Workshop #1 Part 1. Organic Chemistry Nomenclature
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
Activity C14: Rate of a Chemical Reaction 1
... The equation for the reaction is: S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) =========> SO2(g) + S (s) + H2O One way to determine the effect of concentration on the rate of the reaction is to use a Colorimeter to measure the formation of the solid sulfur generated. The solid sulfur will block the light in the Colorimete ...
... The equation for the reaction is: S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) =========> SO2(g) + S (s) + H2O One way to determine the effect of concentration on the rate of the reaction is to use a Colorimeter to measure the formation of the solid sulfur generated. The solid sulfur will block the light in the Colorimete ...
Homo-coupling of terminal alkynes on a noble metal surface
... TB330 K. However, the employed reaction intermediate geometry was obtained by sticking closely to the covalent dimer coordinates. We expect to find transition states yielding smaller barriers by optimizing the tautomer geometry, for example, with respect to its conformation, the position of the H ato ...
... TB330 K. However, the employed reaction intermediate geometry was obtained by sticking closely to the covalent dimer coordinates. We expect to find transition states yielding smaller barriers by optimizing the tautomer geometry, for example, with respect to its conformation, the position of the H ato ...
IChO 2012
... (1875–1946) early in the 20 th century. That is, acids are electron-pair acceptors, whereas bases are electron-pair donors. There are thousands of molecules that can be classified as Lewis acids or bases, and hundreds of studies of the quantitative aspects of Lewis acid-base chemistry were carried o ...
... (1875–1946) early in the 20 th century. That is, acids are electron-pair acceptors, whereas bases are electron-pair donors. There are thousands of molecules that can be classified as Lewis acids or bases, and hundreds of studies of the quantitative aspects of Lewis acid-base chemistry were carried o ...
Document
... Some diamines have very derivative names indicating where they are found e.g putrescine [H2N(CH2)4NH2] and cadaverine [H2N(CH2)5NH2]! 2. Key properties: If it smells of “fish” or “rotting flesh” chances are you have an amine!! Amines behave in a similar way to NH3 but their behaviour is modified by ...
... Some diamines have very derivative names indicating where they are found e.g putrescine [H2N(CH2)4NH2] and cadaverine [H2N(CH2)5NH2]! 2. Key properties: If it smells of “fish” or “rotting flesh” chances are you have an amine!! Amines behave in a similar way to NH3 but their behaviour is modified by ...
Chapter 15 ΠCarboxylic Acids and Esters
... Anhydrides are easier to handle, but more forceful conditions are required for their reaction making them less accessible. As the name suggests removing water from a carboxylic acid can make an anhydride. This direct method only works for compounds that will yield cyclic anhydrides. An example of wh ...
... Anhydrides are easier to handle, but more forceful conditions are required for their reaction making them less accessible. As the name suggests removing water from a carboxylic acid can make an anhydride. This direct method only works for compounds that will yield cyclic anhydrides. An example of wh ...
4 Organic Chemistry
... What we have done is introduce a branch in the carbon chain. Now we must be able to distinguish between these two compounds by giving them different names. In this case it is quite straightforward. We call the straight-chain molecule n-butane and the branched molecule iso-butane. However, when alkan ...
... What we have done is introduce a branch in the carbon chain. Now we must be able to distinguish between these two compounds by giving them different names. In this case it is quite straightforward. We call the straight-chain molecule n-butane and the branched molecule iso-butane. However, when alkan ...
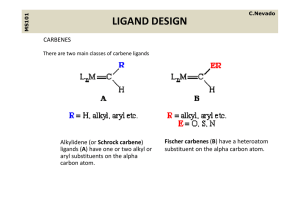
Lecture 4- LIGANDS
... • The terminal CH2 groups of the allyl are twisted about the C−C vector so as to rotate the anti hydrogens (Ha) away from the metal, and the syn hydrogens (Hs) toward the metal. • This allows the bonding p orbital on these carbons to point more directly toward the metal, thus further improving the M ...
... • The terminal CH2 groups of the allyl are twisted about the C−C vector so as to rotate the anti hydrogens (Ha) away from the metal, and the syn hydrogens (Hs) toward the metal. • This allows the bonding p orbital on these carbons to point more directly toward the metal, thus further improving the M ...
Reactions of carboxymethylalginic acid with some N
... acylation. At temperatures above 80°C, these salts partially or fully converted to the parent compounds, and the more heat appears, the more carboxyl groups that can react with a nucleophile is formed. Therefore, when the temperature rises from 80 to 100°C Cs values are increased by more than 5-fold ...
... acylation. At temperatures above 80°C, these salts partially or fully converted to the parent compounds, and the more heat appears, the more carboxyl groups that can react with a nucleophile is formed. Therefore, when the temperature rises from 80 to 100°C Cs values are increased by more than 5-fold ...
A2 CHEMISTRY TRANSITION METALS FAHAD
... This ion has a high Charge Density due to its smaller size. The empty 4th shell orbitals can therefore attract ligands and datively bond to them. The six orbitals shaded above can be used to dative bonding. The number of dative bonds formed depends on the charge density and the size of the attached ...
... This ion has a high Charge Density due to its smaller size. The empty 4th shell orbitals can therefore attract ligands and datively bond to them. The six orbitals shaded above can be used to dative bonding. The number of dative bonds formed depends on the charge density and the size of the attached ...
Terpyridine-based Materials. For Catalytic, Optoelectronic and Life Science Applications Brochure
... Terpyridine-based Materials. For Catalytic, Optoelectronic and Life Science Applications Description: ...
... Terpyridine-based Materials. For Catalytic, Optoelectronic and Life Science Applications Description: ...
