alcohols03
... Alcohols and phenols have similar geometry to HOH. The R-O-H bond angle is approximately tetrahedral (109) and the ‘O’ atom is sp3 hybridized. Because of the presence of the hydroxyl group, alcohols (and phenols) have significantly higher boiling points than their constitutional (structural) is ...
... Alcohols and phenols have similar geometry to HOH. The R-O-H bond angle is approximately tetrahedral (109) and the ‘O’ atom is sp3 hybridized. Because of the presence of the hydroxyl group, alcohols (and phenols) have significantly higher boiling points than their constitutional (structural) is ...
© John Congleton, Orange Coast College Organic Chemistry 220
... Be able to predict whether a reaction will proceed via o SN1 and E1 o S N2 o SN2 and E2 o E2 What makes a good nucleophile? What makes a good base? What makes a good leaving group? What is meant by high and low polarizability? Allylic bromination Understand, be able to predict, and be able to comple ...
... Be able to predict whether a reaction will proceed via o SN1 and E1 o S N2 o SN2 and E2 o E2 What makes a good nucleophile? What makes a good base? What makes a good leaving group? What is meant by high and low polarizability? Allylic bromination Understand, be able to predict, and be able to comple ...
HMDS+TMCS+Pyridine - Sigma
... is readily lost from the transition state during reaction, but possesses sufficient chemical stability in combination with the alkyl silyl group to allow long term storage of the derivatizing agent for use as required. As the formation of the transition state is reversible, the derivatization will o ...
... is readily lost from the transition state during reaction, but possesses sufficient chemical stability in combination with the alkyl silyl group to allow long term storage of the derivatizing agent for use as required. As the formation of the transition state is reversible, the derivatization will o ...
New Applications for Sulfur-Based Leaving Groups in Synthesis
... I’d firstly like to thank my supervisor, Dr. Jon Wilden for his support throughout the past four years. It has been great fun to be able to work on a varied range of chemistry within his group and his stress-free approach to the subject has allowed me to form many of my own ideas and not be afraid t ...
... I’d firstly like to thank my supervisor, Dr. Jon Wilden for his support throughout the past four years. It has been great fun to be able to work on a varied range of chemistry within his group and his stress-free approach to the subject has allowed me to form many of my own ideas and not be afraid t ...
Chapter Three
... Carboxylate anions are protonated in strong acids. RCOO1– + H3O1+ RCOOH + H2O Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
... Carboxylate anions are protonated in strong acids. RCOO1– + H3O1+ RCOOH + H2O Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
Question Bank - Edudel.nic.in
... Why should a solution of a non volatile solute boil at a higher temperature? Explain with the help of a diagram. Derive the relationship between molar mass and elevation in boiling point. ...
... Why should a solution of a non volatile solute boil at a higher temperature? Explain with the help of a diagram. Derive the relationship between molar mass and elevation in boiling point. ...
SMK RAJA PEREMPUAN, IPOH
... (d) aldehydes and ketones (e) carboxylic acids and esters (f) primary amines, amides, and amino acids 12. define the term nucleophile and electrophile 13. describe the relationship between the size of molecules in the homologous series and the melting and boiling points 14. explain the attractive fo ...
... (d) aldehydes and ketones (e) carboxylic acids and esters (f) primary amines, amides, and amino acids 12. define the term nucleophile and electrophile 13. describe the relationship between the size of molecules in the homologous series and the melting and boiling points 14. explain the attractive fo ...
5. Coenzyme HAD+ is derived
... training. Chemistry is a basic science and a powerful tool for studying and learning processes in living systems. Therefore, medical students must thoroughly understand the basic ideas, laws and methods of this science. Program expected to consider the foundations of the most important topics of the ...
... training. Chemistry is a basic science and a powerful tool for studying and learning processes in living systems. Therefore, medical students must thoroughly understand the basic ideas, laws and methods of this science. Program expected to consider the foundations of the most important topics of the ...
Palladium and Ruthenium Catalyzed Reactions By Bryan Jaksic
... activity of commonly used precatalysts with the newly synthesized precatalyst, Pd(η5-C5H5)(η3-1Ph-C3H4), for Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Sonogashira reactions are important as they provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within impor ...
... activity of commonly used precatalysts with the newly synthesized precatalyst, Pd(η5-C5H5)(η3-1Ph-C3H4), for Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Sonogashira reactions are important as they provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within impor ...
Organic Chemistry
... Organic nitriles (R-C≡N) are usually considered together with R-C(=O)-Z compounds in organic chemistry textbooks. This is because nitriles (R-C≡N) are readily hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids (R-C(=O)-OH) via intermediate amides (R-C(=O)-NH2) (Figure 15.13). Figure 15.13 ...
... Organic nitriles (R-C≡N) are usually considered together with R-C(=O)-Z compounds in organic chemistry textbooks. This is because nitriles (R-C≡N) are readily hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids (R-C(=O)-OH) via intermediate amides (R-C(=O)-NH2) (Figure 15.13). Figure 15.13 ...
15: Carbonyl Compounds: Esters, Amides, and Related Molecules
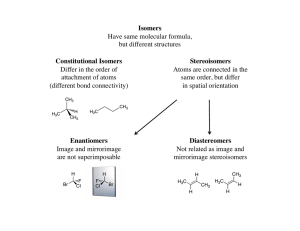
... geometric isomers, we cannot isolate the individual isomers because their lifetimes at room temperature are on the order of 0.5 to 20 seconds. In contrast, you learned in Chapter 8 that we can isolate cis and trans geometric isomers of alkenes. Alkenes have C=C rotational barriers of about 270 kJ/mo ...
