Organic Molecules
... d. Sugar bases 6. Organic molecules called ____________ are insoluble in water, are often found in biological membranes and other waterproof coverings and have the ability to store energy for extended periods of time. a. Nucleic acids b. Proteins c. Carbohydrates d. Lipids 7. Sugars such as glucose, ...
... d. Sugar bases 6. Organic molecules called ____________ are insoluble in water, are often found in biological membranes and other waterproof coverings and have the ability to store energy for extended periods of time. a. Nucleic acids b. Proteins c. Carbohydrates d. Lipids 7. Sugars such as glucose, ...
Microsoft Word
... The foundation of synthetic organic chemistry rests on the ability to form and manipulate carbon-carbon bonds. The increasing demand of coupled products in chemical and pharmaceutical industries has prompted the development of several transition metal catalysts, which aim to exert the highest turnov ...
... The foundation of synthetic organic chemistry rests on the ability to form and manipulate carbon-carbon bonds. The increasing demand of coupled products in chemical and pharmaceutical industries has prompted the development of several transition metal catalysts, which aim to exert the highest turnov ...
Chapter 18 Reactions of aromatics
... Mechanism of NBS (Radical) Reaction • Abstraction of a benzylic hydrogen atom generates an intermediate benzylic radical • Reacts with Br2 to yield product • Br· radical cycles back into reaction to carry chain • Br2 produced from reaction of HBr with NBS ...
... Mechanism of NBS (Radical) Reaction • Abstraction of a benzylic hydrogen atom generates an intermediate benzylic radical • Reacts with Br2 to yield product • Br· radical cycles back into reaction to carry chain • Br2 produced from reaction of HBr with NBS ...
KINETIC AND MECHANISTIC STUDY OF OXIDATION OF ESTER
... temperature by both the flask. In order to prevent the hydrolysis, required volume of given ester was directly added to acid solution with micro pipette just before mixing it with permanganate solution. The course of reaction was followed by measuring the absorbance (optical density) ...
... temperature by both the flask. In order to prevent the hydrolysis, required volume of given ester was directly added to acid solution with micro pipette just before mixing it with permanganate solution. The course of reaction was followed by measuring the absorbance (optical density) ...
Study Guide for Exam 2 Chapter 12
... From their structural or line-angle formulas, write names of aromatic compounds, including those with more than one substituent on the benzene ring, and those in which the benzene ring is regarded as a substituent (phenyl ) group. From their names, draw structural formulas of aromatic compounds incl ...
... From their structural or line-angle formulas, write names of aromatic compounds, including those with more than one substituent on the benzene ring, and those in which the benzene ring is regarded as a substituent (phenyl ) group. From their names, draw structural formulas of aromatic compounds incl ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... Considerations: neither the electrophile (RCN) nor the nucleophile (water) is very reactive. Since we are in acid protonate the CN group to make it a better electrophile. Then attack it with the water nucleophile to add water. This results in reduction of C-N bond order and creation of C to O bonds ...
... Considerations: neither the electrophile (RCN) nor the nucleophile (water) is very reactive. Since we are in acid protonate the CN group to make it a better electrophile. Then attack it with the water nucleophile to add water. This results in reduction of C-N bond order and creation of C to O bonds ...
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 21 – Phenoles and Aryl
... – Formally this results in removal of a pair of electrons and two protons from hydroquinone - This reaction is reversible ...
... – Formally this results in removal of a pair of electrons and two protons from hydroquinone - This reaction is reversible ...
Exp`t 88 - Chemistry Courses
... consider what by-product is formed if acetic acid were used, and how this could affect the equilibrium between reagent and products.) 2. In developing this experiment, precautions were taken to ensure that acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid were mixed together before the isopropyl alcohol was added. ...
... consider what by-product is formed if acetic acid were used, and how this could affect the equilibrium between reagent and products.) 2. In developing this experiment, precautions were taken to ensure that acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid were mixed together before the isopropyl alcohol was added. ...
Problem Set 12-2: Organic Chemistry
... Fewer dispersion forces with alkenes because they have two fewer electrons. 12. Which 4 functional groups are capable of hydrogen bonding when pure? Alcohols, carboxylic acids, amides and amines. 13. Which additional functional groups are capable of forming hydrogen bonding with the hydrogen atom of ...
... Fewer dispersion forces with alkenes because they have two fewer electrons. 12. Which 4 functional groups are capable of hydrogen bonding when pure? Alcohols, carboxylic acids, amides and amines. 13. Which additional functional groups are capable of forming hydrogen bonding with the hydrogen atom of ...
Carboxylic Acids Theory Sheet
... Carboxylic acids are compounds with the formula of that illustrated in Figure 1 and the general formula R-COOH where R is part of a larger organic molecule e.g.CH3, C2H5, C6H5. To name carboxylic acids you must look at the alkyl chain, take its prefix and add “oic acid” to it. CH3CH2COOH is PROPANOI ...
... Carboxylic acids are compounds with the formula of that illustrated in Figure 1 and the general formula R-COOH where R is part of a larger organic molecule e.g.CH3, C2H5, C6H5. To name carboxylic acids you must look at the alkyl chain, take its prefix and add “oic acid” to it. CH3CH2COOH is PROPANOI ...
Synopsis
... corresponding sulfoxides has been developed though non stereoselectively. The diastereomeric sulfilimines behave in a stereoconvergent fashion and afford products with the same configuration at carbon. An efficient route to αhydroxy-β-amino acid derivatives AHDA and AHPBA was developed using a commo ...
... corresponding sulfoxides has been developed though non stereoselectively. The diastereomeric sulfilimines behave in a stereoconvergent fashion and afford products with the same configuration at carbon. An efficient route to αhydroxy-β-amino acid derivatives AHDA and AHPBA was developed using a commo ...
