chapter 4 -aromatic compounds
... MECHANISM: BROMINATION OF BENZENE Step 1: Formation of a stronger electrophile ...
... MECHANISM: BROMINATION OF BENZENE Step 1: Formation of a stronger electrophile ...
Amines
... • When aliphatic primary amines react with HNO2, nitrogen is evolved rapidly and an alcohol is produced. RNH2 + O=N-OH → R-OH + H2O + N2 (g) • For example, ethylamine gives nitrogen and a mixture of ethanol (60%), ethene and other products. C2H5NH2 + O=N-OH → C2H5-OH + H2O + N2 (g) + other products ...
... • When aliphatic primary amines react with HNO2, nitrogen is evolved rapidly and an alcohol is produced. RNH2 + O=N-OH → R-OH + H2O + N2 (g) • For example, ethylamine gives nitrogen and a mixture of ethanol (60%), ethene and other products. C2H5NH2 + O=N-OH → C2H5-OH + H2O + N2 (g) + other products ...
Chapter 11
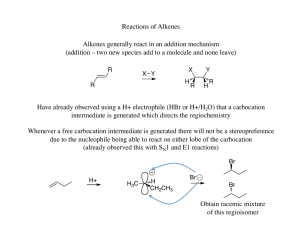
... (do both the X and Y groups add to the same side of the double bond or opposite sides?) ...
... (do both the X and Y groups add to the same side of the double bond or opposite sides?) ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... used as a qualitative test (the Lucas Test) to determine the degree of substitution of an alcohol. Lucas reagent is conc. HCl, saturated with ZnCl2 salt. The Zn+2 ion coordinates (bonds) with the alcohol oxygen even better than H+ and speeds up the rate at which the C+ can form. About ½ mL of al ...
... used as a qualitative test (the Lucas Test) to determine the degree of substitution of an alcohol. Lucas reagent is conc. HCl, saturated with ZnCl2 salt. The Zn+2 ion coordinates (bonds) with the alcohol oxygen even better than H+ and speeds up the rate at which the C+ can form. About ½ mL of al ...
7. Organic halides
... The reactivity of small rings results from their abnormal bond angle (Baeyer strain theory). In cyclopropane the internal bond angle must be 60° (less by 49.5° than the normal tetrahedral bond angle of an sp3-hybridized carbon atom). This compression of internal bond angle causes angle strain, also ...
... The reactivity of small rings results from their abnormal bond angle (Baeyer strain theory). In cyclopropane the internal bond angle must be 60° (less by 49.5° than the normal tetrahedral bond angle of an sp3-hybridized carbon atom). This compression of internal bond angle causes angle strain, also ...
No Slide Title
... 5. The intermediate in Methyl Sulfoxide created by mixing LiAlH4 with argenine was next added dropwise at room temperature via a separatory funnel. 6. Mixture stirred for 12 hours at room temperature, diluted with diethyl ether, filtered and washed. The ether was then distilled from the filtrate to ...
... 5. The intermediate in Methyl Sulfoxide created by mixing LiAlH4 with argenine was next added dropwise at room temperature via a separatory funnel. 6. Mixture stirred for 12 hours at room temperature, diluted with diethyl ether, filtered and washed. The ether was then distilled from the filtrate to ...
NITRO COMPOUNDS
... For nitrating compounds containing electron attracting or deactivating group such as – COOH or when it is desired to introduce more than one nitro group a suitably strong nitrating mixture has to employed and the reaction is carried out at higher temperature . Nitro benzene and m-dinitrobenzene can ...
... For nitrating compounds containing electron attracting or deactivating group such as – COOH or when it is desired to introduce more than one nitro group a suitably strong nitrating mixture has to employed and the reaction is carried out at higher temperature . Nitro benzene and m-dinitrobenzene can ...
Organic Chemistry Notes by Jim Maxka jim.maxka
... First some stuff to memorize: Oxidation means gain of bonds Æ O; Loss of bonds Æ H. Reduction means gain of bonds Æ H; Loss of bonds Æ O. CH4 is the most oxidized or reduced organic molecule? What is the oxidation state of C? What is the most oxidized? What is the oxidation state of C? How about the ...
