Alcohols I Reading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10
... For the chlorinated derivatives of enthanol (ClCH2CH2OH, Cl3CCH2OH), the inductive electron-withdrawing effect of the local halogens enhances the acidity of the parent alcohols; this effect is additive, with trichloroethanol being more acidic than chloroethanol and ethanol. Phenol (an aromatic ring ...
... For the chlorinated derivatives of enthanol (ClCH2CH2OH, Cl3CCH2OH), the inductive electron-withdrawing effect of the local halogens enhances the acidity of the parent alcohols; this effect is additive, with trichloroethanol being more acidic than chloroethanol and ethanol. Phenol (an aromatic ring ...
Review sheet - Paws.wcu.edu.
... Identify potential simple sugars. Classify as monosaccharide or disaccharide. Cyclic hemiacetal form for sugars. Two forms for glucose – alpha and beta The structure and properties of starch and cellulose. Know the following reaction mechanisms: SN1/SN2/E1/E2 reactions: SN2/E2 transition states and ...
... Identify potential simple sugars. Classify as monosaccharide or disaccharide. Cyclic hemiacetal form for sugars. Two forms for glucose – alpha and beta The structure and properties of starch and cellulose. Know the following reaction mechanisms: SN1/SN2/E1/E2 reactions: SN2/E2 transition states and ...
info
... i. NaBH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, or acid chloride to the corresponding alcohol. It will not reduce an acid or an ester. ii. LiAlH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, acid, or ester to the corresponding alcohol. iii. LiAlH(OtBu)3 will reduce an acid chloride to an aldehyde. iv. DIBAL will ...
... i. NaBH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, or acid chloride to the corresponding alcohol. It will not reduce an acid or an ester. ii. LiAlH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, acid, or ester to the corresponding alcohol. iii. LiAlH(OtBu)3 will reduce an acid chloride to an aldehyde. iv. DIBAL will ...
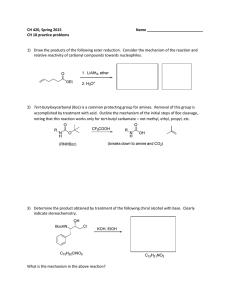
CH 420, Spring 2015 Name ___________________________ CH 18 practice problems
... 1) Draw the products of the following ester reduction. Consider the mechanism of the reaction and relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds towards nucleophiles. ...
... 1) Draw the products of the following ester reduction. Consider the mechanism of the reaction and relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds towards nucleophiles. ...
Alcohols - City University of New York
... Acid Catalyzed Dehydration of an Alcohol, discussed earlier as reverse of hydration Secondary and tertiary alcohols, carbocations Protonation, establishing of good leaving group. Elimination of water to yield carbocation in rate determining step. ...
... Acid Catalyzed Dehydration of an Alcohol, discussed earlier as reverse of hydration Secondary and tertiary alcohols, carbocations Protonation, establishing of good leaving group. Elimination of water to yield carbocation in rate determining step. ...
n - TU Chemnitz
... constants, and finally to understand the kinetics of the reactions. After that, different reactions like substitution, esterification, dehydration, oxidation of the hydroxy-group and 1,3-dipolar Cycloaddition, photolysis, Staudinger reaction of the azido-group should be performed. ...
... constants, and finally to understand the kinetics of the reactions. After that, different reactions like substitution, esterification, dehydration, oxidation of the hydroxy-group and 1,3-dipolar Cycloaddition, photolysis, Staudinger reaction of the azido-group should be performed. ...
Document
... solution containing silver-ammonia complex ions. When an aldehyde group is oxidized by this reagent, the silver ions are reduced to metallic silver, which forms a black precipitate and, if the test tube is clean, a silver mirror on the test tube. (E. Ferric Chloride Test for Phenols) When a phenol i ...
... solution containing silver-ammonia complex ions. When an aldehyde group is oxidized by this reagent, the silver ions are reduced to metallic silver, which forms a black precipitate and, if the test tube is clean, a silver mirror on the test tube. (E. Ferric Chloride Test for Phenols) When a phenol i ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: REPLACING THE -OH GROUP BY A HALOGEN
... 1. a) Describe what you would see if you added a small amount of phosphorus(V) chloride to an alcohol. b) This can only be used as a test for an alcohol if you first eliminate other compounds which also contain an -OH group. Give two completely different examples of something which would react with ...
