Exam 1 Review Sheet Chapter 15 Chemistry 110b
... functional groups. Know the mechanism of formation/hydrolysis for an acetal (e.g., acetaldehyde + 2CH3OH + H+(cat.)). Be aware of the utility of acetals and ketals [and their thio (sulfur) analogs] as protecting groups in organic synthesis. [10e, 744-750; 9e, 699-705] ...
... functional groups. Know the mechanism of formation/hydrolysis for an acetal (e.g., acetaldehyde + 2CH3OH + H+(cat.)). Be aware of the utility of acetals and ketals [and their thio (sulfur) analogs] as protecting groups in organic synthesis. [10e, 744-750; 9e, 699-705] ...
CN>Chapter 22CT>Carbonyl Alpha
... Base-promoted reaction occurs through an enolate anion intermediate. Monohalogenated products are themselves rapidly turned into enolate ...
... Base-promoted reaction occurs through an enolate anion intermediate. Monohalogenated products are themselves rapidly turned into enolate ...
Alcohols from Alkenes: Oxymercuration–Demercuration
... form of the starting material reacts in such a way that it gives a specific stereoisomeric form of the product. ...
... form of the starting material reacts in such a way that it gives a specific stereoisomeric form of the product. ...
Chapter 9: Aldehydes and Ketones
... Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the presence of the carbonyl group, which is perhaps the most important functional group in organic chemistry. Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon atom. The remaining group may be another hydrogen atom or any aliphatic ...
... Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the presence of the carbonyl group, which is perhaps the most important functional group in organic chemistry. Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon atom. The remaining group may be another hydrogen atom or any aliphatic ...
STOICHIOMETRY
... theoretical yield Often, either accidentally or deliberately, one of the reagents in a reaction is present in excess while another reagent is the limiting reagent, i.e., there is not enough of it to use up all the reagent which is in excess. Only the quantity of limiting reagent can be used to d ...
... theoretical yield Often, either accidentally or deliberately, one of the reagents in a reaction is present in excess while another reagent is the limiting reagent, i.e., there is not enough of it to use up all the reagent which is in excess. Only the quantity of limiting reagent can be used to d ...
Tech Info - Davis Instruments
... finalized by dehydration of the alcohol group in a strong base, resulting in the loss of water and the formation of an α,β-unsaturated product (Figure 4). ...
... finalized by dehydration of the alcohol group in a strong base, resulting in the loss of water and the formation of an α,β-unsaturated product (Figure 4). ...
Slide 1
... (1,2,3indanetrione monohydrate) in 50 mL of water. The test mixture is heated to boiling for 15-20 sec; This reaction is important not only because it is a qualitative test, but also because it is the source of the absorbing material that can be measured quantitatively by an automatic amino acid ana ...
... (1,2,3indanetrione monohydrate) in 50 mL of water. The test mixture is heated to boiling for 15-20 sec; This reaction is important not only because it is a qualitative test, but also because it is the source of the absorbing material that can be measured quantitatively by an automatic amino acid ana ...
Lecture12
... Reductive elimination is usually a fast step in the catalytic cycle, so there is less focus on designing ligands to promote it. Reductive elimination is favored by electron deficient ligands (opposite of oxidative addition) and sterically demanding ligands (same as oxidative addition). Main features ...
... Reductive elimination is usually a fast step in the catalytic cycle, so there is less focus on designing ligands to promote it. Reductive elimination is favored by electron deficient ligands (opposite of oxidative addition) and sterically demanding ligands (same as oxidative addition). Main features ...
synthetic approaches for quinoline and isoquinoline
... Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, S.I.T.M, LKO, India Received: 10 March 2011, Revised and Accepted: 11 April 2011 ABSTRACT The Quinoline and Isoquinoline nucleus is found to be very important in pharmacy field. In recent years, a lot of synthetic drugs have been sy ...
... Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, S.I.T.M, LKO, India Received: 10 March 2011, Revised and Accepted: 11 April 2011 ABSTRACT The Quinoline and Isoquinoline nucleus is found to be very important in pharmacy field. In recent years, a lot of synthetic drugs have been sy ...
Organometallic Chemistry between organic and inorganic
... which is the method of choice for clean and efficient synthesis of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals and many larger-scale chemicals. Many plastics (polythene, polypropene, butadiene rubber, ...) and detergents are made via organometallic catalysis. Organometallic chemistry is also the basis for under ...
... which is the method of choice for clean and efficient synthesis of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals and many larger-scale chemicals. Many plastics (polythene, polypropene, butadiene rubber, ...) and detergents are made via organometallic catalysis. Organometallic chemistry is also the basis for under ...
WRL3502.tmp
... General Concepts Alkyl halides are most commonly synthesized from alcohols by replacing the hydroxyl group with a halide substituent. This is an example of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution, which is part of a very important group of reactions. The overall reaction is the same, but the mechanism v ...
... General Concepts Alkyl halides are most commonly synthesized from alcohols by replacing the hydroxyl group with a halide substituent. This is an example of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution, which is part of a very important group of reactions. The overall reaction is the same, but the mechanism v ...
Oxidation Reactions
... Comprehensive Organic Synthesis, Eds. B. M. Trost, I. Fleming, Pergamon, Oxford, 1990, Vol. 7, Chapter 3.2, pp 389-436. Directed epoxidation reactions, as their name implies are reactions in which the reagent containing the oxygen that is to be transferred to the substrate is tethered to the reactin ...
