
ppt
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
104 Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH3
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
Kinetics of Oxidation of Aliphatic Alcohols by Potassium Dichromate
... found to be first-order with respect to both alcohol and oxidant. Pseudo-first-order kinetics were found to be perfectly applicable with ethanol, 1-propanol and 2-propanol while deviation was observed at intermediate stages of the reaction with methanol. The pseudo-first-order rate constants were fo ...
... found to be first-order with respect to both alcohol and oxidant. Pseudo-first-order kinetics were found to be perfectly applicable with ethanol, 1-propanol and 2-propanol while deviation was observed at intermediate stages of the reaction with methanol. The pseudo-first-order rate constants were fo ...
IA Practical Report Properties of Alkanes and Alkenes
... 2.To compare the reactivity of a single bond vs. a double bond. Prelab: Start write up in Lab Book Construct table below in lab book Complete parts 1 and 2 in the chart below. Read method and understand Safety: Cyclohexane, cyclohexene, and bromine are pungent and toxic. Proper ventilation is nece ...
... 2.To compare the reactivity of a single bond vs. a double bond. Prelab: Start write up in Lab Book Construct table below in lab book Complete parts 1 and 2 in the chart below. Read method and understand Safety: Cyclohexane, cyclohexene, and bromine are pungent and toxic. Proper ventilation is nece ...
KHSO4-SiO2-MeOH – An efficient selective solid
... the proton required for the reaction is supplied by the prenyl part which subsequently releases 2-methyl1,3-butadiene. But in a chance discovery we came across the KHSO4-SiO2-MeOH system where the alcohol system is not affected. Results and Discussion ...
... the proton required for the reaction is supplied by the prenyl part which subsequently releases 2-methyl1,3-butadiene. But in a chance discovery we came across the KHSO4-SiO2-MeOH system where the alcohol system is not affected. Results and Discussion ...
Application of IBX Method for the Synthesis of Ketones from
... One of the most common reactions in chemistry is the synthesis of ketones from acids1−4 . First, the acid is changed into its chloride. Then the acid chloride reacts with an organometallic reagent or gives a FriedelCrafts type reaction in the presence of Lewis acids. These methods are very useful fo ...
... One of the most common reactions in chemistry is the synthesis of ketones from acids1−4 . First, the acid is changed into its chloride. Then the acid chloride reacts with an organometallic reagent or gives a FriedelCrafts type reaction in the presence of Lewis acids. These methods are very useful fo ...
Copper-Catalyzed Hydroalkylation of Terminal Alkynes
... sterically, afford little or no hydroalkylation product (entry 3). We found that excess alkyl triflate is necessary for efficient cross coupling (entry 4). Similarly, lower yield of the crosscoupling product was obtained when 0.6 equiv of the silane was used (entry 5). In that case, in addition to the c ...
... sterically, afford little or no hydroalkylation product (entry 3). We found that excess alkyl triflate is necessary for efficient cross coupling (entry 4). Similarly, lower yield of the crosscoupling product was obtained when 0.6 equiv of the silane was used (entry 5). In that case, in addition to the c ...
Lecture 16 Aromatic Diazonium Salts
... Diazonium ions could be reduced by single electron transfer to give an aryl radical and nitrogen. Copper(I) is frequently used for this purpose and the aryl radical is highly reactive capable of abstracting a ligand from the transition metal ion or a hydrogen atom from a covalent bond. Joint initiat ...
... Diazonium ions could be reduced by single electron transfer to give an aryl radical and nitrogen. Copper(I) is frequently used for this purpose and the aryl radical is highly reactive capable of abstracting a ligand from the transition metal ion or a hydrogen atom from a covalent bond. Joint initiat ...
Experiment 7 – Dehydration of Methylcyclohexanols
... your station. Check the temperature periodically but do not leave the thermometer in the sand bath. Recall that hot plates should never be set higher than ½ of the maximum heat setting (med-low to medium is ideal). Keep an eye on temperature and adjust accordingly. It may be appropriate to turn off ...