... 1. a) Describe what you would see if you added a small amount of phosphorus(V) chloride to an alcohol. b) This can only be used as a test for an alcohol if you first eliminate other compounds which also contain an -OH group. Give two completely different examples of something which would react with ...
Alcohols and Ethers - New Paltz Central School District
... • Polar compounds such as water, or organic compounds containing carbon and oxygen, have much higher melting points and boiling points than their hydrocarbon cousins. • Hydocarbons containing only carbon and hydrogen are considered non-polar compounds because they do not have these partial positive ...
... • Polar compounds such as water, or organic compounds containing carbon and oxygen, have much higher melting points and boiling points than their hydrocarbon cousins. • Hydocarbons containing only carbon and hydrogen are considered non-polar compounds because they do not have these partial positive ...
Alcohols, phenols and ethers
... reactions – Reductions decrease the number of C-O bonds and/or increase the number of C-H bonds in a molecule. ...
... reactions – Reductions decrease the number of C-O bonds and/or increase the number of C-H bonds in a molecule. ...
Organic Reactions 2.1- 2.3 - mccormack-sch4u-2013
... • Change in the number of H or O atoms bonded to C • Always occur together • One reactant is oxidized while the other is reduced • For now, lets focus on reactant only… ...
... • Change in the number of H or O atoms bonded to C • Always occur together • One reactant is oxidized while the other is reduced • For now, lets focus on reactant only… ...
Ch. 16: Solutions - Quynh Nguyen Official Website
... They tend to have similar bps to ethers of the same molar mass They tend to have much lower bps than alcohols, because alcohols are much more polar Aldehydes and ketones of 5 C atoms or less are soluble in water ...
... They tend to have similar bps to ethers of the same molar mass They tend to have much lower bps than alcohols, because alcohols are much more polar Aldehydes and ketones of 5 C atoms or less are soluble in water ...
L-13
... whereas no reaction took place by other representative Lewis acids such as AlCl3 and BF3. Introduction Nucleophilic substitution of the hydroxy group in alcohols intrinsically requires an equimolar (or greater) amount of acid because of the poor leaving ability of the OH group. To avoid the use of e ...
... whereas no reaction took place by other representative Lewis acids such as AlCl3 and BF3. Introduction Nucleophilic substitution of the hydroxy group in alcohols intrinsically requires an equimolar (or greater) amount of acid because of the poor leaving ability of the OH group. To avoid the use of e ...
Naming organic compounds
... The functional group in the alcohols is the hydroxyl group (-OH). Alcohols end in the letters '-ol'. The basic rules of naming apply. The position of the hydroxyl functional group is indicated by a number before the '-ol' part of the name. Alcohols can also be termed primary, secondary or tertiary. ...
... The functional group in the alcohols is the hydroxyl group (-OH). Alcohols end in the letters '-ol'. The basic rules of naming apply. The position of the hydroxyl functional group is indicated by a number before the '-ol' part of the name. Alcohols can also be termed primary, secondary or tertiary. ...
Organic Chemistry II
... Alcohols are NOT bases. In fact, some can be acidic (phenol). Can be soluble in polar solvents such as water (hydrocarbons are not soluble in water). ...
... Alcohols are NOT bases. In fact, some can be acidic (phenol). Can be soluble in polar solvents such as water (hydrocarbons are not soluble in water). ...
Alcohols, Penols, and Thiols
... • From black strap molasses (cane sugar)…grain alcohol • C6H12O6 + H2O 4CH3CH2OH + 4CO2 yeast ...
... • From black strap molasses (cane sugar)…grain alcohol • C6H12O6 + H2O 4CH3CH2OH + 4CO2 yeast ...
How to Name Alcohols
... that when bonded to a carbon chain give it a unique quality. Compounds with similar functional groups will have similar qualities and properties. ...
... that when bonded to a carbon chain give it a unique quality. Compounds with similar functional groups will have similar qualities and properties. ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.