... Comprehensive Organic Synthesis, Eds. B. M. Trost, I. Fleming, Pergamon, Oxford, 1990, Vol. 7, Chapter 3.2, pp 389-436. Directed epoxidation reactions, as their name implies are reactions in which the reagent containing the oxygen that is to be transferred to the substrate is tethered to the reactin ...
Document
... Rate of the reaction decreases as the alkyl substitution increases Highly sensitive to the nature of the phosphine ligand Analogous complexes with alkylphosphine ligands are inactive Highly selective for C=C over C=O ...
... Rate of the reaction decreases as the alkyl substitution increases Highly sensitive to the nature of the phosphine ligand Analogous complexes with alkylphosphine ligands are inactive Highly selective for C=C over C=O ...
i m. pharm. - Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences
... The advantage of biocatalysis is that enzyme-catalyzed reactions are often highly enantioselective and regioselective. They can be carried out at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure thus avoiding the use of more extreme conditions that can cause problems with isomerization, racemization, e ...
... The advantage of biocatalysis is that enzyme-catalyzed reactions are often highly enantioselective and regioselective. They can be carried out at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure thus avoiding the use of more extreme conditions that can cause problems with isomerization, racemization, e ...
Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes 1) Which of the following
... 60) Which series of reactions described below, if any, will result in the formation of 2-methylpentan-3one starting with 1-propanol? A) 1. (CH3)2CHMgBr/ diethyl ether ...
... 60) Which series of reactions described below, if any, will result in the formation of 2-methylpentan-3one starting with 1-propanol? A) 1. (CH3)2CHMgBr/ diethyl ether ...
FREE RADICAL REACTIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
... • Overcome by only having a very low concentration of radicals present in a reaction • Now there are many ways to use these highly reactive species in selective (& synthetically useful) organic reactions • Good example is the radical chain process for allylic halogenation activated C-H ...
... • Overcome by only having a very low concentration of radicals present in a reaction • Now there are many ways to use these highly reactive species in selective (& synthetically useful) organic reactions • Good example is the radical chain process for allylic halogenation activated C-H ...
Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
... conjugated enone as it is formed, especially if reaction conditions are pushed, eg high temperature. Mixed or "crossed" Aldol Reactions — If two different carbonyl compounds are allowed to react in an aldol reaction four products usually result; each carbonyl compound forms an enolate and each enola ...
... conjugated enone as it is formed, especially if reaction conditions are pushed, eg high temperature. Mixed or "crossed" Aldol Reactions — If two different carbonyl compounds are allowed to react in an aldol reaction four products usually result; each carbonyl compound forms an enolate and each enola ...
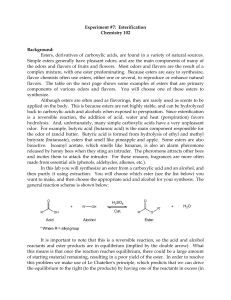
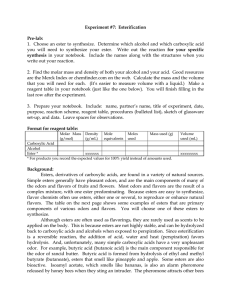
ESTERIFICATION
... flavor chemists often use esters, either one or several, to reproduce or enhance natural flavors. The table on the next page shows some examples of esters that are primary components of various odors and flavors. You will choose one of these esters to synthesize. Although esters are often used as fl ...
... flavor chemists often use esters, either one or several, to reproduce or enhance natural flavors. The table on the next page shows some examples of esters that are primary components of various odors and flavors. You will choose one of these esters to synthesize. Although esters are often used as fl ...
Lab 7_Esterification
... flavor chemists often use esters, either one or several, to reproduce or enhance natural flavors. The table on the next page shows some examples of esters that are primary components of various odors and flavors. You will choose one of these esters to synthesize. Although esters are often used as fl ...
... flavor chemists often use esters, either one or several, to reproduce or enhance natural flavors. The table on the next page shows some examples of esters that are primary components of various odors and flavors. You will choose one of these esters to synthesize. Although esters are often used as fl ...
Discodermolide

(+)-Discodermolide is a polyketide natural product found to stabilize microtubule. (+)-discodermolide was isolated by Gunasekera and his co-workers at the Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute from the deep-sea sponge Discodermia dissoluta in 1990. (+)-Discodermolide was found to be a potent inhibitor of tumor cell growth in several MDR cancer cell lines. (+)-discodermolide also shows some unique characters, including a linear backbone structure, immunosuppressive properties both in vitro and in vivo, potent induction of an accelerated senescence phenotype, and synergistic antiproliferative activity in combination with paclitaxel. Discodermolide was recognized as one of the most potent natural promoters of tubulin assembly. A large number of efforts toward the total synthesis of (+)-discodermolide were directed by its interesting biological activities and extreme scarcity of natural sources (0.002% w/w from frozen marine sponge). The compound supply necessary for complete clinical trials cannot be met by harvesting, isolation, and purification. As of 2005, attempts at synthesis or semi-synthesis by fermentation have proven unsuccessful. As a result, all discodermolide used in preclinical studies and clinical trials has come from large-scale total synthesis.