... geometric isomers, we cannot isolate the individual isomers because their lifetimes at room temperature are on the order of 0.5 to 20 seconds. In contrast, you learned in Chapter 8 that we can isolate cis and trans geometric isomers of alkenes. Alkenes have C=C rotational barriers of about 270 kJ/mo ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
... This carbanion then loses the leaving group (-:L) to form alkene product(s). The E1cb mechanism usually occurs with strong bases and with substrates where groups directly attached to the carbanion center can stabilize the negative charge on that carbanion center. We have not yet introduced most grou ...
... This carbanion then loses the leaving group (-:L) to form alkene product(s). The E1cb mechanism usually occurs with strong bases and with substrates where groups directly attached to the carbanion center can stabilize the negative charge on that carbanion center. We have not yet introduced most grou ...
Document
... Thus, an amide can be prepared from a carboxylic acid by first converting the carboxylic acid to an ester by Fischer esterification and then reaction of the ester with an amine. ...
... Thus, an amide can be prepared from a carboxylic acid by first converting the carboxylic acid to an ester by Fischer esterification and then reaction of the ester with an amine. ...
Alcohols - La Salle University
... • Ethanol has a caloric value of 7.1Cal/g (fat has a value of 9 Cal/g). • Alcohol can cause a degenerative muscle disease called alcoholic myopathy (3 times more common than cirrhosis). ...
... • Ethanol has a caloric value of 7.1Cal/g (fat has a value of 9 Cal/g). • Alcohol can cause a degenerative muscle disease called alcoholic myopathy (3 times more common than cirrhosis). ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
... Based on McMurry, Organic Chemistry, Chapter 19, 6th edition, (c) 2003 ...
... Based on McMurry, Organic Chemistry, Chapter 19, 6th edition, (c) 2003 ...
23.3 Carbonyl Compounds
... • The low-molar-mass members of the aliphatic carboxylic acid series are colorless, volatile liquids. • The higher members of the series are nonvolatile, waxy solids with low melting points. • All aromatic carboxylic acids are solids at room ...
... • The low-molar-mass members of the aliphatic carboxylic acid series are colorless, volatile liquids. • The higher members of the series are nonvolatile, waxy solids with low melting points. • All aromatic carboxylic acids are solids at room ...
MOLECULAR REPRESENTATIONS AND INFRARED
... b) (C2H5)2CHC≡C(CH2)3CH3 or CH3CH2CH(C2H5)C≡C(CH2)3CH3 d) (CH3)2CHCH2S(CH2)2CH(C2H5)C(CH3)3 ...
... b) (C2H5)2CHC≡C(CH2)3CH3 or CH3CH2CH(C2H5)C≡C(CH2)3CH3 d) (CH3)2CHCH2S(CH2)2CH(C2H5)C(CH3)3 ...
Chemistry 360 - Athabasca University
... Welcome to Organic Chemistry 360’s Laboratory Report Workbook This Report Book, along with the 'Chemistry 360 Lab Manual', will help you prepare for four-five days straight of supervised lab instruction. All preparatory work in this report book (~12 h to finish, see list on page 3), may be completed ...
... Welcome to Organic Chemistry 360’s Laboratory Report Workbook This Report Book, along with the 'Chemistry 360 Lab Manual', will help you prepare for four-five days straight of supervised lab instruction. All preparatory work in this report book (~12 h to finish, see list on page 3), may be completed ...
Buchwald-Hartwig Chemistry
... ! Three months after Hartwig's paper is submitted, Buchwald submits the following work, beginning an ongoing trend of indepent, overlapping research ! Buchwald expands the scope of the reaction by generating tin amines in situ Bu 3SnNEt 2 ...
... ! Three months after Hartwig's paper is submitted, Buchwald submits the following work, beginning an ongoing trend of indepent, overlapping research ! Buchwald expands the scope of the reaction by generating tin amines in situ Bu 3SnNEt 2 ...
BIORANSFORMATION
... Glucoronic acid, Sulfate, Glycine to either unchanged drugs or Phase I product having suitable functional groups as COOH,-OH,-NH2,- SH. • Thus is called as Conjugation reactions. • Since the product formed is having high molecular weight so called as synthetic reactions. • The product formed is hydr ...
... Glucoronic acid, Sulfate, Glycine to either unchanged drugs or Phase I product having suitable functional groups as COOH,-OH,-NH2,- SH. • Thus is called as Conjugation reactions. • Since the product formed is having high molecular weight so called as synthetic reactions. • The product formed is hydr ...
The First Chiral Organometallic Triangle for Asymmetric Catalysis
... bisignate band corresponding to naphthyl π f π* transitions and two minor bands due to the other two lower energy π f π* transitions (Figure 1). CD spectra of 1-4 exhibited these three bands similar to L1-4, but with red-shifts in energy and higher intensities. Interestingly, a new intense CD band a ...
... bisignate band corresponding to naphthyl π f π* transitions and two minor bands due to the other two lower energy π f π* transitions (Figure 1). CD spectra of 1-4 exhibited these three bands similar to L1-4, but with red-shifts in energy and higher intensities. Interestingly, a new intense CD band a ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.