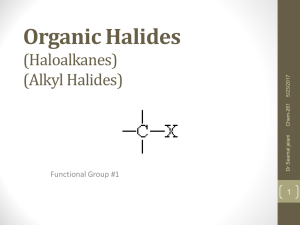Chapter 1--Title
... The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
... The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
CHAPTER 11 BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE:
... Alkyl group names are used for simple alkyl group substituents. When there are two or more substituents, the positions around the ring are numbered beginning with the substituent first in the alphabet. ...
... Alkyl group names are used for simple alkyl group substituents. When there are two or more substituents, the positions around the ring are numbered beginning with the substituent first in the alphabet. ...
Chapter 1--Title - Chemistry Workshop
... The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
... The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
Ch14 Lecture
... • The “1” is usually omitted from the name. • The ring is then numbered to give the next substituent the lower number. ...
... • The “1” is usually omitted from the name. • The ring is then numbered to give the next substituent the lower number. ...
Organic Chemistry - UCR Chemistry
... 7.10 Nucleophilic Hydrogen The Polarity of H in Various Compounds (7.10A) Metal Hydrides are Sources of Nucleophilic H (7.10B) Appendix: Nucleophiles and Leaving Groups ...
... 7.10 Nucleophilic Hydrogen The Polarity of H in Various Compounds (7.10A) Metal Hydrides are Sources of Nucleophilic H (7.10B) Appendix: Nucleophiles and Leaving Groups ...
Revised organic chemistry
... peroxide effect or Kharasch effect. But it does not apply to addition involving HCl, HI or HF ...
... peroxide effect or Kharasch effect. But it does not apply to addition involving HCl, HI or HF ...
Get PDF - Wiley Online Library
... in a nearly quantitative conversion into the desired six-membered ring 37 (entry 4), whereas without 1,4benzoquinone no trace of this product was observed Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 95 – 106 ...
... in a nearly quantitative conversion into the desired six-membered ring 37 (entry 4), whereas without 1,4benzoquinone no trace of this product was observed Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 95 – 106 ...
Document
... – H2, Cl2, Br2, HCl, HBr is added to an unsaturated hyrdrocarbon. Both atoms are added to where the double (or triple) bond was ...
... – H2, Cl2, Br2, HCl, HBr is added to an unsaturated hyrdrocarbon. Both atoms are added to where the double (or triple) bond was ...
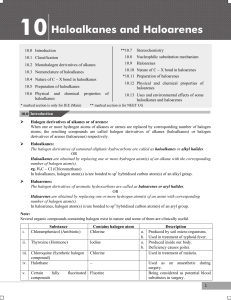
10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
... Therefore, halogenation (chlorination and bromination) of an alkane is not useful for laboratory preparation of alkyl halide, because it gives mixture of different alkyl halides which are difficult to separate. Consequently, the yield of any one component is less due to the formation of other compon ...
... Therefore, halogenation (chlorination and bromination) of an alkane is not useful for laboratory preparation of alkyl halide, because it gives mixture of different alkyl halides which are difficult to separate. Consequently, the yield of any one component is less due to the formation of other compon ...
Neuman Chapter - Department of Chemistry
... This is followed by a step where ethanol, acting as a base, removes a proton from Cβ of the carbocation. This E1 mechanism is analogous to the two-step SN1 substitution mechanism (Chapter 7). The "1" in E1 indicates that the rate determining step of the reaction is unimolecular. This rate determinin ...
... This is followed by a step where ethanol, acting as a base, removes a proton from Cβ of the carbocation. This E1 mechanism is analogous to the two-step SN1 substitution mechanism (Chapter 7). The "1" in E1 indicates that the rate determining step of the reaction is unimolecular. This rate determinin ...
aldehydes and ketones
... lack of hydrogen bonding. However their boiling point is slightly higher than that of corresponding non-polar hydrocarbon or weakly polar ether. This may attributed to reason that aldehydes and ketones are polar compounds and thus possess intermolecular dipoledipole interaction ...
... lack of hydrogen bonding. However their boiling point is slightly higher than that of corresponding non-polar hydrocarbon or weakly polar ether. This may attributed to reason that aldehydes and ketones are polar compounds and thus possess intermolecular dipoledipole interaction ...
3.2 Organic Synthesis (Reaction Pathways)
... In Higher Chemistry the alkylhalides were not particularly important chemicals. In Advanced Higher, however, the significance of halogenoalkanes (alkylhalides) cannot be overstressed. They can be a very important step in many Synthesis Pathways. ...
... In Higher Chemistry the alkylhalides were not particularly important chemicals. In Advanced Higher, however, the significance of halogenoalkanes (alkylhalides) cannot be overstressed. They can be a very important step in many Synthesis Pathways. ...
Review of Organic Chem II
... 3. The types of intermediates involved (cation, anion, or radical) should be consistent with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a r ...
... 3. The types of intermediates involved (cation, anion, or radical) should be consistent with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a r ...
20 More About Oxidation–Reduction Reactions
... In this reaction, Cu+ loses an electron, so Cu+ is oxidized. Fe 3+ gains an electron, so Fe 3+ is reduced. The reaction demonstrates two important points about oxidation– reduction reactions. First, oxidation is always coupled with reduction. In other words, a compound cannot gain electrons (be redu ...
... In this reaction, Cu+ loses an electron, so Cu+ is oxidized. Fe 3+ gains an electron, so Fe 3+ is reduced. The reaction demonstrates two important points about oxidation– reduction reactions. First, oxidation is always coupled with reduction. In other words, a compound cannot gain electrons (be redu ...