... your station. Check the temperature periodically but do not leave the thermometer in the sand bath. Recall that hot plates should never be set higher than ½ of the maximum heat setting (med-low to medium is ideal). Keep an eye on temperature and adjust accordingly. It may be appropriate to turn off ...
Carbonyl The carbonyl function, C=O, exists in a number of organic
... The stereochemistry of Wittig reactions is very interesting, and the detailed mechanisms involved are somewhat cloudy. As shown below the reagents add in a fast step to form an eclipsed betaine (or goes directly to the oxaphosphetane). The oxaphosphetane breaks down by syn elimination to give the tr ...
... The stereochemistry of Wittig reactions is very interesting, and the detailed mechanisms involved are somewhat cloudy. As shown below the reagents add in a fast step to form an eclipsed betaine (or goes directly to the oxaphosphetane). The oxaphosphetane breaks down by syn elimination to give the tr ...
14 - Oxidation of Alcohols - Organic Chemistry at CU Boulder
... is a common organic chemistry practice, based on the principle that dissolved inorganic salts decrease the solubility of most organic compounds in water. The camphor is extracted into ethyl acetate and the resulting solution treated with drying agent. Then, the mixture of solvent and product is deca ...
... is a common organic chemistry practice, based on the principle that dissolved inorganic salts decrease the solubility of most organic compounds in water. The camphor is extracted into ethyl acetate and the resulting solution treated with drying agent. Then, the mixture of solvent and product is deca ...
WRL3502.tmp
... SN2 Mechanism: If the R group cannot support a stable carbocation, such as primary alkyl chains, SN2 reactions occur. The oxonium ion leaves as the halide attacks the same primary carbon, in one rate determining step. ...
... SN2 Mechanism: If the R group cannot support a stable carbocation, such as primary alkyl chains, SN2 reactions occur. The oxonium ion leaves as the halide attacks the same primary carbon, in one rate determining step. ...
File - Dr KHALID SHADID
... (b) The magnesium portion of the Grignard reagent plays an important part in this reaction. What is its ftnction? (c) What product is formed initially? (d) What product forms when water is added? ...
... (b) The magnesium portion of the Grignard reagent plays an important part in this reaction. What is its ftnction? (c) What product is formed initially? (d) What product forms when water is added? ...
Chapter 19 - people.vcu.edu
... o LiAlH4 completely chops off the oxygen of an amide instead of reducing the carbonyl to an alcohol Gabriel synthesis – always makes 1° amines o Phthalimide is deprotonated by a strong base ...
... o LiAlH4 completely chops off the oxygen of an amide instead of reducing the carbonyl to an alcohol Gabriel synthesis – always makes 1° amines o Phthalimide is deprotonated by a strong base ...
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
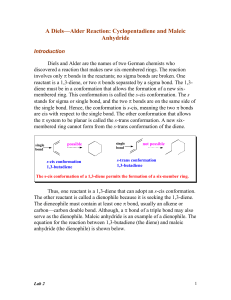
... Typical Dienophiles for Diels-Alder Reactions How does one recognize a Diels-Alder reaction? These reactions are easy to spot, because they involve two organic reactants and only heat as a reactant. One of the reactants (the diene) must have a conjugated diene system, and the other reactant (the die ...
... Typical Dienophiles for Diels-Alder Reactions How does one recognize a Diels-Alder reaction? These reactions are easy to spot, because they involve two organic reactants and only heat as a reactant. One of the reactants (the diene) must have a conjugated diene system, and the other reactant (the die ...
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview
... 1. The more covalent bonds a structure has, the more stable it is 2. Charge separation (formal charges) decreases stability 3. Negative charges on the more electronegative elements and positive charges on the more electropositive elements are ...
... 1. The more covalent bonds a structure has, the more stable it is 2. Charge separation (formal charges) decreases stability 3. Negative charges on the more electronegative elements and positive charges on the more electropositive elements are ...