... First some stuff to memorize: Oxidation means gain of bonds Æ O; Loss of bonds Æ H. Reduction means gain of bonds Æ H; Loss of bonds Æ O. CH4 is the most oxidized or reduced organic molecule? What is the oxidation state of C? What is the most oxidized? What is the oxidation state of C? How about the ...
Alcohols
... or a carboxylic acid. LiAlH4 rather than NaBH4 is needed for the ester and the carboxylic acid ...
... or a carboxylic acid. LiAlH4 rather than NaBH4 is needed for the ester and the carboxylic acid ...
File - Chemistry Workshop
... Multivalent atoms are 1º, 2º, or 3º by bonding to C’s. Univalent atom or group not really 1º, 2º, or 3º on its own - ID depends on type of carbon it is bonded to. ...
... Multivalent atoms are 1º, 2º, or 3º by bonding to C’s. Univalent atom or group not really 1º, 2º, or 3º on its own - ID depends on type of carbon it is bonded to. ...
ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS
... that proceed at the 8-H bond but also with processes that result in cleavage of the C - 0 bond, or changes in the organic group R. The simple ethers, ROR, do not have 0 - H bonds, and most of their reactions are limited to the substituent groups. The chemistry of ethers, therefore, is less varied th ...
... that proceed at the 8-H bond but also with processes that result in cleavage of the C - 0 bond, or changes in the organic group R. The simple ethers, ROR, do not have 0 - H bonds, and most of their reactions are limited to the substituent groups. The chemistry of ethers, therefore, is less varied th ...
$doc.title
... suffix -‐yl from the root of the carboxylic acid – CH3CO: acetyl; CHO: formyl; C6H5CO: benzoyl ...
... suffix -‐yl from the root of the carboxylic acid – CH3CO: acetyl; CHO: formyl; C6H5CO: benzoyl ...
CH 2
... that contains one or more carbon – carbon double bonds. ALKYNES – An unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon – carbon triple bonds. AROMATIC – Organic compounds that contains the characteristics of benzene & benzene ring in its structure. ...
... that contains one or more carbon – carbon double bonds. ALKYNES – An unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon – carbon triple bonds. AROMATIC – Organic compounds that contains the characteristics of benzene & benzene ring in its structure. ...
Year 13 rings polymers and Analysis past papers 1
... Identify the type of bond causing the absorption labelled R and that causing the absorption labelled S. R ............................................................................................................................ S ................................................................... ...
... Identify the type of bond causing the absorption labelled R and that causing the absorption labelled S. R ............................................................................................................................ S ................................................................... ...
Anaysis exam questions
... Identify the type of bond causing the absorption labelled R and that causing the absorption labelled S. R ............................................................................................................................ S ................................................................... ...
... Identify the type of bond causing the absorption labelled R and that causing the absorption labelled S. R ............................................................................................................................ S ................................................................... ...
Organometallics II
... formula C11H22O, are formed in the reaction of methyl lithium with 3-(R)-tertbutylcyclohexanone. These two alcohols are ...
... formula C11H22O, are formed in the reaction of methyl lithium with 3-(R)-tertbutylcyclohexanone. These two alcohols are ...
$doc.title
... They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a fuel addi1ve, ...
... They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a fuel addi1ve, ...
university of london thesis
... investigational work previously carried out into the Sn I like ring opening o f a model molecule, 1-methylcyclohexene oxide. This is followed by a description o f how a new methodology for the acidic ring opening o f epoxides was developed and optimised. This chemistry, leading to the formation o f ...
... investigational work previously carried out into the Sn I like ring opening o f a model molecule, 1-methylcyclohexene oxide. This is followed by a description o f how a new methodology for the acidic ring opening o f epoxides was developed and optimised. This chemistry, leading to the formation o f ...
New Exp8
... Limitations of E1 Reaction: Acid-Catalyzed Dehydrations Competition can occur with SN1 reaction if reaction conditions are not ‘controlled’ (when protic solvents, non-basic nucleophiles are used). Mixtures of products form with the E1 reaction (also SN1). Unsymmetrical reagents and rearrangements po ...
