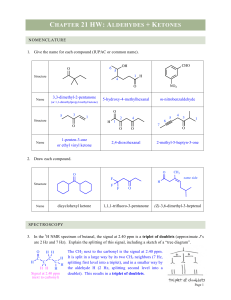
Untitled - St Mungo`s High School
... 50 cm3 of a solution of HCl is exactly neutralised by 20 cm3 of a solution of Ca(OH)2 of concentration 2.0 mol l–1. 2HCl + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + 2H2O Calculate the concentration of the HCl solution in mol l –1. 10. 2.5 l of a solution of NaOH is exactly neutralised by 1.5 l of a solution of HCl of conce ...
... 50 cm3 of a solution of HCl is exactly neutralised by 20 cm3 of a solution of Ca(OH)2 of concentration 2.0 mol l–1. 2HCl + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + 2H2O Calculate the concentration of the HCl solution in mol l –1. 10. 2.5 l of a solution of NaOH is exactly neutralised by 1.5 l of a solution of HCl of conce ...
File
... strong signal at 1691 cm-1. Both signals represent vibration of the same kind of bond. Explain why the absorption in 2-cyclohexenone is at a lower wavenumber, including resonance structures. Both signals represent the IR stretching of the C=O bonds. 2-cyclohexenone has a lower wavenumber absorbance, ...
... strong signal at 1691 cm-1. Both signals represent vibration of the same kind of bond. Explain why the absorption in 2-cyclohexenone is at a lower wavenumber, including resonance structures. Both signals represent the IR stretching of the C=O bonds. 2-cyclohexenone has a lower wavenumber absorbance, ...
Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 1415
... bonds to both ligands of this complex, a Janus molecule should thus have coplanar imides diverging at an angle of ca. 120°, such as in 3 and 4. The bis(bipyridine)2Pd(BF4)2 complexes are not readily soluble in pure chloroform. In the following experiments this was circumvented by adding small amount ...
... bonds to both ligands of this complex, a Janus molecule should thus have coplanar imides diverging at an angle of ca. 120°, such as in 3 and 4. The bis(bipyridine)2Pd(BF4)2 complexes are not readily soluble in pure chloroform. In the following experiments this was circumvented by adding small amount ...
Organic Chemistry
... • describe and identify structural isomers • carboxylic acids with up to 4 carbon atoms Recognise by name, compounds ending in: • -ol as alcohols and -oic acid are carboxylic acids • Recognise from diagrams, the structures of: alkanes, alkenes, alcohols, carboxylic acids Understand that ethanol is u ...
... • describe and identify structural isomers • carboxylic acids with up to 4 carbon atoms Recognise by name, compounds ending in: • -ol as alcohols and -oic acid are carboxylic acids • Recognise from diagrams, the structures of: alkanes, alkenes, alcohols, carboxylic acids Understand that ethanol is u ...
A Brief History of Organic Chemistry
... sediment, rock, or ice where they were subjected to tremendous pressures. In this way, they were transformed into various types of coal. Meanwhile in Earth's prehistoric shallow seas, simple organisms like algae, bacteria and zooplankton thrived. As these tiny organisms died, they formed thick layer ...
... sediment, rock, or ice where they were subjected to tremendous pressures. In this way, they were transformed into various types of coal. Meanwhile in Earth's prehistoric shallow seas, simple organisms like algae, bacteria and zooplankton thrived. As these tiny organisms died, they formed thick layer ...
Chapter One Hemilabile Ligands in Transition
... which is an ether-phosphine ligand. Phosphines are one of the most versatile ligands that can bind to late transition metals, since they produce stable metal-phosphorus bonds.9 Hemilabile phosphines have potentially important industrial applications through the ability to tune the properties of the ...
... which is an ether-phosphine ligand. Phosphines are one of the most versatile ligands that can bind to late transition metals, since they produce stable metal-phosphorus bonds.9 Hemilabile phosphines have potentially important industrial applications through the ability to tune the properties of the ...
Reactions in which some elements change their
... 1. Chlorine will displace bromine from solutions containing bromide ions Cl2 + 2Br- => Br2 + 2Cl- ...
... 1. Chlorine will displace bromine from solutions containing bromide ions Cl2 + 2Br- => Br2 + 2Cl- ...
2Cu 2+ + O 2 2
... but differ in the particular environment of the Fe centers: -Hr coordination sphere is more histidine rich -Hr permits only terminal O2-coordination to a single iron, while sMMO diiron center presents open or labile coordination sites on both Fe -sMMO shows much greater coordinative flexibility upon ...
... but differ in the particular environment of the Fe centers: -Hr coordination sphere is more histidine rich -Hr permits only terminal O2-coordination to a single iron, while sMMO diiron center presents open or labile coordination sites on both Fe -sMMO shows much greater coordinative flexibility upon ...
Mass Spec - Fragmentation
... rules of Lewis structures (i.e. don’t put more than 8 electrons on carbon). ...
... rules of Lewis structures (i.e. don’t put more than 8 electrons on carbon). ...
Synthesis of Several Esters
... through the heating, mix each of the solutions again by carefully removing each test tube one at a time, flicking the bottom, and replacing it. If the water in the beaker or any of the solutions in the test tubes begin to boil, turn down the heat on the hot plate. Do not allow the test tubes with th ...
