LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. Explain Michel addition reaction with an example. 12. Draw correlation diagram for the electrocyclization of 1,3,5-hexatriene for the dis-rotatory approach. State whether the reaction is feasible by thermal or photochemical means. 13. Predict the products in the following pericyclic reactions an ...
... 11. Explain Michel addition reaction with an example. 12. Draw correlation diagram for the electrocyclization of 1,3,5-hexatriene for the dis-rotatory approach. State whether the reaction is feasible by thermal or photochemical means. 13. Predict the products in the following pericyclic reactions an ...
KFUPM
... In the synthesis of aspartame, the starting materials are a racemic mixture (equal quantities of both isomers) of phenylalanine, and aspartic acid. Only the L isomer of phenylalanine is deisred for use. This L isomer may be separated from the D isomer by a chemical pretreatment, followed by a reacti ...
... In the synthesis of aspartame, the starting materials are a racemic mixture (equal quantities of both isomers) of phenylalanine, and aspartic acid. Only the L isomer of phenylalanine is deisred for use. This L isomer may be separated from the D isomer by a chemical pretreatment, followed by a reacti ...
Dehydration of 2-methylcyclohexanol
... This means that any single molecule of 2-methylcyclohexanol can form into 3methylcyclohexene, 1-methylcyclohexene or methylenecyclohexane. One molecule cannot form 3 molecules. Which product alkene do you predict to be the most stable? (Remember Zaitsev’s rule.) The phosphoric acid acts as a catalys ...
... This means that any single molecule of 2-methylcyclohexanol can form into 3methylcyclohexene, 1-methylcyclohexene or methylenecyclohexane. One molecule cannot form 3 molecules. Which product alkene do you predict to be the most stable? (Remember Zaitsev’s rule.) The phosphoric acid acts as a catalys ...
info
... i. NaBH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, or acid chloride to the corresponding alcohol. It will not reduce an acid or an ester. ii. LiAlH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, acid, or ester to the corresponding alcohol. iii. LiAlH(OtBu)3 will reduce an acid chloride to an aldehyde. iv. DIBAL will ...
... i. NaBH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, or acid chloride to the corresponding alcohol. It will not reduce an acid or an ester. ii. LiAlH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, acid, or ester to the corresponding alcohol. iii. LiAlH(OtBu)3 will reduce an acid chloride to an aldehyde. iv. DIBAL will ...
Proteins Self Quiz
... polypeptide molecule? Hint: the mono/di/poly relates to the number of amino acids used, not the number of bonds formed. A monopeptide consists of one amino acid. A dipeptide consists of 2 amino acids. A polypeptide consists of 3 or more amino acids. Therefore this is a polypeptide because it contain ...
... polypeptide molecule? Hint: the mono/di/poly relates to the number of amino acids used, not the number of bonds formed. A monopeptide consists of one amino acid. A dipeptide consists of 2 amino acids. A polypeptide consists of 3 or more amino acids. Therefore this is a polypeptide because it contain ...
Silica Sulfuric Acid Promotes Aza-Michael Addition Reactions under
... This encouraged us to exploit the generality and scope of this reaction catalyzed by SiO2-SO3H by using other Michael acceptors with various aromatic and aliphatic amines. As shown in Table 1, the Michael addition of various aliphatic amines and aryl amines carrying either electron-donating or elect ...
... This encouraged us to exploit the generality and scope of this reaction catalyzed by SiO2-SO3H by using other Michael acceptors with various aromatic and aliphatic amines. As shown in Table 1, the Michael addition of various aliphatic amines and aryl amines carrying either electron-donating or elect ...
Acids and Bases
... A protic solvent is one in which hydrogen is attached to a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen or nitrogen e.g. water Solvation of both acetic acid and acetate ion occurs in water although the acetate is more stabilized by this solvation ...
... A protic solvent is one in which hydrogen is attached to a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen or nitrogen e.g. water Solvation of both acetic acid and acetate ion occurs in water although the acetate is more stabilized by this solvation ...
Document
... A. because proteins (enzymes) are made of chiral subunits they usually react with only one stereoisomer of a molecule. B. because proteins (enzymes) are not made of chiral subunits they react with all stereoisomers of a molecule. C. because proteins (enzymes) are made of chiral subunits they react w ...
... A. because proteins (enzymes) are made of chiral subunits they usually react with only one stereoisomer of a molecule. B. because proteins (enzymes) are not made of chiral subunits they react with all stereoisomers of a molecule. C. because proteins (enzymes) are made of chiral subunits they react w ...
Summary of Organic Compounds -Functional Groups and Reactions
... Hydrogen (hydrogenation) to form alcohols Controlled oxidation of aldehydes to form carboxylic acids Carboxylic acid + alcohol = ester + H2O ...