... Limitations of E1 Reaction: Acid-Catalyzed Dehydrations Competition can occur with SN1 reaction if reaction conditions are not ‘controlled’ (when protic solvents, non-basic nucleophiles are used). Mixtures of products form with the E1 reaction (also SN1). Unsymmetrical reagents and rearrangements po ...
Chemistry 0310 - Organic Chemistry 1 Chapter 12. Reactions of
... - Syn-Hydroxylations of alkenes are most conveniently performed with catalytic OsO4 and NMO (N-methylmorpholine N-oxide) as co-oxidant. Attack occurs from the less-hindered face of the alkene, and a vicinal syn-diol is isolated after reductive workup. - Oxidative cleavage of 1,2-disubstituted alken ...
... - Syn-Hydroxylations of alkenes are most conveniently performed with catalytic OsO4 and NMO (N-methylmorpholine N-oxide) as co-oxidant. Attack occurs from the less-hindered face of the alkene, and a vicinal syn-diol is isolated after reductive workup. - Oxidative cleavage of 1,2-disubstituted alken ...
Microsoft Word
... bromosuccinimide (NBS) and water in toluene at ambient temperature to afford the bromohydrins in moderate to high stereoselectivity in good yields. The regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction can be rationalized by the intermediacy of the sulfoxonium salt formed by the nucleophilic attack of t ...
... bromosuccinimide (NBS) and water in toluene at ambient temperature to afford the bromohydrins in moderate to high stereoselectivity in good yields. The regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction can be rationalized by the intermediacy of the sulfoxonium salt formed by the nucleophilic attack of t ...
Unit-8-Alcohols-Aldehydes
... The decarboxylation of β-keto acids produces ketones The decarboxylation of α-keto acids produces aldehydes ...
... The decarboxylation of β-keto acids produces ketones The decarboxylation of α-keto acids produces aldehydes ...
New Phenylglycine-Derived Primary Amine Organocatalysts for the
... prepared by a Strecker reaction of benzaldehyde, followed by hydrolysis of the nitrile. This racemate is then resolved by diastereomeric salt formation,[18a] with (+)-(1S)-camphor-10-sulfonic acid being a very effective resolving agent for this compound.[19] Therefore, phenylglycine is particularly ...
... prepared by a Strecker reaction of benzaldehyde, followed by hydrolysis of the nitrile. This racemate is then resolved by diastereomeric salt formation,[18a] with (+)-(1S)-camphor-10-sulfonic acid being a very effective resolving agent for this compound.[19] Therefore, phenylglycine is particularly ...
reactions of alcohols with alkenes over an aluminum
... The ethers produced were identified by GLC-MS cracking patterns. Generally the yield of the tertiary alcohol, 2-methyl pentan-2-ol, was between 0.8 and 1.2 mole, which is less than that which could have been produced if all of the interlayer water originally in the clay had been consumed (4.2 mmole) ...
... The ethers produced were identified by GLC-MS cracking patterns. Generally the yield of the tertiary alcohol, 2-methyl pentan-2-ol, was between 0.8 and 1.2 mole, which is less than that which could have been produced if all of the interlayer water originally in the clay had been consumed (4.2 mmole) ...
Document
... – H2, Cl2, Br2, HCl, HBr is added to an unsaturated hyrdrocarbon. Both atoms are added to where the double (or triple) bond was ...
... – H2, Cl2, Br2, HCl, HBr is added to an unsaturated hyrdrocarbon. Both atoms are added to where the double (or triple) bond was ...
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement

The Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement (TDR) is the chemical reaction of a 1-aminomethyl-cycloalkanol with nitrous acid to form an enlarged cycloketone.The Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion, Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement, or TDR, provides an easy way to increase amino-substituted cycloalkanes and cycloalkanols in size by one carbon. Ring sizes from cyclopropane through cyclooctane are able to undergo Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion with some degree of success. Yields decrease as initial ring size increases, and the ideal use of TDR is for synthesis of five, six, and seven membered rings. A principal synthetic application of Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion is to bicyclic or polycyclic systems. Several reviews on this reaction have been published.