... through the heating, mix each of the solutions again by carefully removing each test tube one at a time, flicking the bottom, and replacing it. If the water in the beaker or any of the solutions in the test tubes begin to boil, turn down the heat on the hot plate. Do not allow the test tubes with th ...
Synthesis and Characterization of Dinuclear Metal Complexes
... IR-spectra: The most important band which appeared at 1642 and 1636 cm−1 due to ν(C=N) stretching in the free ligand is shifted to the lower field in the prepared complexes. This is usually indicates that the (C=N) groups of the ligands are involved in coordination with metal atom through the azomet ...
... IR-spectra: The most important band which appeared at 1642 and 1636 cm−1 due to ν(C=N) stretching in the free ligand is shifted to the lower field in the prepared complexes. This is usually indicates that the (C=N) groups of the ligands are involved in coordination with metal atom through the azomet ...
Practice Test Material - Directorate of Education
... Calculate the pH of 0.10M ammonia solution. Calculate the pH after 50.0 ml of this solution is treated with 25.0 ml of 0.10M HCl. The dissociation constant of ammonia (Kb) is 1.77×10–5. Hint – In the final condition, basic buffer is formed due to the presence of NH4Cl and NH4OH in the same solution. ...
... Calculate the pH of 0.10M ammonia solution. Calculate the pH after 50.0 ml of this solution is treated with 25.0 ml of 0.10M HCl. The dissociation constant of ammonia (Kb) is 1.77×10–5. Hint – In the final condition, basic buffer is formed due to the presence of NH4Cl and NH4OH in the same solution. ...
A Chapter 3
... Common in square planar and octahedral complexes but not in tetrahedral complexes because all tetrahedral complexes [such as Ma4 , Ma2b2 , Mabcd, where a,b,c,d represents ligands ]exist in only one geometric form in which all positions are adjacent to each other. Existence of two different compounds ...
... Common in square planar and octahedral complexes but not in tetrahedral complexes because all tetrahedral complexes [such as Ma4 , Ma2b2 , Mabcd, where a,b,c,d represents ligands ]exist in only one geometric form in which all positions are adjacent to each other. Existence of two different compounds ...
PDF - International Journal of Chemical Studies
... represent the ν(C=O) of moiety. Three or four bands at (621-1143) cm-1 region also indicated the ν1 , ν2 , ν3, ν4 bands of ( ClO4-1) moiety. These stretching frequencies suggested the coordination of perchlorate to the metal through the O atom. A medium band at (416-443) cm-1 region is tentatively a ...
... represent the ν(C=O) of moiety. Three or four bands at (621-1143) cm-1 region also indicated the ν1 , ν2 , ν3, ν4 bands of ( ClO4-1) moiety. These stretching frequencies suggested the coordination of perchlorate to the metal through the O atom. A medium band at (416-443) cm-1 region is tentatively a ...
Chem. Mater. - ACS Publications
... above and below the layers. Another two cobalt complexes, centered by Co3 and Co4, are attached as pendants on both sides of the layers, also by hydrogen bonds. Each pillar hydrogen bonds to the layer with one of its sulfonate groups and to a pendant metal complex with the other sulfonate group. The ...
... above and below the layers. Another two cobalt complexes, centered by Co3 and Co4, are attached as pendants on both sides of the layers, also by hydrogen bonds. Each pillar hydrogen bonds to the layer with one of its sulfonate groups and to a pendant metal complex with the other sulfonate group. The ...
the chemistry of life: organic and biological chemistry
... The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry Although biological systems are almost unimaginably complex, they are nevertheless constructed of molecules of quite modest size, put together in nature to form a host of complex, interacting structures. The example of phenylalanine and PKU ill ...
... The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry Although biological systems are almost unimaginably complex, they are nevertheless constructed of molecules of quite modest size, put together in nature to form a host of complex, interacting structures. The example of phenylalanine and PKU ill ...
Lecture 6.
... traditionally termed 'compounds', even though they do not strictly conform to the definition of a compound; more closely resembling common alloys such as steel. In such hydrides, hydrogen can exist as either atomic, or diatomic entities. Mechanical or thermal processing, such as bending, striking, o ...
... traditionally termed 'compounds', even though they do not strictly conform to the definition of a compound; more closely resembling common alloys such as steel. In such hydrides, hydrogen can exist as either atomic, or diatomic entities. Mechanical or thermal processing, such as bending, striking, o ...
Chapter 20 - Cengage Learning
... A carbon atom can form a maximum of four covalent bonds with other atoms. The VSEPR model tells us that electron pairs try to spread out as far as possible. The shape assumed by a carbon atom bonded to four atoms is a tetrahedron. Carbon can bond to fewer than four other atoms when it forms a double ...
... A carbon atom can form a maximum of four covalent bonds with other atoms. The VSEPR model tells us that electron pairs try to spread out as far as possible. The shape assumed by a carbon atom bonded to four atoms is a tetrahedron. Carbon can bond to fewer than four other atoms when it forms a double ...
Synthesis and Properties of a New Kind of One
... This new conductor type consists of squareplanar metal complexes which are polymerised to linear chains by means of bridging ligands. The formation of a continuous yr-system along the chain, and the conformation stability of these are essential to the property of conduction, and the latter is ensure ...
... This new conductor type consists of squareplanar metal complexes which are polymerised to linear chains by means of bridging ligands. The formation of a continuous yr-system along the chain, and the conformation stability of these are essential to the property of conduction, and the latter is ensure ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.