Transition Metal Chemistry 2 2011.12.2 Ⅰ Fundamental
... (4) Role of transition metal catalysts in industrial acetic acid synthesis. Acetic acid is one of the most important chemicals and was produced by (destructive distillation of coal. History of acetic acid production revealed importance of transition metal catalysts. (4-1) Hydration of acetylene---M ...
... (4) Role of transition metal catalysts in industrial acetic acid synthesis. Acetic acid is one of the most important chemicals and was produced by (destructive distillation of coal. History of acetic acid production revealed importance of transition metal catalysts. (4-1) Hydration of acetylene---M ...
Derivatization reagents
... ● Purified, dried and packaged under nitrogen in convenient 50mL Hypo-Vial Sample Storage Vials ● Supplied with elastomer septa, allowing immediate access to the sample without exposure to moisture and oxygen ● Use polar solvents (acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, pyridine, tetrahy ...
... ● Purified, dried and packaged under nitrogen in convenient 50mL Hypo-Vial Sample Storage Vials ● Supplied with elastomer septa, allowing immediate access to the sample without exposure to moisture and oxygen ● Use polar solvents (acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, pyridine, tetrahy ...
Carboxylic Acids, Amines, and Amides
... Formic acid, HCOOH: Chemical that is present in the sting of ants. Acetic acid, CH3COOH: dilute (5%) aqueous acetic acid is known as vinegar. Butyric acid, CH3CH2CH2COOH: Chemical responsible for odor of rancid butter. ...
... Formic acid, HCOOH: Chemical that is present in the sting of ants. Acetic acid, CH3COOH: dilute (5%) aqueous acetic acid is known as vinegar. Butyric acid, CH3CH2CH2COOH: Chemical responsible for odor of rancid butter. ...
26th IChO Theory Problem No
... Show all non-bonding electrons. b) Carefully draw the geometries of the same 5 molecules. (Disregard small deviations from "ideal" angles.) c) A compound, consisting of sulfur (one atom per molecule), oxygen, and one or more of the elements F, Cl, Br, and I, was examined. A small amount of the subst ...
... Show all non-bonding electrons. b) Carefully draw the geometries of the same 5 molecules. (Disregard small deviations from "ideal" angles.) c) A compound, consisting of sulfur (one atom per molecule), oxygen, and one or more of the elements F, Cl, Br, and I, was examined. A small amount of the subst ...
Biology Name: TEACHER KEY Life Substances Notes
... Class of macromolecules that do not dissolve in water ii. Lipids usually serve one of three functions: 1. Energy storage 2. structural support in cell membranes (phospholipids) 3. serve as reactants ( starting materials) for metabolic reactions iii. Fatty acids are the building blocks (or monomers) ...
... Class of macromolecules that do not dissolve in water ii. Lipids usually serve one of three functions: 1. Energy storage 2. structural support in cell membranes (phospholipids) 3. serve as reactants ( starting materials) for metabolic reactions iii. Fatty acids are the building blocks (or monomers) ...
Lecture 14a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... from d= ~3.1-3.7 ppm and d= ~5.2-5.4 ppm Presence of the aromatic and ferrocene protons with the appropriate splitting pattern and integration The oxidation product only displays one protons for the five-membered ring at d= ~6.5 ppm 13C-NMR spectrum Presence of two additional carbon atoms (o ...
... from d= ~3.1-3.7 ppm and d= ~5.2-5.4 ppm Presence of the aromatic and ferrocene protons with the appropriate splitting pattern and integration The oxidation product only displays one protons for the five-membered ring at d= ~6.5 ppm 13C-NMR spectrum Presence of two additional carbon atoms (o ...
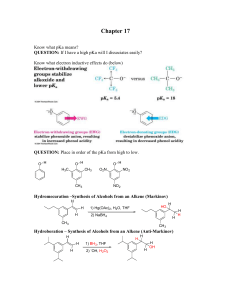
Chapter 17 - Ellis Benjamin
... Chapter 17 Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
... Chapter 17 Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
Chapter 19 - people.vcu.edu
... o LiAlH4 completely chops off the oxygen of an amide instead of reducing the carbonyl to an alcohol Gabriel synthesis – always makes 1° amines o Phthalimide is deprotonated by a strong base ...
... o LiAlH4 completely chops off the oxygen of an amide instead of reducing the carbonyl to an alcohol Gabriel synthesis – always makes 1° amines o Phthalimide is deprotonated by a strong base ...
Organic Chemistry (HL) Revision Questions
... Benzene, C6H6, is a planar compound which differs from the non-planar structure of cyclohexane, C6H12. The structures of benzene and the most stable form of cyclohexane are represented below. ...
... Benzene, C6H6, is a planar compound which differs from the non-planar structure of cyclohexane, C6H12. The structures of benzene and the most stable form of cyclohexane are represented below. ...
Enantiodivergent conversion of chiral secondary alcohols into
... •Only works for aryl alcohols •Aryl boranes (e.g. Ph-9-BBN) incompatible due to protodeboronation during aqueous oxidative work-up •Indanol-derived carbamate gives same enantiomer (retention) with triethyl borane or ethylboronic acid (pyramidalization of geometrically constrained carbanion) ...