RESEARCH ACTIVITIES IX Center for Integrative Bioscience
... Mononuclaer Peroxo iron(III) complexes have been proposed as a key intermediate in various oxidation reactions catalyzed by mononuclear non-heme iron enzymes and their functional model complexes. Various types of synthetic mononuclear iron(III) complexes having η2-peroxo, η1-hydroperoxo, and alkylpe ...
... Mononuclaer Peroxo iron(III) complexes have been proposed as a key intermediate in various oxidation reactions catalyzed by mononuclear non-heme iron enzymes and their functional model complexes. Various types of synthetic mononuclear iron(III) complexes having η2-peroxo, η1-hydroperoxo, and alkylpe ...
... All the compounds and solvents used were purchased from Aldrich and Sigma and used as received without further purification. Elemental microanalyses of the separated ligands for C, H, and N were determined on Automatic Analyzer CHNS Vario ELIII, Germany. The 1H-NMR spectrum was obtained with a JEOL ...
Preparation of a Coordination Compound
... Transition metal salts found on the laboratory shelf are good examples of coordination complexes. For example, a bottle labelled NiCl2·6H2O should really be labelled as [Ni(H2O)6]Cl2,, because the six water molecules are actually ligands which coordinate to the nickel centre to form an octahedral co ...
... Transition metal salts found on the laboratory shelf are good examples of coordination complexes. For example, a bottle labelled NiCl2·6H2O should really be labelled as [Ni(H2O)6]Cl2,, because the six water molecules are actually ligands which coordinate to the nickel centre to form an octahedral co ...
35 IChO Problems 1-13
... particles such as protons (p) and electrons (e) there exist antiparticles which differ from their counterparts usually in one property only, but have the same mass. Antielectrons (or positrons) are positively charged, whereas antiprotons ( p ) are negatively charged. Antimatter composed of antiparti ...
... particles such as protons (p) and electrons (e) there exist antiparticles which differ from their counterparts usually in one property only, but have the same mass. Antielectrons (or positrons) are positively charged, whereas antiprotons ( p ) are negatively charged. Antimatter composed of antiparti ...
An Introduction to Transition Metal Chemistry
... For example, the sum of the first three energies of Tc is 52.08 eV, about 8% less than for Mn. These lower I E's and reduced steric interactions (Why?) both favor high oxidation states. Thus, the most stable fluorides of Nb, Mo, Tc and Ru are NbF5 , MoF6 , TcF6 , and RuF5, respectively. (Compare the ...
... For example, the sum of the first three energies of Tc is 52.08 eV, about 8% less than for Mn. These lower I E's and reduced steric interactions (Why?) both favor high oxidation states. Thus, the most stable fluorides of Nb, Mo, Tc and Ru are NbF5 , MoF6 , TcF6 , and RuF5, respectively. (Compare the ...
Organic Chemistry
... NMR (400 MHz, acetone) δ 11.16 (s, 3H), 8.57 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 3H), 7.74 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 3H), 7.35 (dt, J = 22.8, 7.2 Hz, 6H). 2.3.2 3,8,13-Tribromo-10,15-dihydro-5Hdiindolo [3,2-a:3’,2’-c]carbazole (5): A solution of N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) (0.28 g, 1.55 mmol) in dimethylformamide (2 mL) was added d ...
... NMR (400 MHz, acetone) δ 11.16 (s, 3H), 8.57 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 3H), 7.74 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 3H), 7.35 (dt, J = 22.8, 7.2 Hz, 6H). 2.3.2 3,8,13-Tribromo-10,15-dihydro-5Hdiindolo [3,2-a:3’,2’-c]carbazole (5): A solution of N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) (0.28 g, 1.55 mmol) in dimethylformamide (2 mL) was added d ...
Review Unit 8 Test (Chp 15,17)
... (d) If a suitable solid catalyst were placed in the reaction vessel, would the final total pressure of the gases at equilibrium be greater than, less than, or equal to the final total pressure of the gases at equilibrium without the catalyst? Justify your answer. (Assume that the volume of the soli ...
... (d) If a suitable solid catalyst were placed in the reaction vessel, would the final total pressure of the gases at equilibrium be greater than, less than, or equal to the final total pressure of the gases at equilibrium without the catalyst? Justify your answer. (Assume that the volume of the soli ...
Full-Text PDF
... studied Rh catalyzed reaction pathways exhibited singlet ground state, as ruthenium homologous mechanism [50,65–68], but differently with respect to iron [42,43]. However, here the rhodium center might be disproportionate, or lose one chloride, like Castarlenas et al. have recently demonstrated [53] ...
... studied Rh catalyzed reaction pathways exhibited singlet ground state, as ruthenium homologous mechanism [50,65–68], but differently with respect to iron [42,43]. However, here the rhodium center might be disproportionate, or lose one chloride, like Castarlenas et al. have recently demonstrated [53] ...
Recent Developments on the Mechanism and Kinetics
... It was investigated the esterification of octanoic acid and n-octyl alcohol utilizing metallic chlorides (KCl, CoCl2, MgCl2, ZnCl2, FeCl3 etc.) in a stirred tank reactor (Santos, 1996). The results showed that the best efficiency of the formatted ester (n-octyl octanoate) was obtained with ferric ch ...
... It was investigated the esterification of octanoic acid and n-octyl alcohol utilizing metallic chlorides (KCl, CoCl2, MgCl2, ZnCl2, FeCl3 etc.) in a stirred tank reactor (Santos, 1996). The results showed that the best efficiency of the formatted ester (n-octyl octanoate) was obtained with ferric ch ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.