Asymmetric Glycine Enolate Aldol Reactions
... H, NH), 3.85-4.60 (m,3 H, NCHCH,), 2.88 (m,2 H, PhCH,); I3C reaction mixture was stirred at 0 OC for an additional 15 min and then N M R (22.5 MHz, CDCI,) d 159.9, 136.0, 129.1, 128.8, 127.0, 69.4, 53.6, quenched by the addition of 0.56 mL of water, 0.56 mL of aqueous 15% 41; [aID+4.9' (EtOH, c 1.10 ...
... H, NH), 3.85-4.60 (m,3 H, NCHCH,), 2.88 (m,2 H, PhCH,); I3C reaction mixture was stirred at 0 OC for an additional 15 min and then N M R (22.5 MHz, CDCI,) d 159.9, 136.0, 129.1, 128.8, 127.0, 69.4, 53.6, quenched by the addition of 0.56 mL of water, 0.56 mL of aqueous 15% 41; [aID+4.9' (EtOH, c 1.10 ...
Chapter 20 Amines-part 2
... t The nitrogen lone pair can also make a carbon nucleophilic by resonance ...
... t The nitrogen lone pair can also make a carbon nucleophilic by resonance ...
Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition to the
... The Wittig reaction is highly selective for ketones and aldehydes; esters, lactones, nitriles and amides will not react but are tolerated in the substrate. Acidic groups (alcohols, amine and carboxylic acids) are not tolerated. O O ...
... The Wittig reaction is highly selective for ketones and aldehydes; esters, lactones, nitriles and amides will not react but are tolerated in the substrate. Acidic groups (alcohols, amine and carboxylic acids) are not tolerated. O O ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... Recall that we can create carbocations in several ways: 1. As shown above by a group leaving. ...
... Recall that we can create carbocations in several ways: 1. As shown above by a group leaving. ...
- Thieme Connect
... was subjected to the reaction conditions, after acidic workup only 4-bromobenzaldehyde was obtained. This result could be explained by much faster oxidation of the aminal than the acetal function by KMnO4, or by assuming that the intermediate leading to an amide is an imine rather than an aminal. In ...
... was subjected to the reaction conditions, after acidic workup only 4-bromobenzaldehyde was obtained. This result could be explained by much faster oxidation of the aminal than the acetal function by KMnO4, or by assuming that the intermediate leading to an amide is an imine rather than an aminal. In ...
Chapter 4. Functional Group Transformations: Oxidation and
... t-Butyl Peroxybenzoate: copper(I) salts catalyze the allylic oxidation of alkenes in the presence of peresters, such as tert-BuO2COPh, to afford the corresponding allylic benozate esters. ...
... t-Butyl Peroxybenzoate: copper(I) salts catalyze the allylic oxidation of alkenes in the presence of peresters, such as tert-BuO2COPh, to afford the corresponding allylic benozate esters. ...
Practice Paper - 3
... Five reason for the following (a) Grignard reagents should be prepared under an hydrous condition? (b) Ethanol has higher B. P. in comparison to methoxy methane. OR (a) Explain how does the –OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring , activate it towards electrophilic substitution? (b) Alcohols ...
... Five reason for the following (a) Grignard reagents should be prepared under an hydrous condition? (b) Ethanol has higher B. P. in comparison to methoxy methane. OR (a) Explain how does the –OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring , activate it towards electrophilic substitution? (b) Alcohols ...
ALDOL CONDENSATION
... In the first step of the mechanism, an α‐proton is removed by a strong base, resulting in the formation of an enolate anion, which is made relatively stable by the delocalization of electrons. ¾ Next, the carbonyl carbon of the (other) ester is nucleophilically attacked by the enolate anion. ...
... In the first step of the mechanism, an α‐proton is removed by a strong base, resulting in the formation of an enolate anion, which is made relatively stable by the delocalization of electrons. ¾ Next, the carbonyl carbon of the (other) ester is nucleophilically attacked by the enolate anion. ...
69. A general approach to the enantioselective -oxidation of aldehydes via synergistic catalysis
... 4, 6, and 13–14). Finally, subjection of (S)- and (R)-citronellal to oxidation yields the desired anti and syn products, respectively (entries 13–14). These experiments clearly demonstrate the value of catalyst-induced stereocontrol in preference to substratedirected induction. As shown in Scheme 1, ...
... 4, 6, and 13–14). Finally, subjection of (S)- and (R)-citronellal to oxidation yields the desired anti and syn products, respectively (entries 13–14). These experiments clearly demonstrate the value of catalyst-induced stereocontrol in preference to substratedirected induction. As shown in Scheme 1, ...
Get PDF - Wiley Online Library
... compounds 7b and 8, we decided to investigate the influence of allylic methyl and phenyl substituents on the formation of six-membered cyclic dehydroamino acids via RCM. This required the synthesis of substituted halides 15 and 16, which can then be used in the alkylation of the protected dehydroala ...
... compounds 7b and 8, we decided to investigate the influence of allylic methyl and phenyl substituents on the formation of six-membered cyclic dehydroamino acids via RCM. This required the synthesis of substituted halides 15 and 16, which can then be used in the alkylation of the protected dehydroala ...
applied sciences Chiral β-Amino Alcohols as Ligands for the N
... enantioselection of the process slightly improved to 78% ee. In order to try to improve the yield, the reaction was repeated and an upward temperature gradient was applied: after stirring for 1 h at 0 °C, the reaction was allowed to gradually reach room temperature. We were delighted to see that, un ...
