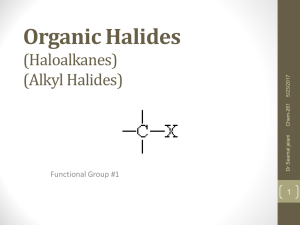ethane - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... enantiomers) must be used. When a chiral probe is used to resolve a racemic mixture into its enantiomers, it is called a resolving agent. Traditionally, the method for resolving a racemic mixture is to react the racemate with an enantiomerically pure compound (often a readily available natural produ ...
... enantiomers) must be used. When a chiral probe is used to resolve a racemic mixture into its enantiomers, it is called a resolving agent. Traditionally, the method for resolving a racemic mixture is to react the racemate with an enantiomerically pure compound (often a readily available natural produ ...
10 | Carbon: More Than Just Another Element
... octet configuration. In contrast, the elements boron and nitrogen form three bonds in molecular compounds; oxygen forms two bonds; and hydrogen and the halogens form one bond. With a larger number of bonds comes the opportunity to create more complex structures. This will become increasingly evident ...
... octet configuration. In contrast, the elements boron and nitrogen form three bonds in molecular compounds; oxygen forms two bonds; and hydrogen and the halogens form one bond. With a larger number of bonds comes the opportunity to create more complex structures. This will become increasingly evident ...
Catalytic Asymmetric Induction. Highly Enantioselective Addition of
... asymmetric alkylation. The enantiomeric excess was determined carefully by HPLC analysis using a chiral stationary phase. Enantioselectivity of the reaction of p-substituted benzaldehydes is generally high. Certain a,@unsaturated or aliphatic aldehydes can be also alkylated with a high degree of ena ...
... asymmetric alkylation. The enantiomeric excess was determined carefully by HPLC analysis using a chiral stationary phase. Enantioselectivity of the reaction of p-substituted benzaldehydes is generally high. Certain a,@unsaturated or aliphatic aldehydes can be also alkylated with a high degree of ena ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... • OH- is a poor leaving group, i.e., is not displaced directly by nucleophiles. Reaction in acid media protonates the OH group producing a better leaving group (H2O). 2 and 3 alcohols react by SN1 but Me° and 1 alcohols react by SN2. H2O ...
... • OH- is a poor leaving group, i.e., is not displaced directly by nucleophiles. Reaction in acid media protonates the OH group producing a better leaving group (H2O). 2 and 3 alcohols react by SN1 but Me° and 1 alcohols react by SN2. H2O ...
anhydride cured-epoxy matrices
... epoxy molecules linked together through the reactive sites of the anhydride curing agent. The majority of anhydrides used for curing epoxy resin matrices are liquids but solid dianhydrides also find limited use as curing agents in fiber reinforced composite applications. The reactivity of most liqui ...
... epoxy molecules linked together through the reactive sites of the anhydride curing agent. The majority of anhydrides used for curing epoxy resin matrices are liquids but solid dianhydrides also find limited use as curing agents in fiber reinforced composite applications. The reactivity of most liqui ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Items essentials for human survival such as, food, medicine etc. are produced by chemical reactions directly or indirectly in nature or in industry. Other items such as cosmetics, which are also deemed essentials in affluent societies, are also obtained by above means. It is the biggest challenge in ...
... Items essentials for human survival such as, food, medicine etc. are produced by chemical reactions directly or indirectly in nature or in industry. Other items such as cosmetics, which are also deemed essentials in affluent societies, are also obtained by above means. It is the biggest challenge in ...
HOMOLOGATION OF HETEROCYCLES BY A SEQUENTIAL REDUCTIVE OPENING LITHIATION – S
... Oxetanes (2) undergo reductive opening by means of alkali metals in the presence of an arene, but thietane itself or alkyl substituted thietanes are stable compounds towards the same reductive reagents because they are less strained heterocycles due to the longer carbonheteroatom bond distances. How ...
... Oxetanes (2) undergo reductive opening by means of alkali metals in the presence of an arene, but thietane itself or alkyl substituted thietanes are stable compounds towards the same reductive reagents because they are less strained heterocycles due to the longer carbonheteroatom bond distances. How ...
Chemistry - Andhra University
... b) hydrolysis by benzotrichlorides. c) Kolbe reaction. Physical properties: Hydrogen bonding, dimeric association, acidity- strength of acids with examples of trimethyl acetic acid and trichloroacetic acid. Relative differences in the acidities of aromatic and aliphatic acids. Chemical properties: R ...
... b) hydrolysis by benzotrichlorides. c) Kolbe reaction. Physical properties: Hydrogen bonding, dimeric association, acidity- strength of acids with examples of trimethyl acetic acid and trichloroacetic acid. Relative differences in the acidities of aromatic and aliphatic acids. Chemical properties: R ...
New Exp8
... steps. Limitations of E1 Reaction: Acid-Catalyzed Dehydrations Competition can occur with SN1 reaction if reaction conditions are not ‘controlled’ (when protic solvents, non-basic nucleophiles are used). Mixtures of products form with the E1 reaction (also SN1). Unsymmetrical reagents and rearrangem ...
... steps. Limitations of E1 Reaction: Acid-Catalyzed Dehydrations Competition can occur with SN1 reaction if reaction conditions are not ‘controlled’ (when protic solvents, non-basic nucleophiles are used). Mixtures of products form with the E1 reaction (also SN1). Unsymmetrical reagents and rearrangem ...