... Hydrogen (hydrogenation) to form alcohols Controlled oxidation of aldehydes to form carboxylic acids Carboxylic acid + alcohol = ester + H2O ...
TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... regiochemically pure enolates Other carbanions in synthesis - dithianes and corresponding sulfoxides, nitrocompound, cyanoalkanes Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed ...
... regiochemically pure enolates Other carbanions in synthesis - dithianes and corresponding sulfoxides, nitrocompound, cyanoalkanes Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed ...
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... • With unsubstituted NH2 group. replace -oic acid or -ic acid with -amide, or by replacing the carboxylic acid ending with –carboxamide • If the N is further substituted, identify the substituent groups (preceded by “N”) and then the ...
... • With unsubstituted NH2 group. replace -oic acid or -ic acid with -amide, or by replacing the carboxylic acid ending with –carboxamide • If the N is further substituted, identify the substituent groups (preceded by “N”) and then the ...
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... Waxes - contain esters formed from long-chain (C16C36) carboxylic acids and long-chain alcohols (C24-C36) Triacontyl hexadecanoate is in beeswax ...
... Waxes - contain esters formed from long-chain (C16C36) carboxylic acids and long-chain alcohols (C24-C36) Triacontyl hexadecanoate is in beeswax ...
Carbon Chemistry
... Simple sugar formula – C6H12O6 Exist as straight chains or rings Carbohydrates are made up of simple sugars, more complex sugars, and polymers. ...
... Simple sugar formula – C6H12O6 Exist as straight chains or rings Carbohydrates are made up of simple sugars, more complex sugars, and polymers. ...
Microsoft Word
... We found that La(NO3)36H2O is an efficient and mild acidic catalyst for the acetylation of alcohols with Ac2O under solvent-free conditions. In order to establish the catalytic activity of La(NO3)36H2O, we carried out the acetylation of glucose diacetonide (1 mmol) with acetic anhydride (1.2 mmol) u ...
... We found that La(NO3)36H2O is an efficient and mild acidic catalyst for the acetylation of alcohols with Ac2O under solvent-free conditions. In order to establish the catalytic activity of La(NO3)36H2O, we carried out the acetylation of glucose diacetonide (1 mmol) with acetic anhydride (1.2 mmol) u ...
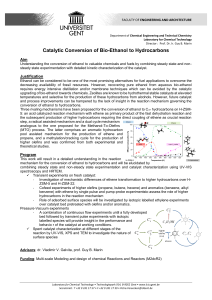
VG-Catalytic Conversion of Bio
... decreasing availability of fossil resources. However, recovering pure ethanol from aqueous bio-ethanol requires energy intensive distillation and/or membrane techniques which can be avoided by the catalytic upgrading of bio-ethanol towards chemicals. Zeolites are known to be hydrothermal stable cata ...
... decreasing availability of fossil resources. However, recovering pure ethanol from aqueous bio-ethanol requires energy intensive distillation and/or membrane techniques which can be avoided by the catalytic upgrading of bio-ethanol towards chemicals. Zeolites are known to be hydrothermal stable cata ...
AMINO ACID OXIDATION AND THE PRODUCTION OF UREA
... a. During the normal synthesis and degradation of cellular proteins, some amino acids that are released from protein breakdown and are not needed for new protein synthesis undergo oxidative degradation. b. When a diet is rich in protein and the ingested amino acids exceed the body’s needs for protei ...
... a. During the normal synthesis and degradation of cellular proteins, some amino acids that are released from protein breakdown and are not needed for new protein synthesis undergo oxidative degradation. b. When a diet is rich in protein and the ingested amino acids exceed the body’s needs for protei ...
Experiments
... the addition of water (removing the H+ from the HSO3- group), there is a milky ppt. A solution of fuming sulphuric acid is used here to provide the attacking molecule, SO3. Refluxing for several hours is sometimes necessary with benzene, though not with methyl or methoxybenzene. Sulphonation is us ...
... the addition of water (removing the H+ from the HSO3- group), there is a milky ppt. A solution of fuming sulphuric acid is used here to provide the attacking molecule, SO3. Refluxing for several hours is sometimes necessary with benzene, though not with methyl or methoxybenzene. Sulphonation is us ...
Chapter 18 - Aldehydes and Ketones
... Boiling point: since there are no hydrogen bonding in aldehydes or ketones, the boiling point will be lower than those of alcohols of similar molecular weights but higher than those non-polar molecules like alkanes, ethers, etc…because of the strong dipole. ...
... Boiling point: since there are no hydrogen bonding in aldehydes or ketones, the boiling point will be lower than those of alcohols of similar molecular weights but higher than those non-polar molecules like alkanes, ethers, etc…because of the strong dipole. ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.