... enantioselection of the process slightly improved to 78% ee. In order to try to improve the yield, the reaction was repeated and an upward temperature gradient was applied: after stirring for 1 h at 0 °C, the reaction was allowed to gradually reach room temperature. We were delighted to see that, un ...
Topic 8 Assessed Homework Task - A
... A dilute aqueous solution of ethanol can be produced by the fermentation of an aqueous solution of glucose. It is claimed that the ethanol obtained from this solution is a carbon-neutral biofuel. Write an equation for this fermentation reaction. Give two other essential conditions for this reaction ...
... A dilute aqueous solution of ethanol can be produced by the fermentation of an aqueous solution of glucose. It is claimed that the ethanol obtained from this solution is a carbon-neutral biofuel. Write an equation for this fermentation reaction. Give two other essential conditions for this reaction ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nitriles
... clean, usually affording the amine in >80% yield. However, because nitriles are often made from amides, it is often easier to convert the amide to the amine, rather than go through the nitrile. The only real exception to this is in the preparation of amino acids, which we shall discuss in the weeks ...
... clean, usually affording the amine in >80% yield. However, because nitriles are often made from amides, it is often easier to convert the amide to the amine, rather than go through the nitrile. The only real exception to this is in the preparation of amino acids, which we shall discuss in the weeks ...
Chapter 12- Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds, Redox Reactions
... solution • Ex. Note: 1) Count your carbons! 2) Watch out for reactions with other functionalities! (alkenes) ...
... solution • Ex. Note: 1) Count your carbons! 2) Watch out for reactions with other functionalities! (alkenes) ...
Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides
... • Alcohols and ethers are not good electrophiles (they do not contain a good leaving group). • Must convert the hydroxyl group (in alcohols) or the alkoxy group (in ethers) into a good leaving group before substitution or elimination will occur • Epoxides are strained three‐memb ...
... • Alcohols and ethers are not good electrophiles (they do not contain a good leaving group). • Must convert the hydroxyl group (in alcohols) or the alkoxy group (in ethers) into a good leaving group before substitution or elimination will occur • Epoxides are strained three‐memb ...
(C3H7)3NH[CrO3X],(X=F, Cl), Reagents for Oxidation of
... Oxidation of organic compounds in general, and of alcohols in particular, under mild, aprotic conditions is an important reaction in synthetic organic chemistry [1] . For this purpose different Cr(VI) based oxidants are reported in the literature. However, some of the reported chromium ...
... Oxidation of organic compounds in general, and of alcohols in particular, under mild, aprotic conditions is an important reaction in synthetic organic chemistry [1] . For this purpose different Cr(VI) based oxidants are reported in the literature. However, some of the reported chromium ...
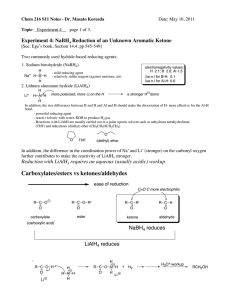
Carboxylates/esters vs ketones/aldehydes
... BH3 becomes B(OC2H5)3 by reacting with ethanol, then, when heated with water, becomes B(OH)3. The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Becau ...
... BH3 becomes B(OC2H5)3 by reacting with ethanol, then, when heated with water, becomes B(OH)3. The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Becau ...
Stereoselective synthesis: chiral auxiliaries
... • Aldehyde will place substituent in pseudo-equatorial position (1,3-diaxail strain) • Therefore alkene geometry controls the relative stereochemistry (like aldol rct) 123.702 Organic Chemistry ...
... • Aldehyde will place substituent in pseudo-equatorial position (1,3-diaxail strain) • Therefore alkene geometry controls the relative stereochemistry (like aldol rct) 123.702 Organic Chemistry ...
Chapter 4 - WordPress.com
... • Write formula for each reactant and product on the correct side of the “reaction arrow” • Count atoms of each element on both sides of arrow • Start with the compound which has the most complex formula • Add coefficients to chemical formulas to balance numbers of each atom • Trial and error begins ...
... • Write formula for each reactant and product on the correct side of the “reaction arrow” • Count atoms of each element on both sides of arrow • Start with the compound which has the most complex formula • Add coefficients to chemical formulas to balance numbers of each atom • Trial and error begins ...
Discodermolide

(+)-Discodermolide is a polyketide natural product found to stabilize microtubule. (+)-discodermolide was isolated by Gunasekera and his co-workers at the Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute from the deep-sea sponge Discodermia dissoluta in 1990. (+)-Discodermolide was found to be a potent inhibitor of tumor cell growth in several MDR cancer cell lines. (+)-discodermolide also shows some unique characters, including a linear backbone structure, immunosuppressive properties both in vitro and in vivo, potent induction of an accelerated senescence phenotype, and synergistic antiproliferative activity in combination with paclitaxel. Discodermolide was recognized as one of the most potent natural promoters of tubulin assembly. A large number of efforts toward the total synthesis of (+)-discodermolide were directed by its interesting biological activities and extreme scarcity of natural sources (0.002% w/w from frozen marine sponge). The compound supply necessary for complete clinical trials cannot be met by harvesting, isolation, and purification. As of 2005, attempts at synthesis or semi-synthesis by fermentation have proven unsuccessful. As a result, all discodermolide used in preclinical studies and clinical trials has come from large-scale total synthesis.

















![(C3H7)3NH[CrO3X],(X=F, Cl), Reagents for Oxidation of](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015838257_1-b7e4138a4ed1f989d8dc5b682bb74b7a-300x300.png)