Carbohidratos
... • Relevant ketoses have between three and six carbons. • For each naturally occurring D isomer, there is an L enanKomer. ...
... • Relevant ketoses have between three and six carbons. • For each naturally occurring D isomer, there is an L enanKomer. ...
Alcohols, Penols, and Thiols
... • Function as weak bases, too • Have unshared electron pair on O…Lewis bases • Protonated by strong acids • 1st step in dehydration to alkenes and conversion to alkyl halides • Product is analogous to oxonium, H3O+ ...
... • Function as weak bases, too • Have unshared electron pair on O…Lewis bases • Protonated by strong acids • 1st step in dehydration to alkenes and conversion to alkyl halides • Product is analogous to oxonium, H3O+ ...
Alkenes 3 - ChemWeb (UCC)
... Notice that the requirements for a -elimination reaction are: (i) A base (ii) A leaving group in the substrate such as halide, tosylate etc. and ... (iii) A C-H bond - to the leaving group. We have already seen that most strong bases are also good nucleophiles - and vice versa. For this reason nuc ...
... Notice that the requirements for a -elimination reaction are: (i) A base (ii) A leaving group in the substrate such as halide, tosylate etc. and ... (iii) A C-H bond - to the leaving group. We have already seen that most strong bases are also good nucleophiles - and vice versa. For this reason nuc ...
CHM-373 American Women in Science and Society
... • Grignard or organolithium reagent + nitrile ketone (after hydrolysis) ...
... • Grignard or organolithium reagent + nitrile ketone (after hydrolysis) ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... • The presence of a halide makes the molecule more polar. • Since water is also polar and “like dissolves like”, alkyl halides are soluble in water. The more halides connected to the parent chain, the more polar the molecule. • The polar nature of the molecule means that boiling and melting points o ...
... • The presence of a halide makes the molecule more polar. • Since water is also polar and “like dissolves like”, alkyl halides are soluble in water. The more halides connected to the parent chain, the more polar the molecule. • The polar nature of the molecule means that boiling and melting points o ...
Crystallization and Determination of Melting and Boiling Points
... The melting point is used by organic chemists not only to identify compounds, but also to verify their purity. To measure the melting point, a small amount of sample is heated in an apparatus equipped with a thermometer while two temperatures are noted. The first is the point at which the first drop ...
... The melting point is used by organic chemists not only to identify compounds, but also to verify their purity. To measure the melting point, a small amount of sample is heated in an apparatus equipped with a thermometer while two temperatures are noted. The first is the point at which the first drop ...
Alkenes notes
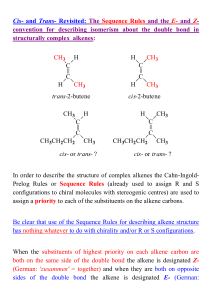
... attached to different groups, then two different structures arise which cannot be interconverted. This is known as E-Z isomerism Stereoisomers are molecules with the same molecular formula and the same arrangement of covalent bonds but with different spatial orientations of the groups. E-Z stereoiso ...
... attached to different groups, then two different structures arise which cannot be interconverted. This is known as E-Z isomerism Stereoisomers are molecules with the same molecular formula and the same arrangement of covalent bonds but with different spatial orientations of the groups. E-Z stereoiso ...
Carbonyl α-substitution and Condensation Reactions
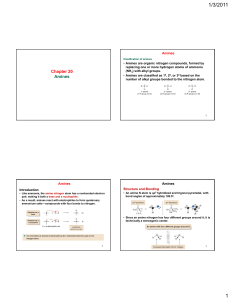
... ammonia with one or more alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen. The chemistry of amines is dominated by the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen of amines is a powerful electron source, so the most important chemical properties of amines are their basicity and ...
... ammonia with one or more alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen. The chemistry of amines is dominated by the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen of amines is a powerful electron source, so the most important chemical properties of amines are their basicity and ...
Chapter 20 Amines - FIU Faculty Websites
... • 10 Amines are named using either systematic or common names. • To assign a systematic name, find the longest continuous chain bonded to the amine nitrogen, and change the –e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix –amine. Then use the usual rules of nomenclature to number the chain and name the ...
... • 10 Amines are named using either systematic or common names. • To assign a systematic name, find the longest continuous chain bonded to the amine nitrogen, and change the –e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix –amine. Then use the usual rules of nomenclature to number the chain and name the ...
the suzuki-miyaura reaction and boron reagents – mechanism
... The reaction failed when bicarbonate was used (pKa = 6.4) but proceeded smoothly using carbonate (pKa = 10.3). This was taken as evidence for the generation of trihydroxyboronate (R-B(OH)2, pKa = 8.8) as an essential step for coupling via the boronate pathway A. ...
... The reaction failed when bicarbonate was used (pKa = 6.4) but proceeded smoothly using carbonate (pKa = 10.3). This was taken as evidence for the generation of trihydroxyboronate (R-B(OH)2, pKa = 8.8) as an essential step for coupling via the boronate pathway A. ...
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement

The Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement (TDR) is the chemical reaction of a 1-aminomethyl-cycloalkanol with nitrous acid to form an enlarged cycloketone.The Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion, Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement, or TDR, provides an easy way to increase amino-substituted cycloalkanes and cycloalkanols in size by one carbon. Ring sizes from cyclopropane through cyclooctane are able to undergo Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion with some degree of success. Yields decrease as initial ring size increases, and the ideal use of TDR is for synthesis of five, six, and seven membered rings. A principal synthetic application of Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion is to bicyclic or polycyclic systems. Several reviews on this reaction have been published.