Sodium Borohydride Reduction of Vanillin
... Sodium borohydride reductions are usually carried out in a dilute (~1 M) aqueous NaOH solution or an alcohol. The reagent is not stable at low pH, and even in a neutral aqueous solution it decomposes to the extent of about 4.5% per hour at 25°C. Acidic functional groups, such as COOH and the OH grou ...
... Sodium borohydride reductions are usually carried out in a dilute (~1 M) aqueous NaOH solution or an alcohol. The reagent is not stable at low pH, and even in a neutral aqueous solution it decomposes to the extent of about 4.5% per hour at 25°C. Acidic functional groups, such as COOH and the OH grou ...
Chapter 16: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides
... the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Crown Ethers (Please read) ...
... the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Crown Ethers (Please read) ...
File - TGHS Level 3 Chemistry
... Soaps are the sodium salts of fatty acids (long chain acids). These salts are soluble in water as they are ionised, but they have a carbon chain end that is soluble in fats and oils. This allows them to dissolve and break down dirt. Sodium laurate is the name of the soap molecule made from coconut o ...
... Soaps are the sodium salts of fatty acids (long chain acids). These salts are soluble in water as they are ionised, but they have a carbon chain end that is soluble in fats and oils. This allows them to dissolve and break down dirt. Sodium laurate is the name of the soap molecule made from coconut o ...
[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School
... pair of electrons. Since N is less electronegative than oxygen, therefore lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more easily available for bond formation. In other hand, nucleophillic attack occurs through N and hence silver nitrite predominantly gives nitro compounds. Q9. Explain, why the t ...
... pair of electrons. Since N is less electronegative than oxygen, therefore lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more easily available for bond formation. In other hand, nucleophillic attack occurs through N and hence silver nitrite predominantly gives nitro compounds. Q9. Explain, why the t ...
Chapter 11 Carboxylic Anhydrides, Esters, and Amides
... Hydrolysis of Amides Amides require more vigorous conditions for hydrolysis in both acid and base than do esters. • Hydrolysis in hot aqueous acid gives a carboxylic acid and an ammonium ion. • Hydrolysis is driven to completion by the acid-base reaction between ammonia or the amine and the acid to ...
... Hydrolysis of Amides Amides require more vigorous conditions for hydrolysis in both acid and base than do esters. • Hydrolysis in hot aqueous acid gives a carboxylic acid and an ammonium ion. • Hydrolysis is driven to completion by the acid-base reaction between ammonia or the amine and the acid to ...
PDF document
... the presence and absence of PEG1000-DAIL catalytic system. In the absence of PEG1000-DAIL, the reaction proceeded very slowly and the yield was only 26% after 24 hours (Table 1, entry 1). When the reaction was catalyzed with only 0.02 equivalents of PEG1000-DAIL, the yield increased to 57% in 8 hour ...
... the presence and absence of PEG1000-DAIL catalytic system. In the absence of PEG1000-DAIL, the reaction proceeded very slowly and the yield was only 26% after 24 hours (Table 1, entry 1). When the reaction was catalyzed with only 0.02 equivalents of PEG1000-DAIL, the yield increased to 57% in 8 hour ...
... Organic reactions in water have recently attracted great interests [1]. The substitution of organic solvent as reaction media by water minimizes the environmental impact, besides lowering the cost and decreasing operational danger. In addition to the economic and human aspects, water presents many p ...
Hofmann–Löffler reaction

The Hofmann–Löffler reaction (also referred to as Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Hofmann reaction, as well as Löffler's method) is an organic reaction in which a cyclic amine 2 (pyrrolidine or, in some cases, piperidine) is generated by thermal or photochemical decomposition of N-halogenated amine 1 in the presence of a strong acid (concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated CF3CO2H). The Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction proceeds via an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer to a nitrogen-centered radical and is an example of a remote intramolecular free radical C–H functionalization.


















![[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015878975_1-55791b331e05591620375059b6f74bac-300x300.png)



