 for alcohols, use an acid with a non-nucleophilic conjugate base (H ...
... E1 vs. E2 vs. SN1 vs. SN2 - Summary •As a general rule, elimination reactions can always compete with substitution reactions. We can, however, alter the reaction conditions to favour one process over another. •To favour E1 over SN1 for alcohols, use an acid with a non-nucleophilic conjugate base (H ...
Fatty Acids and Derivatives from Coconut Oil
... such as sulfation, ethoxylation, amination, phosphatization, sulfitation, and others. Fatty alcohol can be fractionated to separate the C8–C10 fraction, known as plasticizer range alcohol, and the C12–C18, known as the detergent range alcohol. The plasticizer range alcohol is a liquid with good diss ...
... such as sulfation, ethoxylation, amination, phosphatization, sulfitation, and others. Fatty alcohol can be fractionated to separate the C8–C10 fraction, known as plasticizer range alcohol, and the C12–C18, known as the detergent range alcohol. The plasticizer range alcohol is a liquid with good diss ...
Chapter 11
... To overcome these drawbacks organocuprates can also deliver an R- source as a nucleophile ...
... To overcome these drawbacks organocuprates can also deliver an R- source as a nucleophile ...
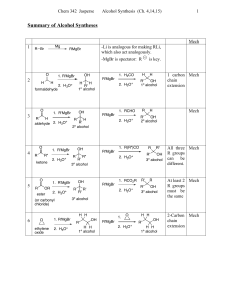
Alcohols
... molecules and therefore make its formation less likely and the corresponding acid necessarily weaker The more easily the alkoxide ion is solvated by water the more stable it is and the more its formation is energetically favored ...
... molecules and therefore make its formation less likely and the corresponding acid necessarily weaker The more easily the alkoxide ion is solvated by water the more stable it is and the more its formation is energetically favored ...
Diastereoselective Allylation of Carbonyl Compounds and Imines:
... bind to the electrophile activating it toward nucleophilic attack, and chiral Lewis bases.5 Double activation could be also achieved by using chiral bifunctional catalysts.6 In this case, the simultaneous activation of both electrophilic and nucleophilic reaction partners occurs ideally through a co ...
... bind to the electrophile activating it toward nucleophilic attack, and chiral Lewis bases.5 Double activation could be also achieved by using chiral bifunctional catalysts.6 In this case, the simultaneous activation of both electrophilic and nucleophilic reaction partners occurs ideally through a co ...
Class Notes
... Super Strong Bases and Nucleophiles • The counterion metal is a spectator • Stability-reactivity principle: very unstable à very reactive • This great reactivity is very useful (as nucleophile) • This great reactivity (as base) has implication for proper technical use (see following) 7. Solvent and ...
... Super Strong Bases and Nucleophiles • The counterion metal is a spectator • Stability-reactivity principle: very unstable à very reactive • This great reactivity is very useful (as nucleophile) • This great reactivity (as base) has implication for proper technical use (see following) 7. Solvent and ...
IR handout
... or acyl halide. The an aldehyde may be confirmed with C-H absorption from 2840 to 2720 cm-1. 3. the O-H or N-H absorption between 3200 and 3600 cm-1. This indicates either an alcohol, N-H containing amine or amide, or carboxylic acid. For -NH2 a doublet will be observed. 4.the C-O absorption between ...
... or acyl halide. The an aldehyde may be confirmed with C-H absorption from 2840 to 2720 cm-1. 3. the O-H or N-H absorption between 3200 and 3600 cm-1. This indicates either an alcohol, N-H containing amine or amide, or carboxylic acid. For -NH2 a doublet will be observed. 4.the C-O absorption between ...
Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
... 24.3 Directed Aldol Reactions A directed aldol reaction is a variation of the crossed aldol reaction that clearly defines which carbonyl compound becomes the nucleophilic enolate and which reacts at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon. The strategy of a directed aldol reaction is as follows: [1] Prepa ...
... 24.3 Directed Aldol Reactions A directed aldol reaction is a variation of the crossed aldol reaction that clearly defines which carbonyl compound becomes the nucleophilic enolate and which reacts at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon. The strategy of a directed aldol reaction is as follows: [1] Prepa ...
View/Open
... The rings of cycloalkenes containing five carbon atoms or fewer exist only in the cis form (Fig. 7.3). The introduction of a trans double bond into rings this small would, if it were possible, introduce greater strain than the bonds of the ring atoms could accommodate. ...
... The rings of cycloalkenes containing five carbon atoms or fewer exist only in the cis form (Fig. 7.3). The introduction of a trans double bond into rings this small would, if it were possible, introduce greater strain than the bonds of the ring atoms could accommodate. ...
Microsoft Word
... analogy and further confirmed by 1H NMR–NOE analysis of the acetonides derived from the diols. In conclsion, a highly regio– and stereoselective synthesis of diastereomeric stereotriads and tetrads by oxymercuration–demercuration of cyclopropylcarbinols employing an intramolecular sulfinyl group as ...
... analogy and further confirmed by 1H NMR–NOE analysis of the acetonides derived from the diols. In conclsion, a highly regio– and stereoselective synthesis of diastereomeric stereotriads and tetrads by oxymercuration–demercuration of cyclopropylcarbinols employing an intramolecular sulfinyl group as ...
Document
... Counting from each direction find the carbon where the alkyl group is attached (the lower number) J Deutsch 2003 ...
... Counting from each direction find the carbon where the alkyl group is attached (the lower number) J Deutsch 2003 ...
Ch. 11 Notes with Answers
... • 2º alcohols are way slower • 1º alcohols can’t react at all via this mechanism, because 1º R+ are too unstable. • Ditto for vinyl or aryl alcohols 5. HBr can also react with 1º ROH to give 1º RBr, although it is not often the method of choice • The mechanism is different, but rather interesting (n ...
... • 2º alcohols are way slower • 1º alcohols can’t react at all via this mechanism, because 1º R+ are too unstable. • Ditto for vinyl or aryl alcohols 5. HBr can also react with 1º ROH to give 1º RBr, although it is not often the method of choice • The mechanism is different, but rather interesting (n ...
Aldehydes and ketones
... aromatic). The other bond to the carbonyl is either to a Hatom or another carbon group: General formula for an ester: ...
... aromatic). The other bond to the carbonyl is either to a Hatom or another carbon group: General formula for an ester: ...
Aromatic heterocycles 1: structures and reactions
... ring. This makes it an imine. Most of the imines you have met before (in Chapter 14, for example), have been unstable intermediates in carbonyl group reactions, but in pyridine we have a stable imine—stable because of its aromaticity. All imines are more weakly basic than saturated amines and pyridi ...
... ring. This makes it an imine. Most of the imines you have met before (in Chapter 14, for example), have been unstable intermediates in carbonyl group reactions, but in pyridine we have a stable imine—stable because of its aromaticity. All imines are more weakly basic than saturated amines and pyridi ...
Adv_H_Unit_3_Pupil_N.. - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Heterolytic fission is more likely when a bond is already polar. For example, bromomethane contains a polar carbon to bromine bond and under certain conditions this can break heterolytically (Figure 1). Figure 1 ...
... Heterolytic fission is more likely when a bond is already polar. For example, bromomethane contains a polar carbon to bromine bond and under certain conditions this can break heterolytically (Figure 1). Figure 1 ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.