... •Only works for aryl alcohols •Aryl boranes (e.g. Ph-9-BBN) incompatible due to protodeboronation during aqueous oxidative work-up •Indanol-derived carbamate gives same enantiomer (retention) with triethyl borane or ethylboronic acid (pyramidalization of geometrically constrained carbanion) ...
Reaction types and Stoichiometry
... 19. Which of the following is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction shown above? A Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 B 2Al + 3H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2 _ C 2Al + 3H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 D 2Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 20. Which of these is the general formula for a double-replacement reaction? A B ...
... 19. Which of the following is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction shown above? A Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 B 2Al + 3H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2 _ C 2Al + 3H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 D 2Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 20. Which of these is the general formula for a double-replacement reaction? A B ...
Fisher Esterification - OpenBU
... Your TF will then heat your reaction for 10 minutes under microwave irradiation. When the reaction is complete, allow the mixture to cool to room temperature. It is actually a good idea to either vent the vessel with a syringe needle or cool in an ice bath to make sure there is no sudden pressure re ...
... Your TF will then heat your reaction for 10 minutes under microwave irradiation. When the reaction is complete, allow the mixture to cool to room temperature. It is actually a good idea to either vent the vessel with a syringe needle or cool in an ice bath to make sure there is no sudden pressure re ...
Chapter Three
... Draw curved-arrow mechanisms to illustrate proton transfer reactions between Hydronium ion and bisulfide ion (SH-) ...
... Draw curved-arrow mechanisms to illustrate proton transfer reactions between Hydronium ion and bisulfide ion (SH-) ...
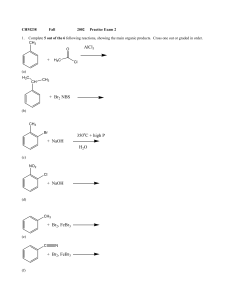
+ NaOH 350 C + high P H2O + H3C AlCl3 + NaOH + Br2, FeBr3
... processes can be accomplished with 2 steps, but there is more than one correct answer for each. Assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated. ...
... processes can be accomplished with 2 steps, but there is more than one correct answer for each. Assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated. ...
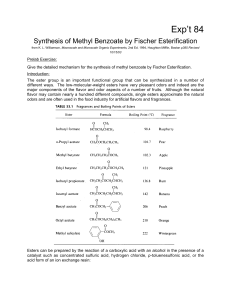
Synthesis of Methyl Benzoate by Fisher Esterification
... position of the equilibrium can be shifted by adding more of the acid or of the alcohol, depending on cost or availability. The mechanism of the reaction involves initial protonation of the carboxyl group, attack by the nucleophilic hydroxyl, a proton transfer, and loss of water followed by loss of ...
... position of the equilibrium can be shifted by adding more of the acid or of the alcohol, depending on cost or availability. The mechanism of the reaction involves initial protonation of the carboxyl group, attack by the nucleophilic hydroxyl, a proton transfer, and loss of water followed by loss of ...
Notes, Part II
... Methanol (common: methyl alcohol) Used to “denature” ethanol; “poisons” the ethanol making it unfit to drink. Why do that? Ethanol (common: ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol) The “alcohol” in alcoholic beverages – the intoxicating substance Naturally produced through fermentation of glucose 2 ...
... Methanol (common: methyl alcohol) Used to “denature” ethanol; “poisons” the ethanol making it unfit to drink. Why do that? Ethanol (common: ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol) The “alcohol” in alcoholic beverages – the intoxicating substance Naturally produced through fermentation of glucose 2 ...
Document
... 21.7: Preparation of Amines by Alkylation of Ammonia Ammonia and other alkylamines are good nucleophiles and react with 1° and 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction yielding alkyl amines. ...
... 21.7: Preparation of Amines by Alkylation of Ammonia Ammonia and other alkylamines are good nucleophiles and react with 1° and 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction yielding alkyl amines. ...
aminoalkanes (or amines)
... The low molecular mass aminoalkanes have relatively high melting and boiling point due to hydrogen bonds, but the properties of larger aminoalkanes are dominated by the alkyl groups and weak dipole-dipole interactions Aminomethane and aminoethane are gases Aminopropane and aminobutane are volatile ...
... The low molecular mass aminoalkanes have relatively high melting and boiling point due to hydrogen bonds, but the properties of larger aminoalkanes are dominated by the alkyl groups and weak dipole-dipole interactions Aminomethane and aminoethane are gases Aminopropane and aminobutane are volatile ...
protein practice exam
... c. synthesis of cholesterol d. the removal of the nitrogen group from an amino acid 8. All of the following are functions of protein in the body EXCEPT: a. growth and maintenance b. production of enzymes c. production of cholesterol d. antibody formation 9. Which is the source of COMPLETE protein a ...
... c. synthesis of cholesterol d. the removal of the nitrogen group from an amino acid 8. All of the following are functions of protein in the body EXCEPT: a. growth and maintenance b. production of enzymes c. production of cholesterol d. antibody formation 9. Which is the source of COMPLETE protein a ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.