Spring 2005
... a. (3 pts) What action should you take? b. (3 pts) What action should your lab partner take? 19. (6 pts) Draw the Lewis structure for H2SO4 including any resonance structures. 20. (10 pts) Ammonia is produced commercially by the Haber process: 3 H2 (g) + N2 (g) ! 2 NH3 (g) The yield from this reacti ...
... a. (3 pts) What action should you take? b. (3 pts) What action should your lab partner take? 19. (6 pts) Draw the Lewis structure for H2SO4 including any resonance structures. 20. (10 pts) Ammonia is produced commercially by the Haber process: 3 H2 (g) + N2 (g) ! 2 NH3 (g) The yield from this reacti ...
Rhenium- and molybdenum-catalyzed dehydration reactions
... needs to be (at least partially) converted or removed when dealing with biomass. One of the most direct methods of removing hydroxyl functionalities is the dehydration reaction. The dehydration reaction in terms of relevant biomass transformations can be divided in three categories: sugar dehydratio ...
... needs to be (at least partially) converted or removed when dealing with biomass. One of the most direct methods of removing hydroxyl functionalities is the dehydration reaction. The dehydration reaction in terms of relevant biomass transformations can be divided in three categories: sugar dehydratio ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... Ether Synthesis through Solvolysis of Haloalkanes or other Electrophiles 1) Solvolysis = nucleophilic substitution by solvent 2) Alcoholysis = solvolysis when solvent = ROH 3) Simple SN1 conditions can give complex ethers by solvolysis Br ...
... Ether Synthesis through Solvolysis of Haloalkanes or other Electrophiles 1) Solvolysis = nucleophilic substitution by solvent 2) Alcoholysis = solvolysis when solvent = ROH 3) Simple SN1 conditions can give complex ethers by solvolysis Br ...
Carbonyl Compounds
... • The carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones are polarised because of the difference in the electronegativity of carbon and oxygen. • The carbon atom carries a partial positive charge while oxygen atom carries a partial negative charge. • Aldehydes and ketones are susceptible to attack both by nuc ...
... • The carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones are polarised because of the difference in the electronegativity of carbon and oxygen. • The carbon atom carries a partial positive charge while oxygen atom carries a partial negative charge. • Aldehydes and ketones are susceptible to attack both by nuc ...
Module 2 Asymmetric Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions
... styrene, in the case of Mo-based system, RORCM product is formed with 92% ee. The substrate used for the Ru-catalyzed ROCM process, proceed polymerization in the presence of Mo-catalyst instead of ROCM process. Scheme 7 shows the comparison of the Ru-catalyzed ROCM of norbornenes. The catalysts 7 an ...
... styrene, in the case of Mo-based system, RORCM product is formed with 92% ee. The substrate used for the Ru-catalyzed ROCM process, proceed polymerization in the presence of Mo-catalyst instead of ROCM process. Scheme 7 shows the comparison of the Ru-catalyzed ROCM of norbornenes. The catalysts 7 an ...
Modern Synthetic Methods for Copper-Mediated C(aryl
... detail the remarkable simplicity of the new reaction conditions. A mixture of the phenol (1 equiv), aryl boronic acid (2–3 equiv), anhydrous Cu(OAc)2 (1–2 equiv), and Et3N (2– 3 equiv) in dichloromethane were stirred at room temperature for 1–2 days and then the product was isolated in good yield af ...
... detail the remarkable simplicity of the new reaction conditions. A mixture of the phenol (1 equiv), aryl boronic acid (2–3 equiv), anhydrous Cu(OAc)2 (1–2 equiv), and Et3N (2– 3 equiv) in dichloromethane were stirred at room temperature for 1–2 days and then the product was isolated in good yield af ...
Synthetic Strategies for the Construction of Enantiomeric
... is too high.22 The second preparative step is a disproportionation and loss of SO2 to afford the sulfur diimide. We now wish to report that the two steps from p-toluenesulfonamide proceed conveniently in one pot from ptoluenesulfonamide and thionyl chloride if a purge is maintained to remove liberat ...
... is too high.22 The second preparative step is a disproportionation and loss of SO2 to afford the sulfur diimide. We now wish to report that the two steps from p-toluenesulfonamide proceed conveniently in one pot from ptoluenesulfonamide and thionyl chloride if a purge is maintained to remove liberat ...
File
... H CH3 H CF3 destabilizes the δ+ of the carbonyl, H CH3 G G+H-hydrate making the CF3 carbonyl higher in energy than the aldehyde. This makes the hydrate reaction of the CF3 carbonyl downhill, resulting in a higher amount of hydrate. 16. In each pair, predict which would have a greater percentage of h ...
... H CH3 H CF3 destabilizes the δ+ of the carbonyl, H CH3 G G+H-hydrate making the CF3 carbonyl higher in energy than the aldehyde. This makes the hydrate reaction of the CF3 carbonyl downhill, resulting in a higher amount of hydrate. 16. In each pair, predict which would have a greater percentage of h ...
Alkene-Addn-PartB-2012-ques
... Question The product isolated from the acid-catalyzed hydration of (E)- or (Z)-3-methyl-2-pentene is: A) optically active B) an optically inactive racemic mixture C) an optically inactive enantiomer ...
... Question The product isolated from the acid-catalyzed hydration of (E)- or (Z)-3-methyl-2-pentene is: A) optically active B) an optically inactive racemic mixture C) an optically inactive enantiomer ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.