Biochemistry Assessment
... A change in the state of matter in the reactants B net release of free energy C transfer of energy from one form to another D transfer of electrons between atoms _______8. Organic compounds contain ______________________. A carbon and usually other elements B only carbon C many kinds of elements exc ...
... A change in the state of matter in the reactants B net release of free energy C transfer of energy from one form to another D transfer of electrons between atoms _______8. Organic compounds contain ______________________. A carbon and usually other elements B only carbon C many kinds of elements exc ...
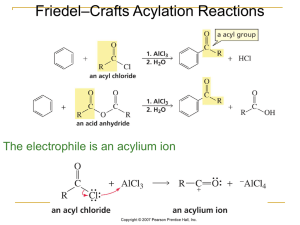
Organic Reactions Note – Student
... Oxidizing agents and oxidation reactions will be discussed in more detail later in this course In inorganic chemistry an oxidizing agent accepts electrons during a chemical reaction In organic chemistry an oxidizing agent increases the number of carbon to oxygen bonds in an organic molecule The symb ...
... Oxidizing agents and oxidation reactions will be discussed in more detail later in this course In inorganic chemistry an oxidizing agent accepts electrons during a chemical reaction In organic chemistry an oxidizing agent increases the number of carbon to oxygen bonds in an organic molecule The symb ...
sample paper - CBSE PORTAL
... Q.9 What do you mean by activity and selectivity of catalysts? Q.10 Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Q.11 Mention the factors which affect the rate of a chemical reaction. Q.12 How will you convert – 1. Toluene to benzyl alcohol 2. But –1-ene to But -2-e ...
... Q.9 What do you mean by activity and selectivity of catalysts? Q.10 Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Q.11 Mention the factors which affect the rate of a chemical reaction. Q.12 How will you convert – 1. Toluene to benzyl alcohol 2. But –1-ene to But -2-e ...
Synthetic Polymers
... Describe the polymerisation of amino acids to form proteins, hence compare the structural similarities & differences of nylon & proteins. ...
... Describe the polymerisation of amino acids to form proteins, hence compare the structural similarities & differences of nylon & proteins. ...
Amino Acids
... Autotrophic organisms make their own food and are not dependant on other organisms for nutrition. Green plants take in inorganic substances and combine them to form organic materials such as sugars. ...
... Autotrophic organisms make their own food and are not dependant on other organisms for nutrition. Green plants take in inorganic substances and combine them to form organic materials such as sugars. ...
Eliminations
... unless a strong hindered base is used in which case E2 will be favored. For example, t-‐butoxide is a sterically hindered base. Due to its bulk, it is not very nucleophilic. (2) Secondary alkyl h ...
... unless a strong hindered base is used in which case E2 will be favored. For example, t-‐butoxide is a sterically hindered base. Due to its bulk, it is not very nucleophilic. (2) Secondary alkyl h ...
Reactions to know from Chapters 17, 18, 19
... Starting with either an aldehyde or a ketone, you can see that the hemiacetals formed are characterized by having a carbon bonded to an OH- group and an OR- group. Here, the oxygen of the alcohol attacks and bonds with the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde or ketone If the alcohol group and the ...
... Starting with either an aldehyde or a ketone, you can see that the hemiacetals formed are characterized by having a carbon bonded to an OH- group and an OR- group. Here, the oxygen of the alcohol attacks and bonds with the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde or ketone If the alcohol group and the ...
CH 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... • Carboxylic acids transfer a proton to a base to give anions, which are good nucleophiles in SN2 reactions • Like ketones, carboxylic acids undergo addition of nucleophiles to the carbonyl group • In addition, carboxylic acids undergo other reactions characteristic of neither alcohols nor ketones ...
... • Carboxylic acids transfer a proton to a base to give anions, which are good nucleophiles in SN2 reactions • Like ketones, carboxylic acids undergo addition of nucleophiles to the carbonyl group • In addition, carboxylic acids undergo other reactions characteristic of neither alcohols nor ketones ...
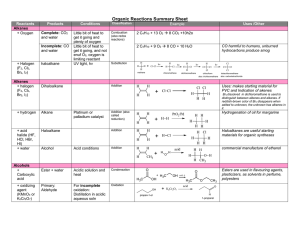
Organic Reactions Summary Sheet
... neutralize each other. Other rxns that “protect” F.G. are required ...
... neutralize each other. Other rxns that “protect” F.G. are required ...
Exam 3 Review
... What is the name for this alcohol / ether / aldehyde / ketone? Is an alcohol 1°, 2°, or 3°? Describe hydrogen bonding in alcohols, and compare alcohol polarity to ether polarity. What are the acid/base properties of alcohols? Rank these compounds in order of acidity. How are Grignard reagents prepar ...
... What is the name for this alcohol / ether / aldehyde / ketone? Is an alcohol 1°, 2°, or 3°? Describe hydrogen bonding in alcohols, and compare alcohol polarity to ether polarity. What are the acid/base properties of alcohols? Rank these compounds in order of acidity. How are Grignard reagents prepar ...
Yeast Reduction #812
... Treatment of a ketone with either agent will reduce the carbonyl group to yield an alcohol. However, these reducing agents do not react to form a chiral alcohol because the hydride can attack both sides of the planar carbonyl group yielding a mixture of both enantiomers.4 In order to achieve a chira ...
... Treatment of a ketone with either agent will reduce the carbonyl group to yield an alcohol. However, these reducing agents do not react to form a chiral alcohol because the hydride can attack both sides of the planar carbonyl group yielding a mixture of both enantiomers.4 In order to achieve a chira ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.